
Levy Sound Design 48V Phantom Powered Electret Condenser Microphone
To measure the phantom voltage at your mixer's mic input, get a DC voltmeter and measure between XLR pins 1 and 2. Do the same between pins 1 and 3. Be aware of phantom-voltage sag. Microphones draw current through the phantom-supply's resistors, and that current causes a voltage drop E = IR across each resistor.

Skema Membuat Mic Condenser Apa Itu Mikrofon Condenser Kenali Kelebihannya Dibandingkan
Condenser microphones need phantom power to operate their internal circuitry. Phantom power is supplied to the mic through its 2-conductor shielded cable. The power can be supplied either from a stand-alone device or from a mixing console (at each mic connector). The microphone receives power from, and sends audio to, the mixer along the same.

Skema PreAmp Mic Condenser 1 Transistor by Ronica Tutorial, Desain & Hoby
Phantom power is a way of carrying electric current to power microphones without using a separate power supply. It's typically used to power condenser microphones and the 48V DC power itself is supplied by most mixers, audio interfaces, and preamps. If you're shopping for a microphone or audio interface, you've probably seen the term phantom power.

Skema Rangkaian Mic Condenser / Skema Rangkaian Preamp Mic Sederhana Ilmu Listrik Dan Elektronik
The short version: Phantom power is the standard method for powering professional condenser microphones via the XLR-3 connector and balanced cables. The XLR-connector's pin 2 and pin 3 both carry +48 volts ±4 volts DC. Pin 1 is 0 volt. The name "phantom power" refers to the "invisibility" when connecting balanced microphones that do not need.
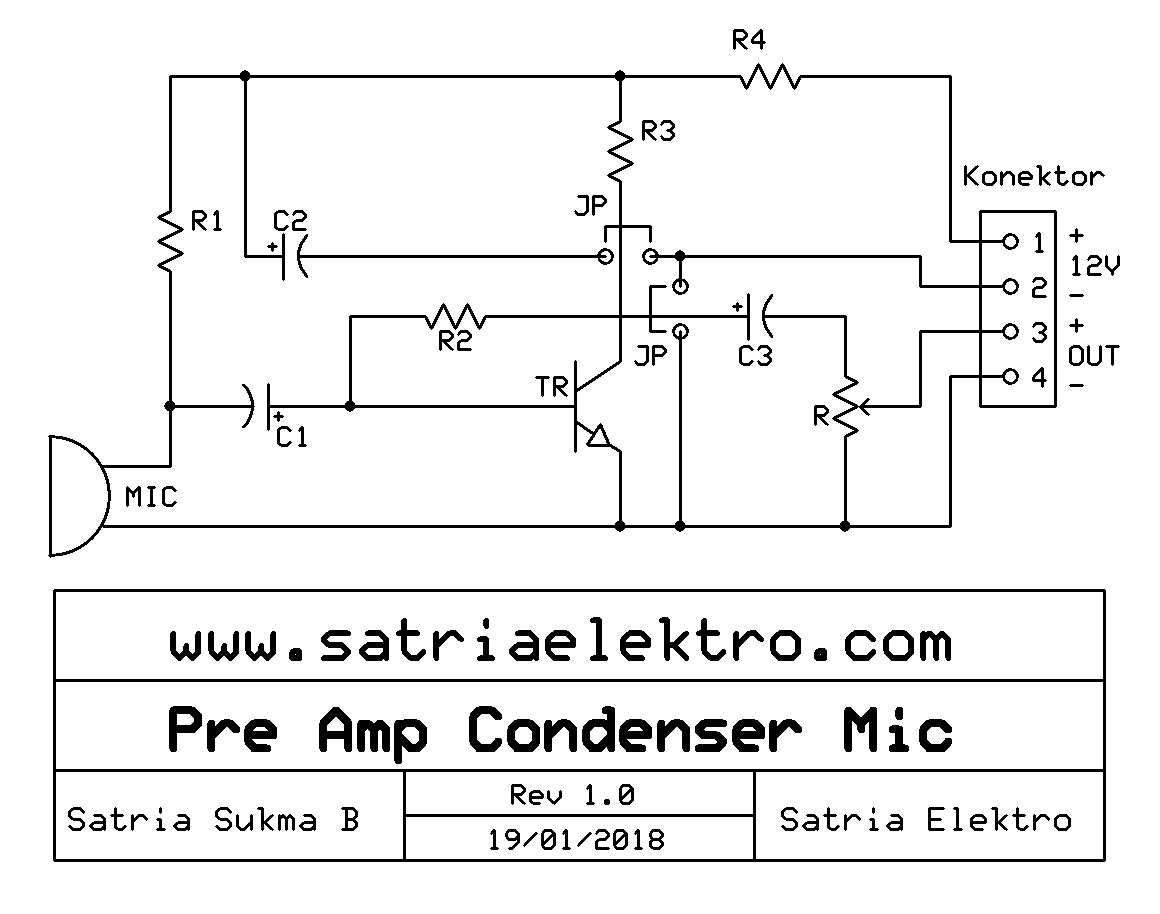
Skema Pre Amplifier Microphone Kondenser dan Dinamik Satria Elektro
Scenario 1: camcorder + condenser XLR microphone. In this scenario, we connect the condenser microphone with an XLR cable into the Sony AX2000's built-in XLR input — input 1 in this case. Once everything is connected, we need to toggle phantom power ON, which, in this camcorder model, is done by pushing the input 1 switch to "MIC +48V.".

rangkaian pre amp simulasi proteus/ power phantom mic condensor YouTube
A condenser microphone is a type of microphone that is meant to be more sensitive than alternatives like dynamic microphones. This sensitivity means they can pick up much more detail than dynamic microphones in many cases. There are two types of condenser microphones: large-diaphragm condenser microphones and small-diaphragm condenser.

Tegangan Phantom Power Yang Aman Untuk Mic Condenser BM800 BM700 BM8000 dan LGT240 YouTube
Phantom Power is typically delivered through the same microphone cable that carries the audio signal. It is a DC (direct current) voltage, usually set at +48 volts, although some equipment may use +12 volts or +24 volts. This voltage is applied equally to the two balanced lines in a microphone cable. The magic happens inside the microphone.

Electronic Phantom Power Circuit Comparison Valuable Tech Notes
The amount of current available from a phantom-powered mic input is often an issue. Condenser mics draw a certain amount of current - up to 10 milli-amps (mA) in some models. The phantom power supply must provide as much current as the mic draws, or else the mic will distort at a lower SPL than is

How to Setup BM800 Condenser Mic w/ V8 Sound Card & Power Phantom! Easy Tutorial YouTube
Episode 1: Learn how to build a DIY microphone. Is it really as simple as promised? If you like this video, please comment and let us know. You can support o.

Skema Modifikasi Mic Clip On Unbal (dengan Baterai) jadi Inbal XLR Phantom 48V (tanpa Baterai
2. The product you linked is the one for the job. And since you give to your condenser mic the power it needs to operate, you can connect it anywhere you could connect any dynamic mic, such as a simple XLR-USB audio interface. Share. Improve this answer.

Skema PreAmp Mic Dynamic (Mic Spul) 1 Transistor Tutorial, Desain & Hoby
Phantom power is commonly used with condenser microphones, and with DJ controllers, mixers. control surfaces and other audio equipment that is associated with condenser microphones. Phantom power eliminates the need to connect a battery source to your microphone or to run a secondary power cable to the microphone. 3 How Phantom Power Works.

Skema PreAmp Mic Condenser 1 Transistor by Ronica Tutorial, Desain & Hoby
Explanation on how phantom power is used with condenser microphones. Phantom power supplies use two conductors within an XLR cable: one carries positive voltage (+48V), while the other carries negative voltage (-48V). Together they act as a balanced audio circuit while also providing DC voltage. However, not all condenser microphones require.
Mic Preamp Phantom Power Schematic Wiring Diagram and Schematics
Phantom power sends a DC current from a preamp or mixer, through the XLR cable, and to the condenser microphone to power the internal active circuitry. The global standard for phantom is 11V to 52V DC, with studio mics running on +48V. You'll often find phantom written as +48V on preamps, mixers, audio interfaces, and the like.
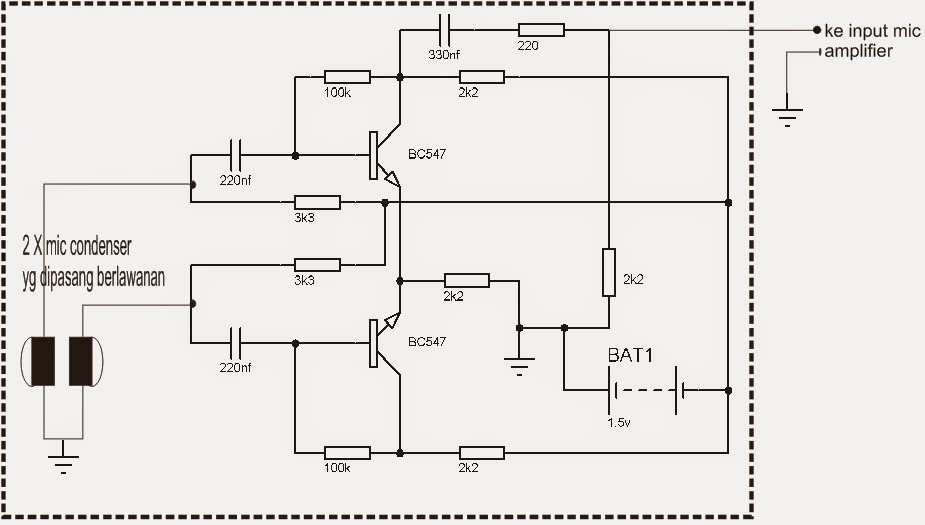
Preamp Mic Condensor Catatan Ku
Phantom power is a way to provide power to microphones that require electricity to operate, typically condensers. On the other hand, dynamic mics—the ubiquitous Shure SM57 and SM58, for example—do not require power. Phantom power involves a clever scheme that leverages the multiple wires in a typical balanced-XLR cable to provide voltage to.
Gambar Skema Mic Condenser Untuk Hp Lengkap Skematronik
All condenser microphones (which are relatively large) need phantom power. All condenser microphones are relatively large and typically have very sophisticated pop-filters or foam covers to protect the sensitive diaphragm of the mic. These mics are usually larger, more square, or have a far larger or longer functional microphone section.
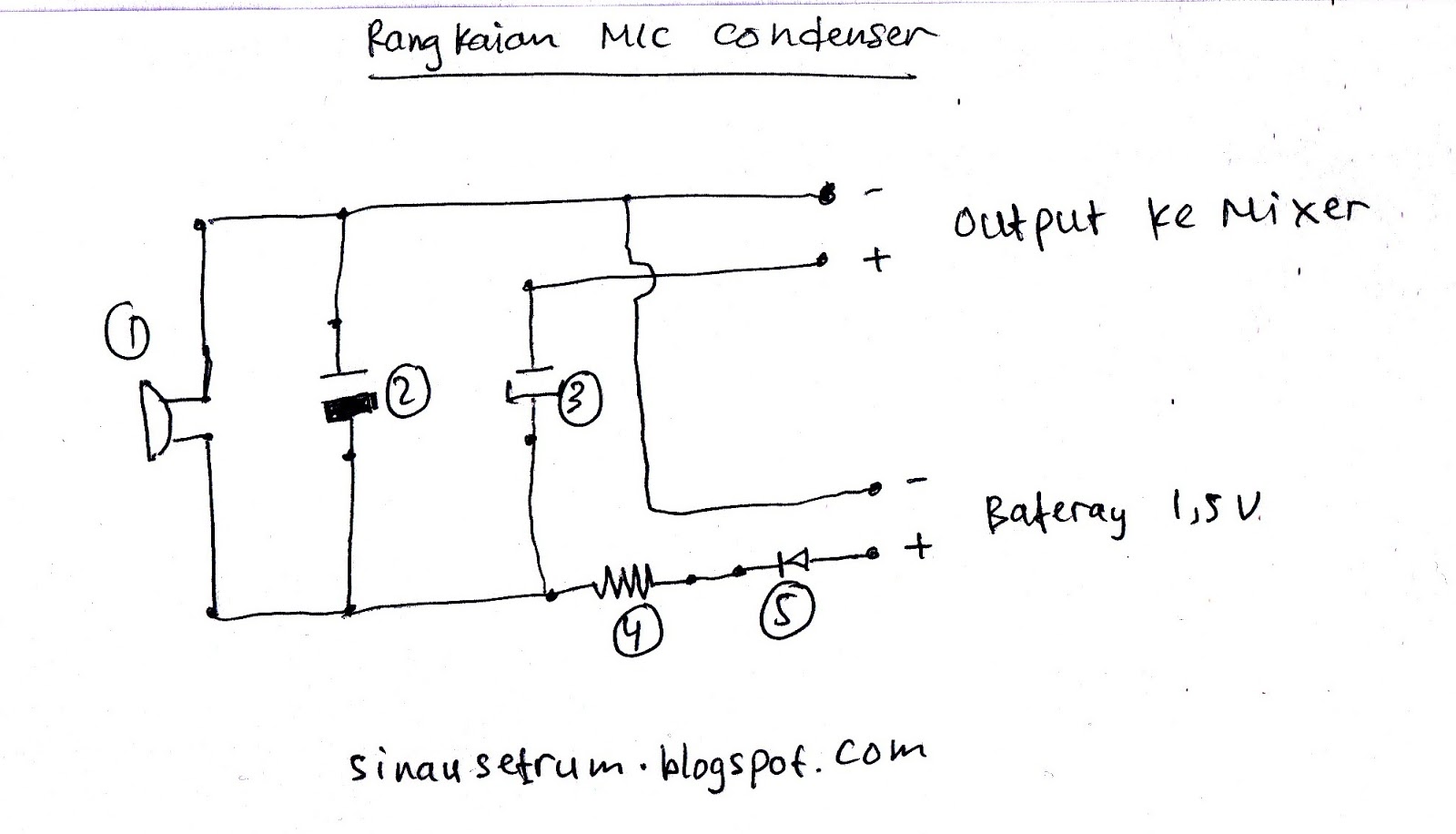
Rangkaian Mic Condenser Tanpa Baterai Eminence Solutions
Why Is It Called Phantom Power? Condenser microphones made in the 1930s, 1940s, and 1950s required a special power supply to operate. This power supply would often be located quite near the microphone and was usually large, heavy, and cumbersome. In the 1960s, work began on a new powering concept that would eliminate the need for a separate.