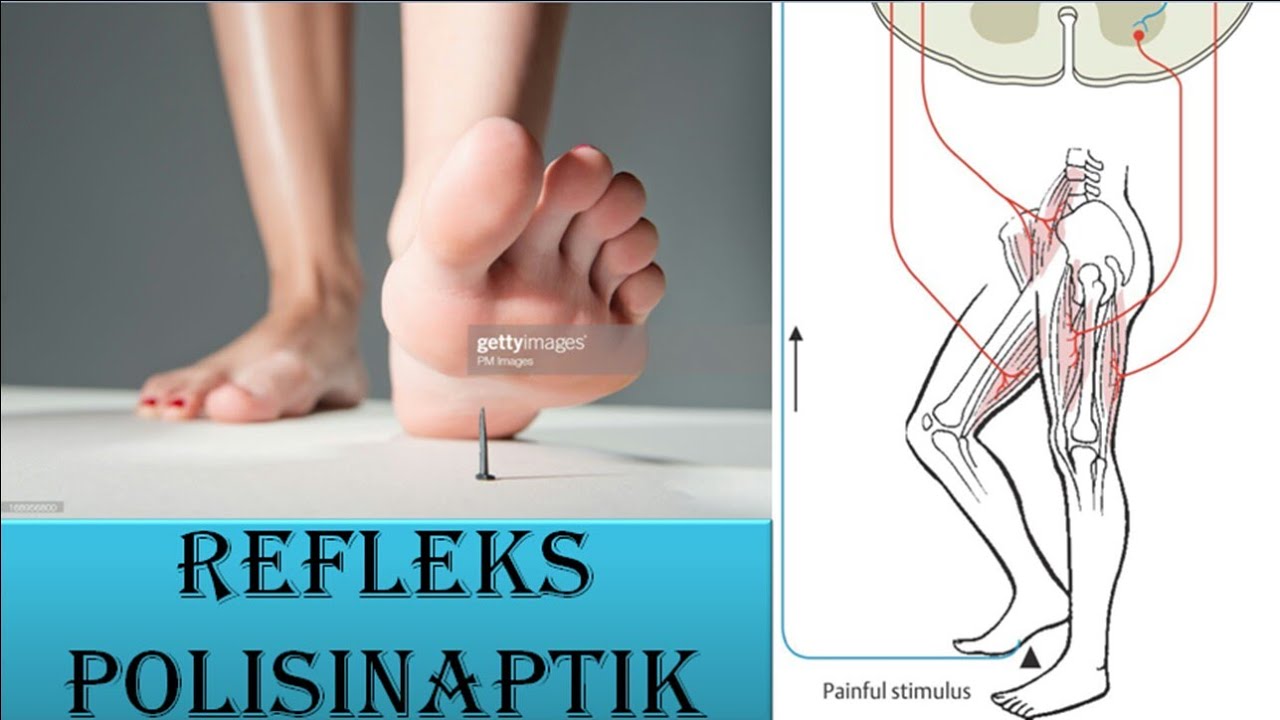
Video 6 Refleks Polisinaptik YouTube
2. Polisinaptik. Beda dari gerak refleks monosinaptik yang sangat simpel, gerakan ini lumayan rumit karena ngelibatin satu saraf lagi. Satu saraf tersebut adalah interneuron di dalam sumsum tulang belakang yang menghubungkan neuron sensorik dan neuron motorik. Mekanisme gerak refleks polisinaptik (Dok.

Monosynaptic vs. Polysynaptic Reflexes Diagram Quizlet
Monosynaptic and polysynaptic reflexes. Motor responses to discrete stimuli that require only two or more neurons to complete the circuit or arc. When the arc consists of one sensory and motor neuron, it is referred to as a monosynaptic reflex (with 'monosynaptic' referring to one synapse). Monosynaptic reflexes include, for example, the.
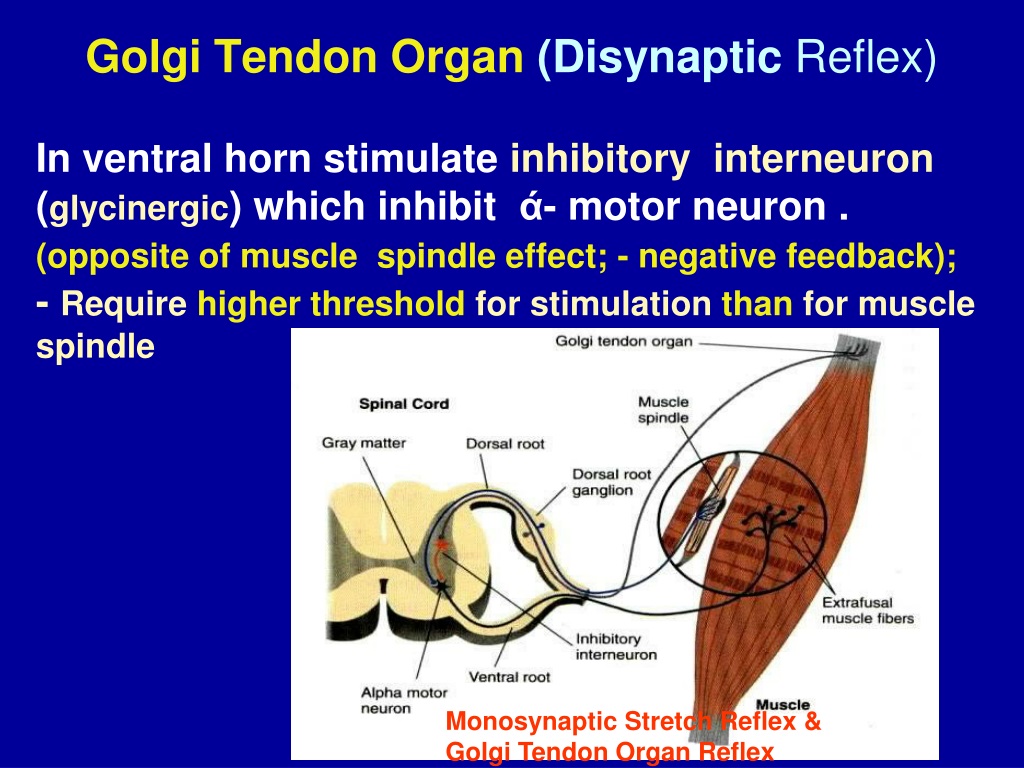
PPT Golgi Tendon Organ. & Polysynaptic Reflexes PowerPoint Presentation ID9571327
The reflex is an automatic response to a stimulus that does not receive or need conscious thought as it occurs through a reflex arc. Reflex arcs act on an impulse before that impulse reaches the brain. [1] Reflex arcs can be. Monosynaptic i.e., contain only two neurons, a sensory and a motor neuron.

MJM Week 8 Monosynaptic and Polysynaptic Reflexes Diagram Quizlet
Quick Reference. Any reflex with more than one synapse (1), not counting the synapse between neuron and muscle, and hence involving one or more interneurons. In humans, all reflexes except stretch reflexes are polysynaptic. Compare monosynaptic reflex. [From Greek polys many + neuron a nerve] From: polysynaptic reflex in A Dictionary of.
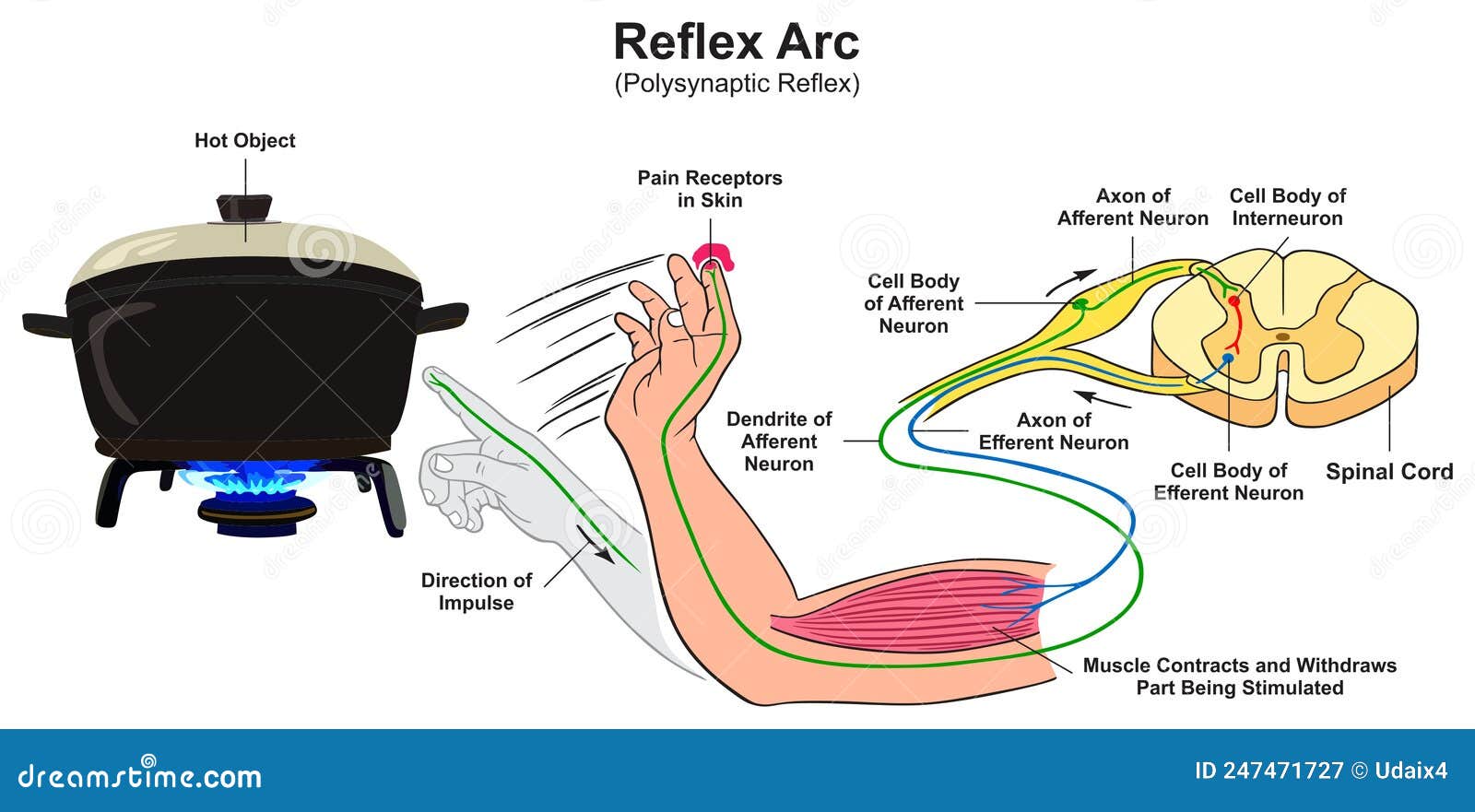
Reflex Arc Polysynaptic Infographic Diagram Stock Vector Illustration of infographic, body
The sympathetic skin response (SSR) is a polysynaptic reflex that requires integrity of hypothalamic, brainstem and spinal circuits, and postganglionic sympathetic sudomotor axons. The SSR is generated in deep layers of the skin by sympathetically-mediated activation of sweat glands. The morphology of the SSR potential is determined by the.
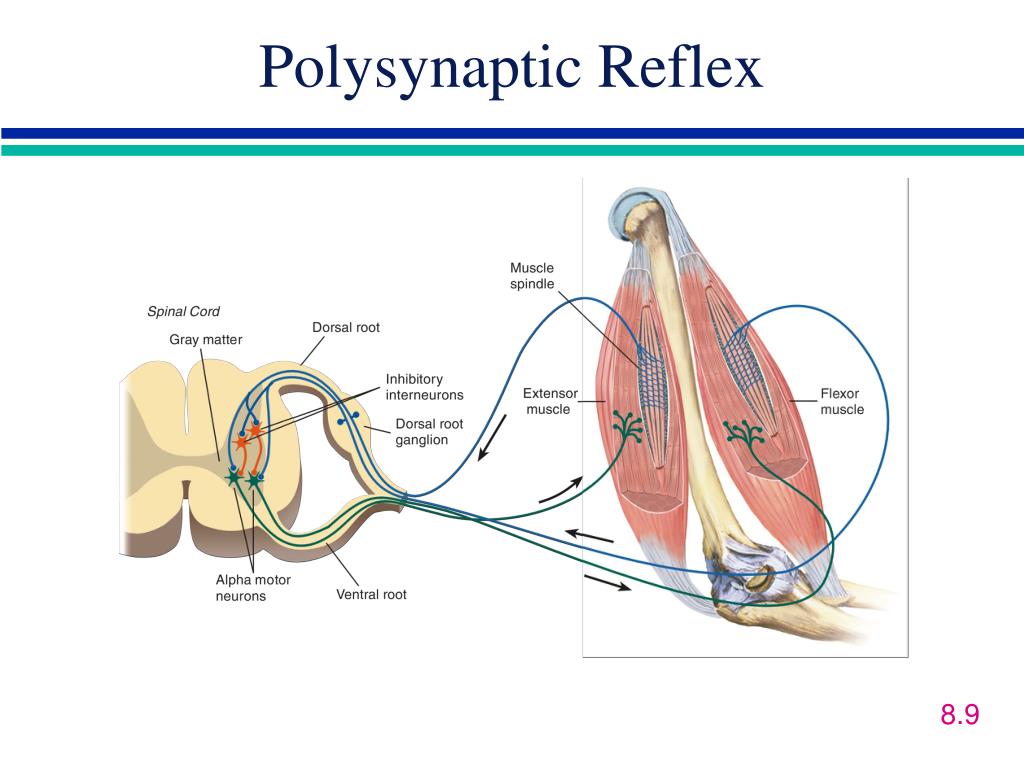
PPT Carlson (7e) Chapter 8 Control of Movement PowerPoint Presentation ID1278345
An integrating center, the point at which the neurons that compose the gray matter of the spinal cord or brainstem synapse. Efferent nerve fibers carry motor nerve signals from the anterior horn to the muscles. Effector muscle innervated by the efferent nerve fiber carries out the response. A reflex arc, then, is the pathway followed by nerves.
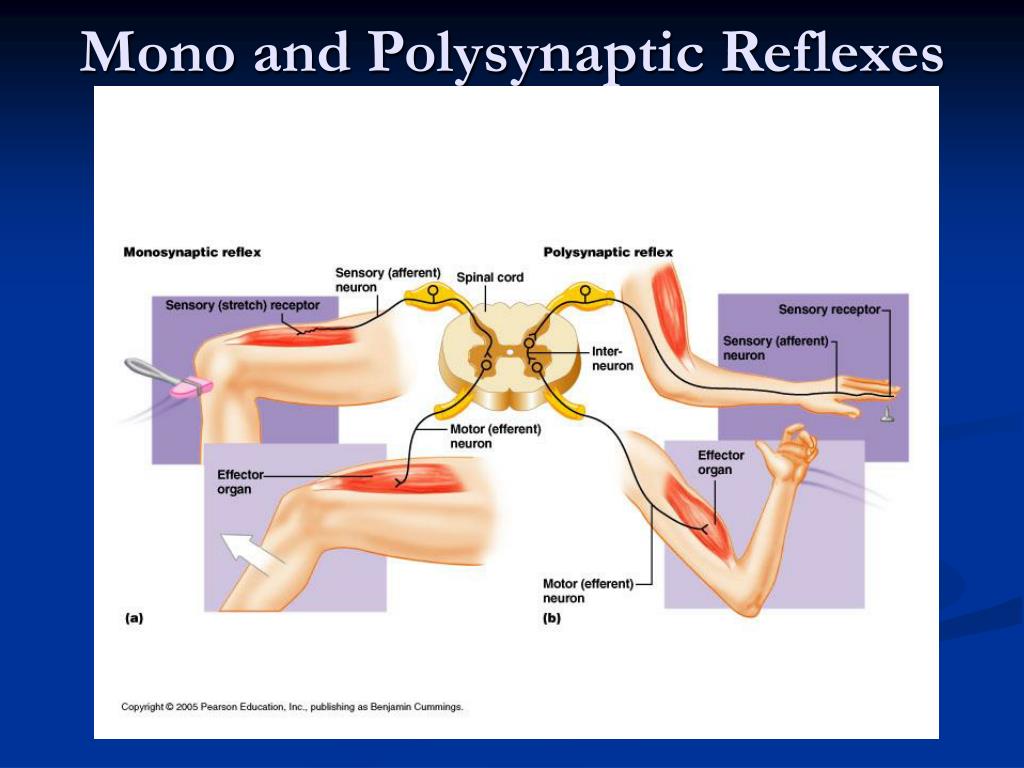
PPT Chapter 14 PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID455742
Secara garis besar, mekanisme refleks polisinaptik hampir sama dengan mekanisme refleks monosinaptik. Bedanya, impuls dari neuron sensorik yang masuk ke sumsum tulang belakang tidak langsung disambungkan ke neuron motorik. Melainkan, melewati neuron delay terlebih dahulu. Neuron delay merupakan interneuron yang berada dalam sumsum tulang.

2 Schematic representation of the monosynaptic (1, 2) and polysynaptic... Download Scientific
The monosynaptic stretch reflex, or sometimes also referred to as the muscle stretch reflex, deep tendon reflex, is a reflex arc that provides direct communication between sensory and motor neurons innervating the muscle. This reflex begins inside the muscle spindle of the muscle, which detects both the amount and rate of muscle stretch. When the muscle experiences a stretch stimulus, sensory.
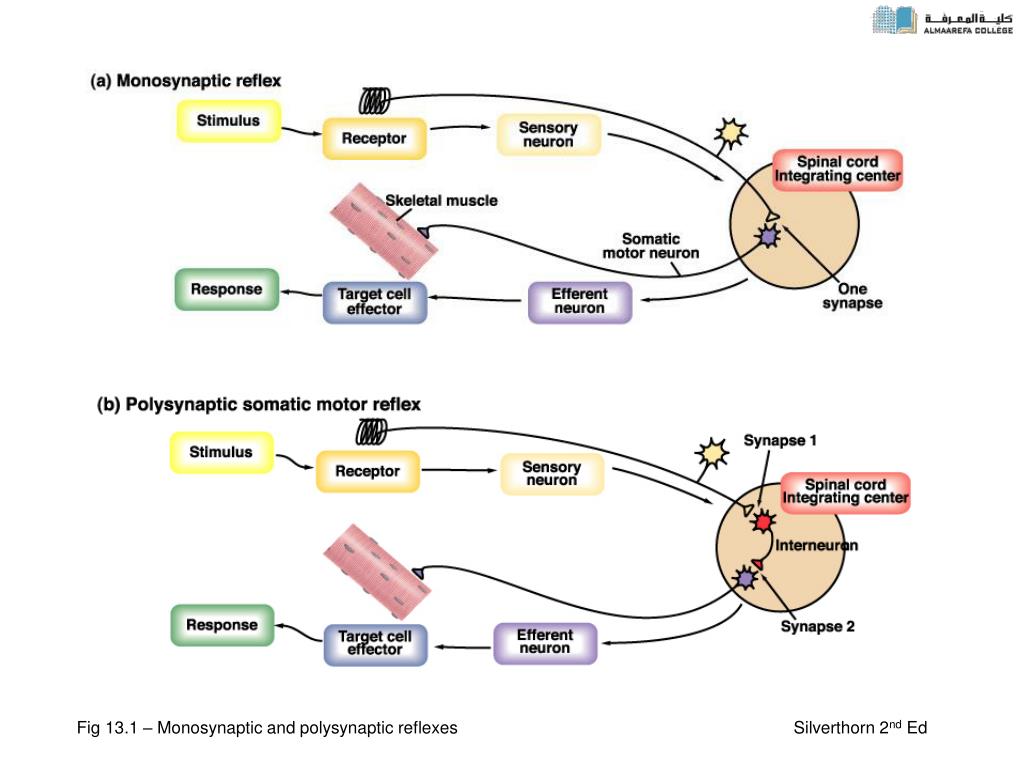
PPT Spinal Cord Reflexes PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID1747380
Motoneuron. 1/4. Synonyms: Neuron motorium. A major part of the spinal cord function is regulated by the brain. Many functions of the spinal cord are also executed independently from the brain, such as a spinal reflex. The definition of a spinal reflex as well as their components, functions, pathways, and physiology will be described in this.
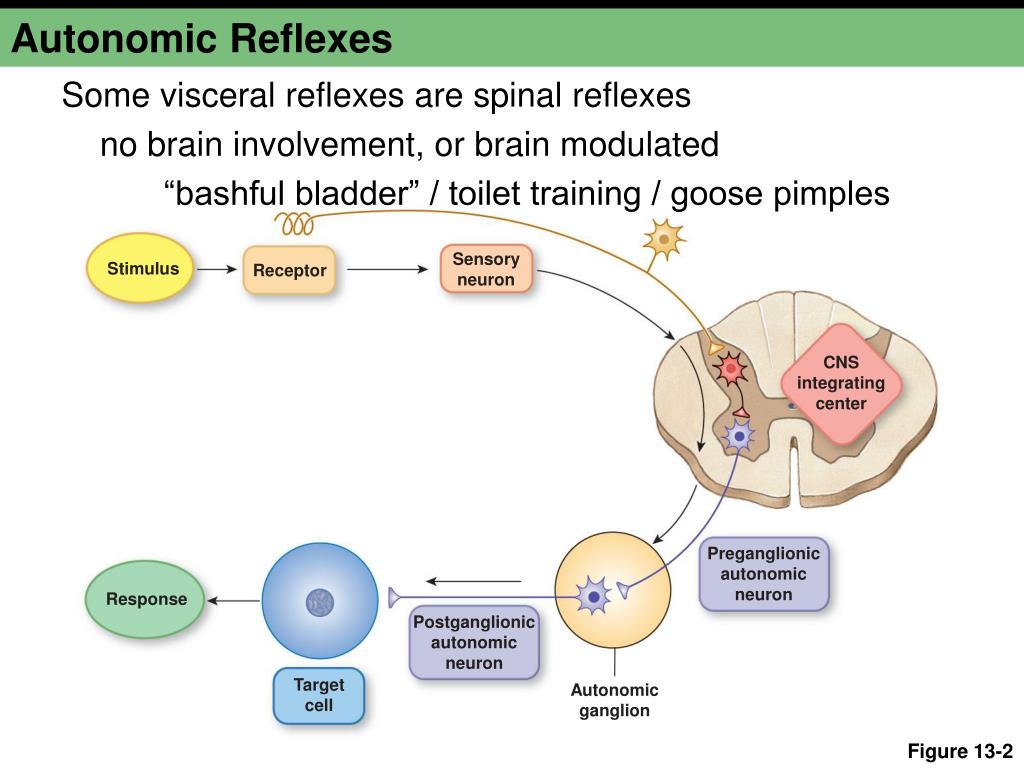
PPT Chapter 13 PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID395883
Reflexes. Reflexes are involuntary motor responses that are performed automatically and independent of brain signals (although some can be suppressed voluntarily, with extra effort). Reflexes involve very simple circuits, sometimes consisting of only two populations of neurons: Sensory information comes in from the periphery, synapsing onto.

Structure & Function of the Withdrawal Reflex, a Polysynaptic Reflex YouTube
The withdrawal reflex is a spinal reflex intended to protect the body from damaging stimuli. It is a polysynaptic reflex, causing stimulation of sensory, association, and motor neurons. In this article we will discuss the basic anatomy, the neural pathways and also the clinical relevance of this reflex. Key facts about the withdrawal reflex.

Normal monosynaptic but abnormal polysynaptic stretchreflex... Download Scientific Diagram
Description. A reflex action, also known as a reflex, is an involuntary and nearly instantaneous movement in response to a stimulus. When a person accidentally touches a hot object, they automatically jerk their hand away without thinking. A reflex does not require any thought input. The path taken by the nerve impulses in a reflex is called a.
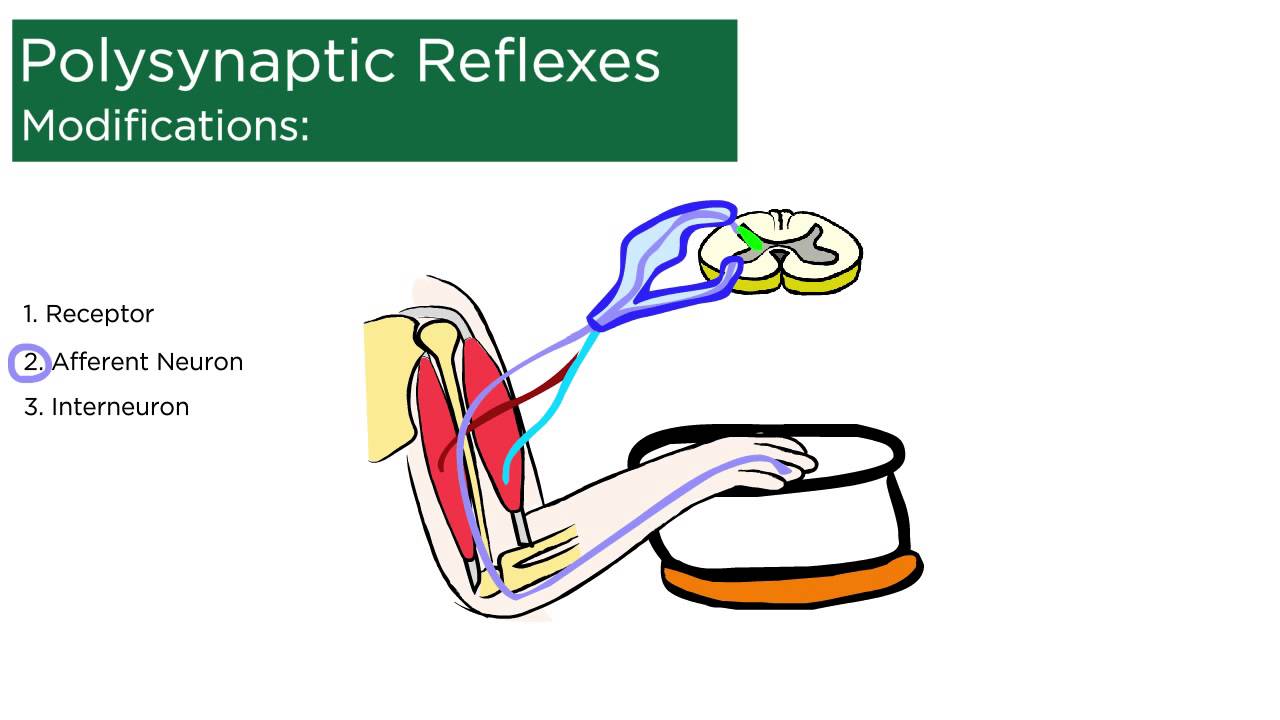
Polysynaptic Reflexes YouTube
The withdrawal response (reflex), also known as the nociceptive flexion reflex, is an automatic response of the spinal cord that is critical in protecting the body from harmful stimuli. The first known definition of a reflex dates back to 1649 when René Descartes noted that specific bodily movements occurred instantaneously and independent of the process of thought. Modern definitions state.

Simple polysynaptic spinal reflex arc the 5 components! YouTube
Reflexes can be spinal or cranial, depending on the nerves and central components that are involved.The body uses both spinal and cranial reflexes to rapidly respond to important stimuli. All reflex arcs include five basic components; (1) a receptor, (2) a sensory neuron, (3) an integration center, (4) a motor neuron, and (5) an effector.The effector may be a skeletal muscle, as is the case in.
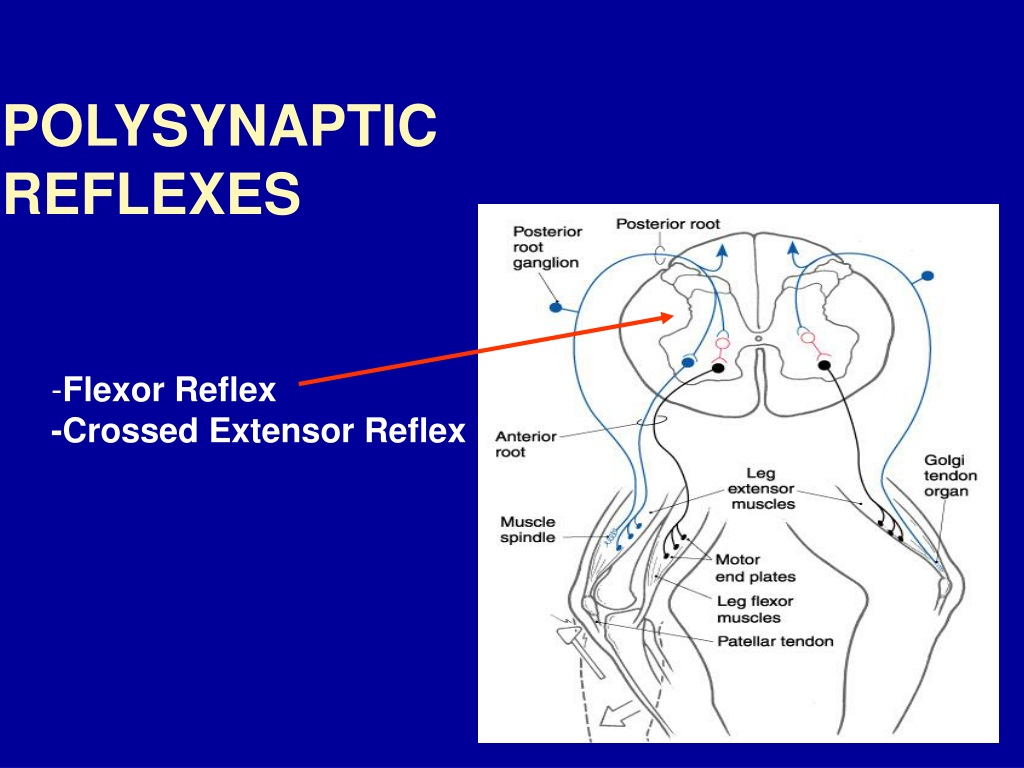
PPT Golgi Tendon Organ. & Polysynaptic Reflexes PowerPoint Presentation ID9571327
Reflexes. Reflexes are involuntary motor responses that are performed automatically and independent of brain signals (although some can be suppressed voluntarily, with extra effort). Reflexes involve very simple circuits, sometimes consisting of only two populations of neurons: Sensory information comes in from the periphery, synapsing onto motor neurons in the brainstem or spinal cord.

The top panel in this figure shows a long reflex, where the spinal cord is connected to the
2.1. Human Subjects. Data were derived from eight individuals with a median age (interquartile range; IQR) of 25.0 years (21.8-26.5 years) who had been referred to a clinical program for the treatment of lower-extremity spasticity by EES of the lumbar spinal cord [].All subjects had traumatic, motor-complete SCI in the chronic stage post-injury (3.4 years (2.6-4.7 years)), six classified.