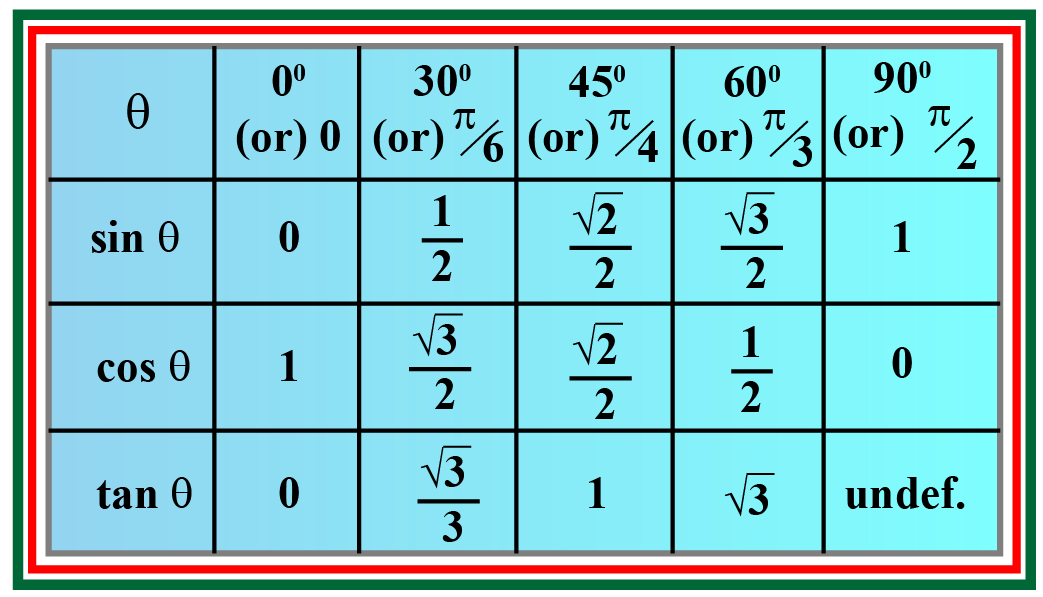
sin cos tan definitions, facts and solved examples Cuemath
Get detailed solutions to your math problems with our Trigonometric Identities step-by-step calculator. Practice your math skills and learn step by step with our math solver. Check out all of our online calculators here. sec ( x) 2 + csc ( x) 2 = 1 sin ( x) 2 · cos ( x) 2. Go! Math mode. Text mode.
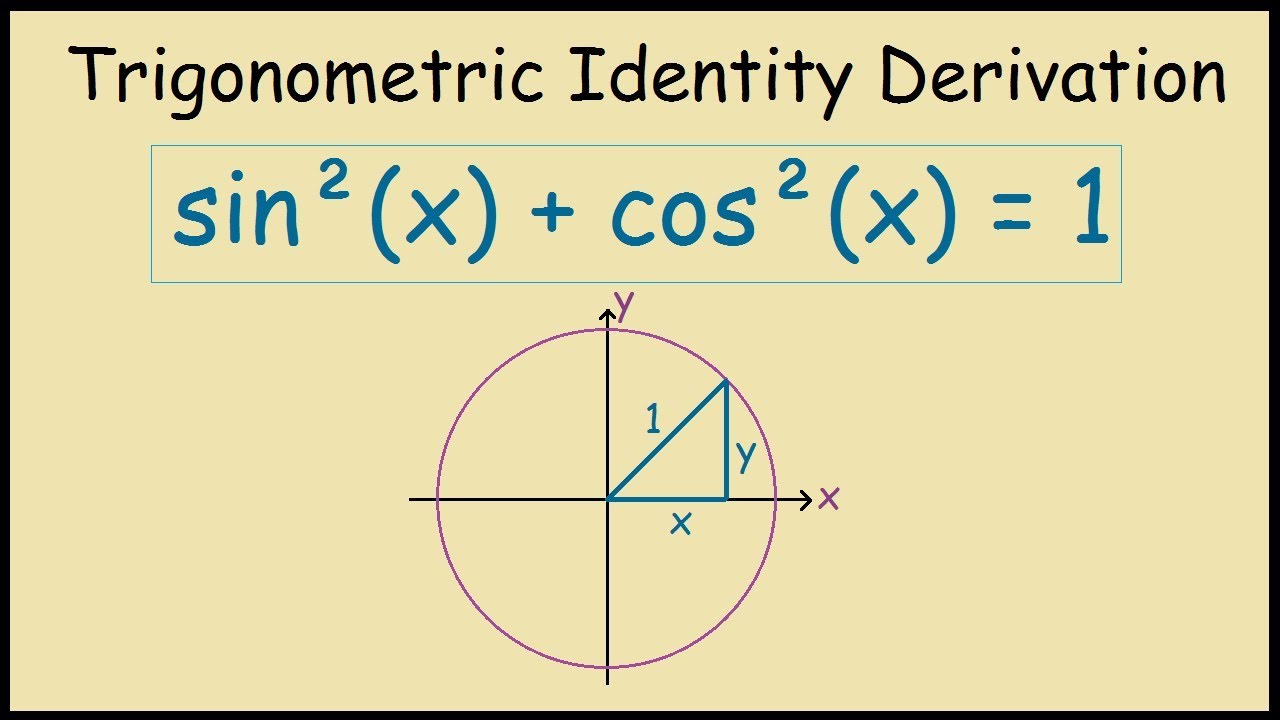
sin^2(x) + cos^2(x) = 1 Trig Identity Graphical Proof YouTube
Free trigonometric identity calculator - verify trigonometric identities step-by-step.

sin^2 a + cos^2 a = ? (formula with example)
Free math problem solver answers your trigonometry homework questions with step-by-step explanations.

cos^2(x)+sin^2(x)=1 et le cercle trigonométrique YouTube
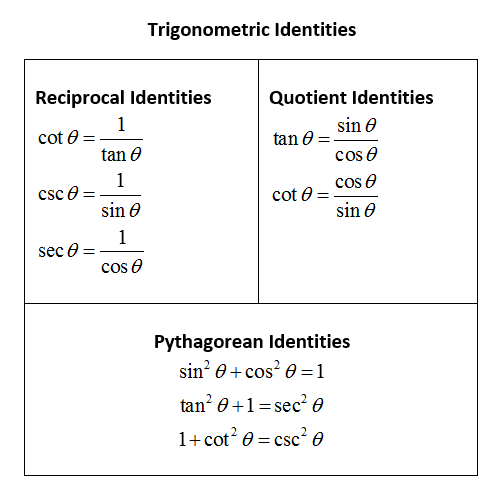
The Trigonometric Identities are equations that are true for Right Angled Triangles. Periodicity of trig functions. Sine, cosine, secant, and cosecant have period 2π while tangent and cotangent have period π. Identities for negative angles. Sine, tangent, cotangent, and cosecant are odd functions while cosine and secant are even functions.
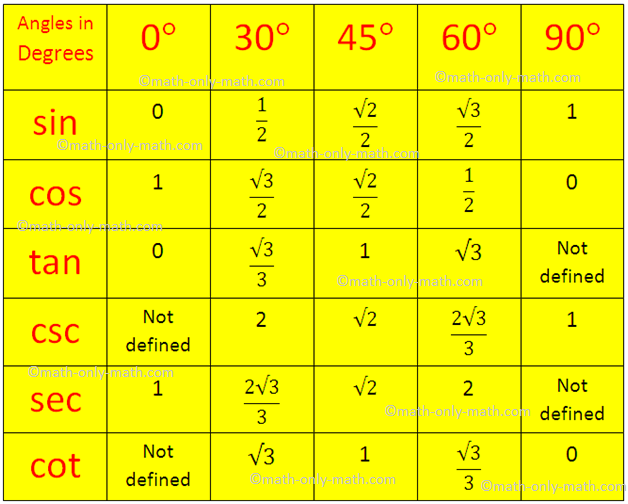
Trigonometrical Ratios Table Trigonometric Standard Angles Standard
Show that (sin A + cosec A) 2 + (cos A + sec A) 2 = 7 + tan 2 A + cot 2 A Using these identities, we can solve various mathematical problems. All you need to know about trigonometry and its applications are just a click away, visit BYJU'S to learn more.
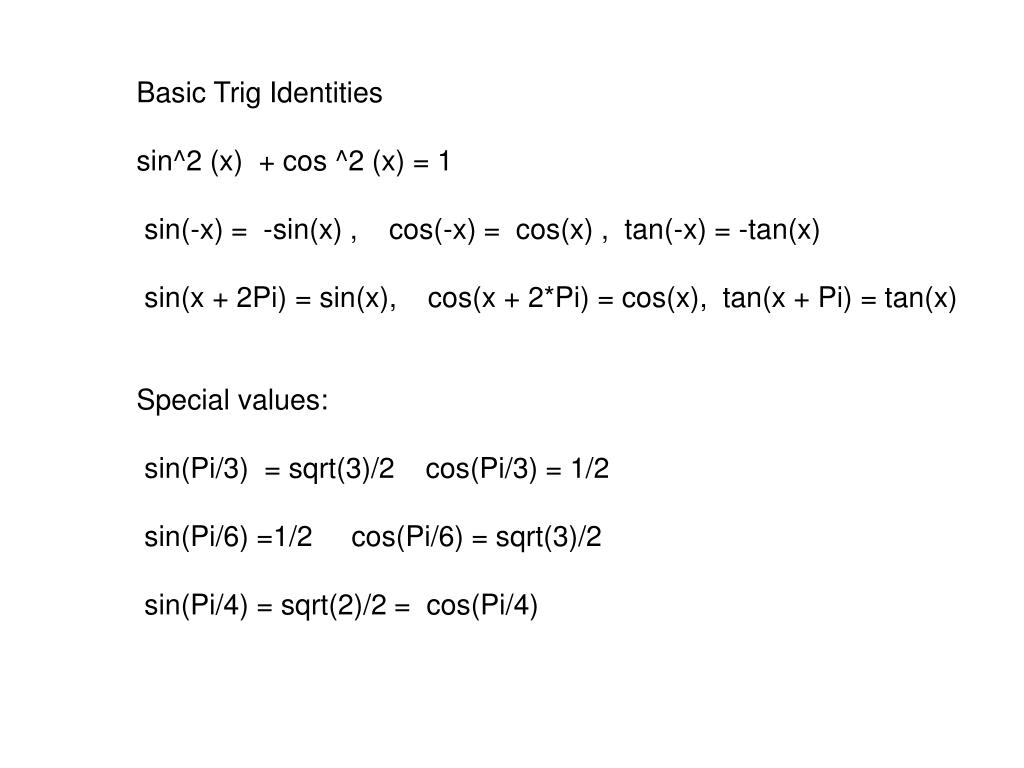
PPT Basic Trig Identities sin^2 (x) + cos ^2 (x) = 1 PowerPoint Presentation ID4307181
simplify\:\tan^4(x)+2\tan^2(x)+1 ; simplify\:\tan^2(x)\cos^2(x)+\cot^2(x)\sin^2(x) Show More; Description. Simplify trigonometric expressions to their simplest form step-by-step. trigonometric-simplification-calculator. en. Related Symbolab blog posts. High School Math Solutions - Trigonometry Calculator, Trig Simplification.

proof sin^2 +cos^2=1 why sin squred plus cos squred = 1 YouTube
The area, 1 / 2 × base × height, of an isosceles triangle is calculated, first when upright, and then on its side. When upright, the area = sin θ cos θ {\displaystyle \sin \theta \cos \theta } .
Trig Identities Simplify Expressions (solutions, examples, videos)
The following (particularly the first of the three below) are called "Pythagorean" identities. sin 2 ( t) + cos 2 ( t) = 1. tan 2 ( t) + 1 = sec 2 ( t) 1 + cot 2 ( t) = csc 2 ( t) Advertisement. Note that the three identities above all involve squaring and the number 1. You can see the Pythagorean-Thereom relationship clearly if you consider.

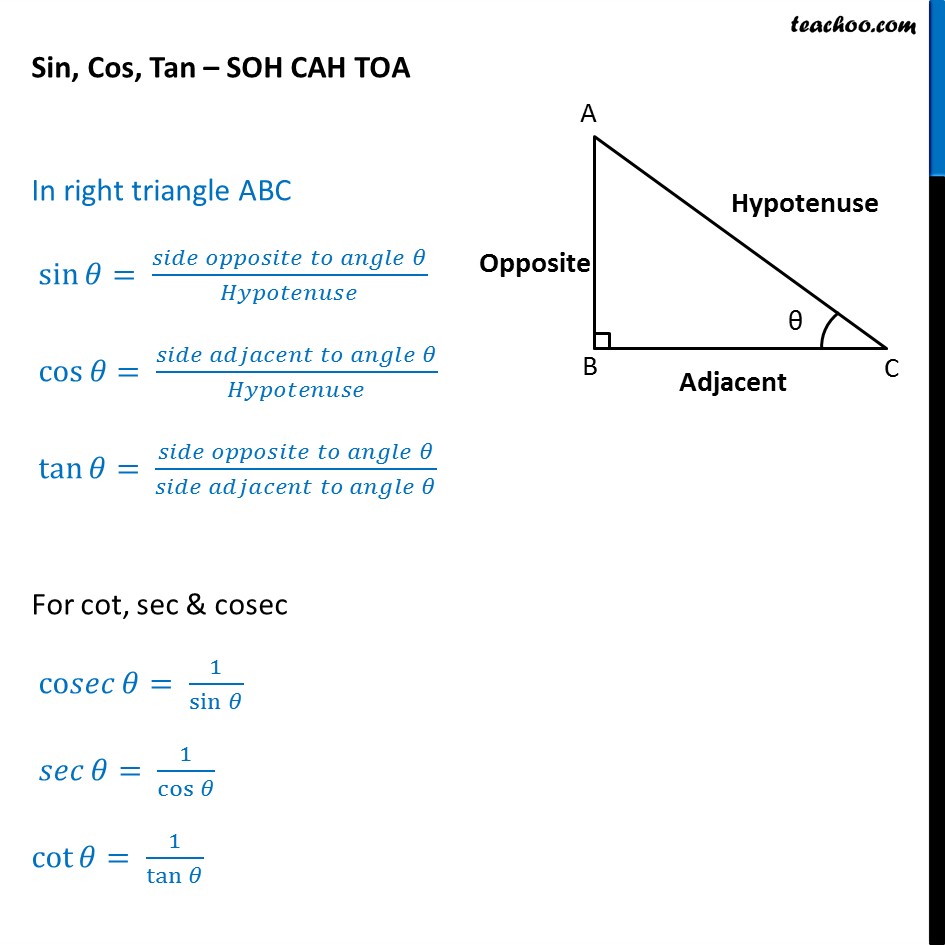
What are sin cos tan? SOHCAHTOA With Examples Teachoo
The three basic trigonometric functions are: Sine (sin), Cosine (cos), and Tangent (tan). What is trigonometry used for? Trigonometry is used in a variety of fields and applications, including geometry, calculus, engineering, and physics, to solve problems involving angles, distances, and ratios.

Solve the Trigonometric Equation cos^2(x) sin^2(x) = 1 YouTube
You would need an expression to work with. For example: Given sinα = 3 5 and cosα = − 4 5, you could find sin2α by using the double angle identity. sin2α = 2sinαcosα. sin2α = 2(3 5)( − 4 5) = − 24 25. You could find cos2α by using any of: cos2α = cos2α −sin2α. cos2α = 1 −2sin2α. cos2α = 2cos2α − 1.

Why sin^2 x + cos^2 x = 1 YouTube
3/1. 4/0. Given Triangle abc, with angles A,B,C; a is opposite to A, b opposite B, c opposite C: a/sin (A) = b/sin (B) = c/sin (C) (Law of Sines) c ^2 = a ^2 + b ^2 - 2ab cos (C) b ^2 = a ^2 + c ^2 - 2ac cos (B) a ^2 = b ^2 + c ^2 - 2bc cos (A) (Law of Cosines)

Come Ricordare la Tavola Trigonometrica 6 Passaggi
Introduction to Systems of Equations and Inequalities; 9.1 Systems of Linear Equations: Two Variables; 9.2 Systems of Linear Equations: Three Variables; 9.3 Systems of Nonlinear Equations and Inequalities: Two Variables; 9.4 Partial Fractions; 9.5 Matrices and Matrix Operations; 9.6 Solving Systems with Gaussian Elimination; 9.7 Solving Systems with Inverses; 9.8 Solving Systems with Cramer's Rule

Proof Sin^2+cos^2=1 YouTube
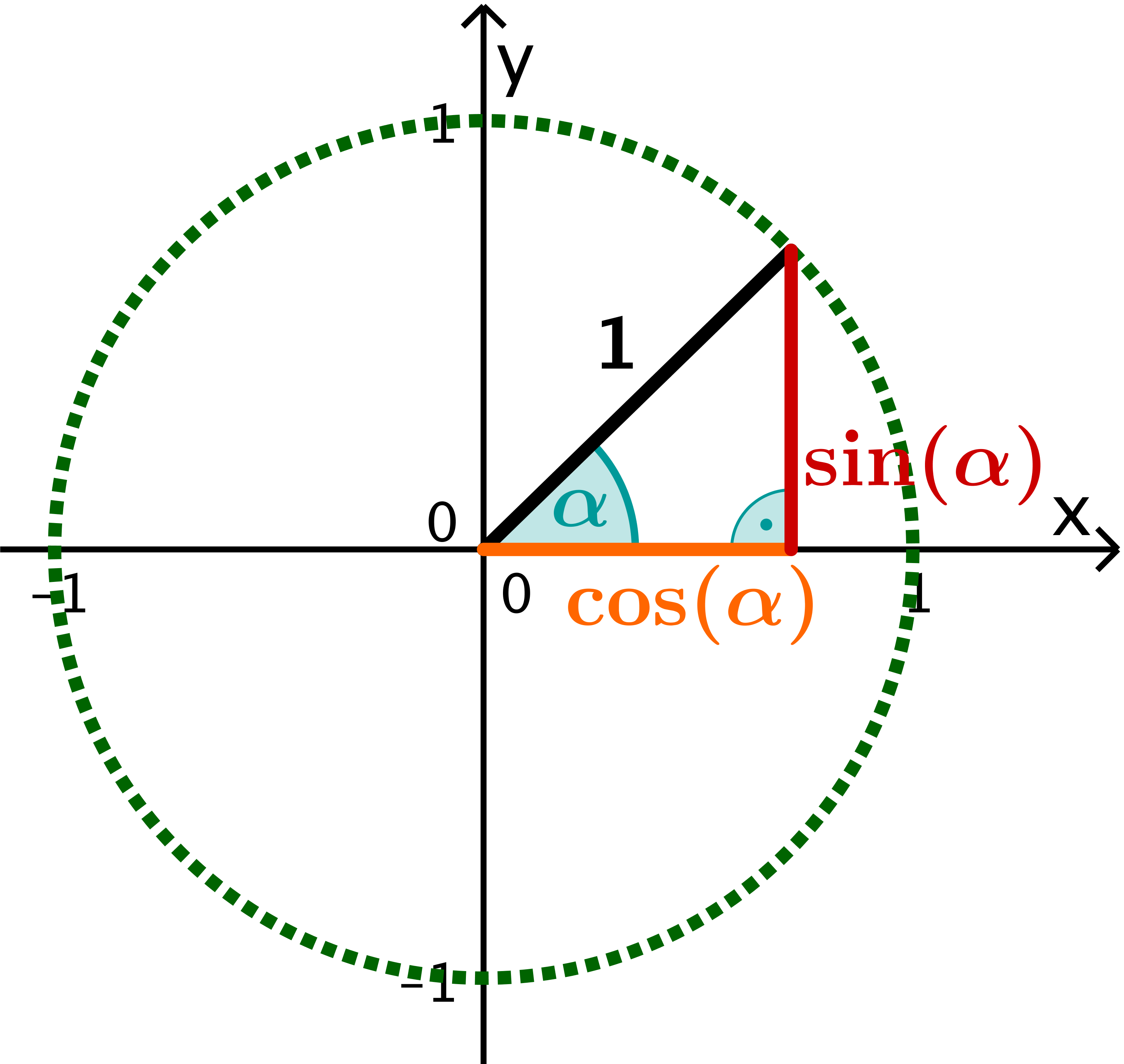
We see that the graph of \(Y_1=\cos ^2 \theta+\sin ^2 \theta\) appears identical to the horizontal line \(Y_2=1\). In fact, the graphs are identical, and the equation \(\cos ^2 \theta+\sin ^2 \theta=1\) is an identity. It is important enough to earn a special name. Pythagorean Identity.

Trigonometry (Proving sin^2 + cos^2 = 1) YouTube
It so happens that sin^2 (x) + cos^2 (x) = 1 is one of the easier identities to prove using other methods, and so is generally done so. Still, be all that as it may, let's do a proof using the angle addition formula for cosine: cos (alpha + beta) = cos (alpha)cos (beta) - sin (alpha)sin (beta) (A proof of the above formula may be found here.
Trigonometry Formulas and Identities Full list Teachoo
Pythagoras Theorem. For the next trigonometric identities we start with Pythagoras' Theorem: The Pythagorean Theorem says that, in a right triangle, the square of a plus the square of b is equal to the square of c: a 2 + b 2 = c 2. Dividing through by c2 gives. a2 c2 + b2 c2 = c2 c2. This can be simplified to: (a c)2 + (b c)2 = 1.
Trigonometrie am Einheitskreis lernen mit Serlo!
Trigonometry is a branch of mathematics concerned with relationships between angles and side lengths of triangles. In particular, the trigonometric functions relate the angles of a right triangle with ratios of its side lengths. The field emerged in the Hellenistic world during the 3rd century BC from applications of geometry to astronomical.