
What is the Trendelenburg Position? (with pictures)
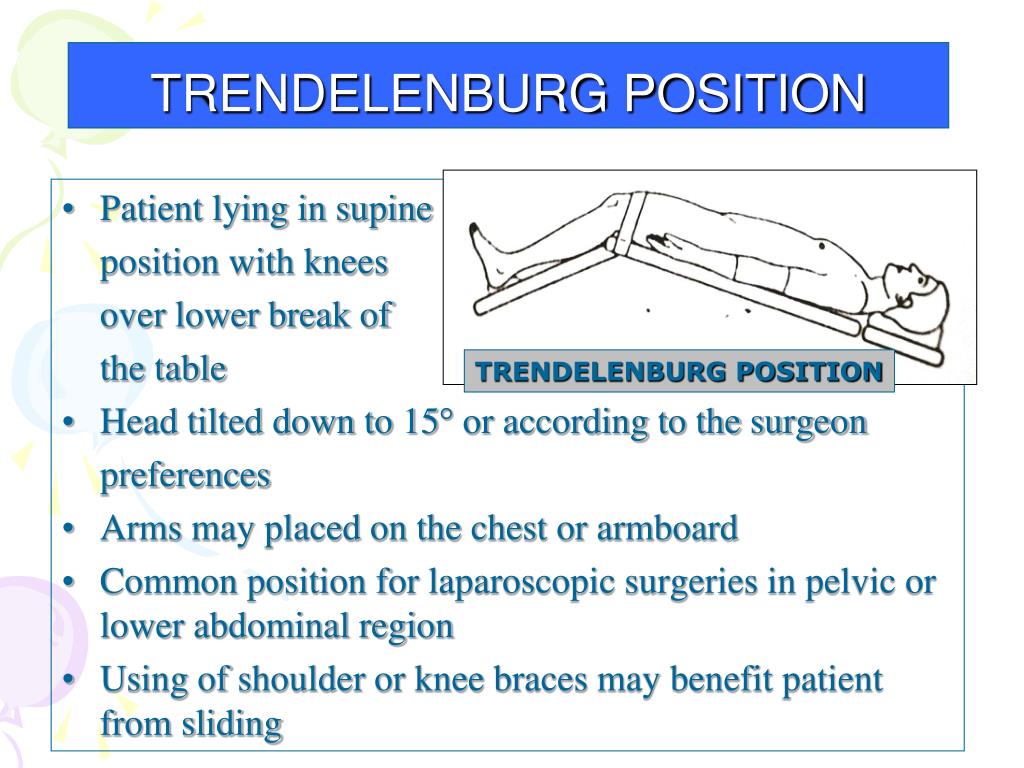
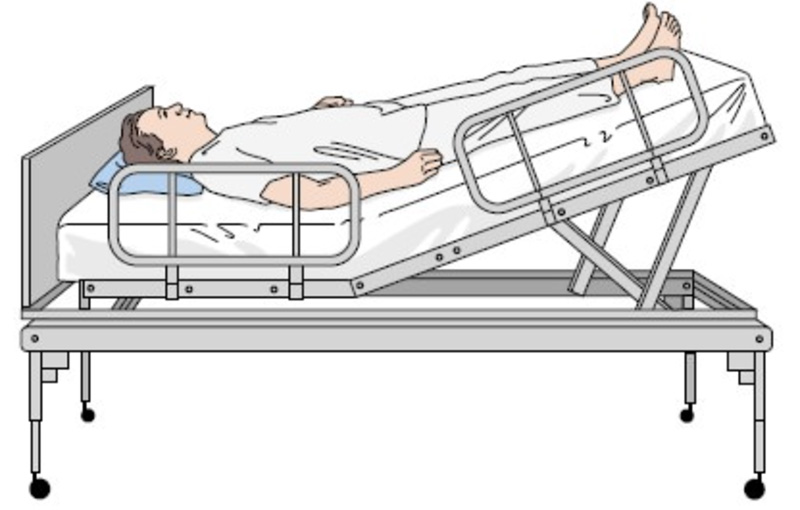
The Trendelenburg position places a person in a supine position (lying face up) on an incline between 15 and 30 degrees to get the legs higher than the head. A modified version of the technique only raises the legs. The healthcare provider or user should minimize the degree of the Trendelenburg position as much as possible; if possible, the.
What is the Trendelenburg position and when is it essential?
The Trendelenburg position is a conventional maneuver commonly used by practitioners to increase the vein size, as well as other advantages, such as the prevention of air embolism . However, the Trendelenburg position was reported to impair gas exchange and cardiac functions . This position may be disadvantageous, especially in obese patients.

Storm Anesthesia Reverse Trendelenburg
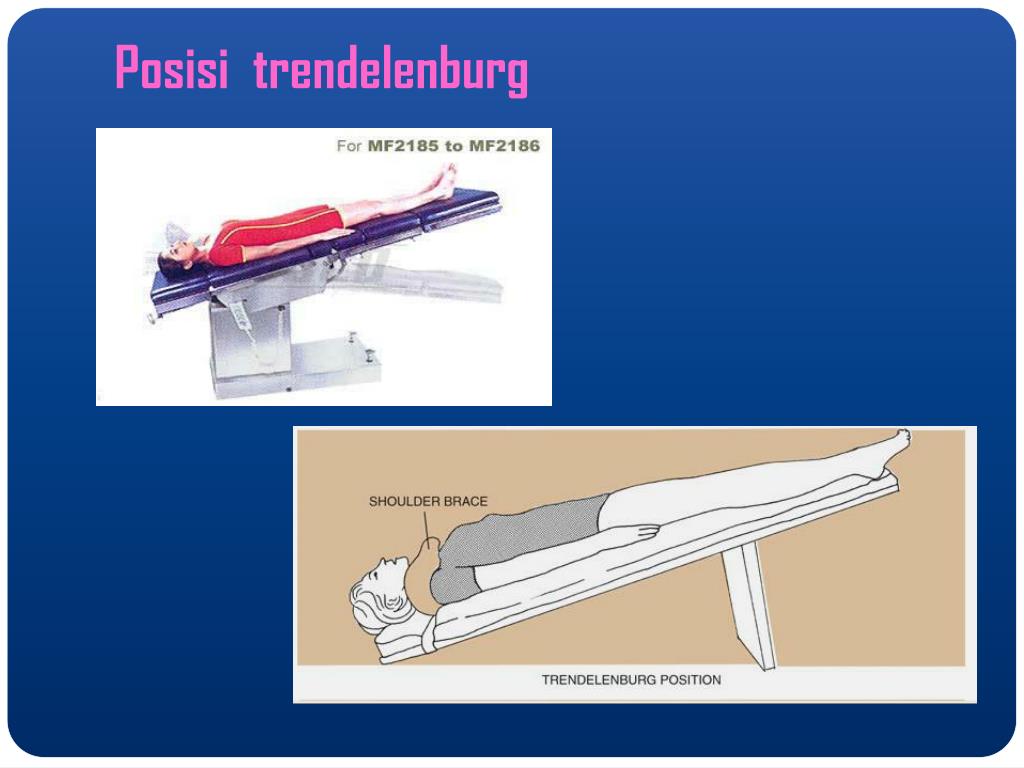
Posisi Trendelenburg. By Nugraha Fauzi September 1, 2021 0 628 2 Mins Read. Dalam posisi Trendelenburg, tubuh dibaringkan terlentang atau rata di punggung pada kemiringan 15-30 derajat dengan bagian kepala lebih rendah dari bagian kaki. Posisi Reverse Trendelenburg, sama, menempatkan tubuh terlentang tetapi dengan bagian kepala yang leih tinggi.

TRENDELENBURG POSITION REVERSE TRENDELENBURG POSITION [DEFINITION AND USES] YouTube
The Trendelenburg position involves placing the patient head down and elevating the feet. It is named after German surgeon Friedrich Trendelenburg (1844-1924), who created the position to improve surgical exposure of the pelvic organs during surgery. In World War I, Walter Cannon, the famous American physiologist, popularized the use of.

Pengaturan Posisi Pasien Panduan Lengkap untuk Perawat Nerslicious
Posisi Trendelenburg, atau posisi anti-syok, adalah posisi di mana pasien ditempatkan jika terjadi syok atau saat melakukan pemeriksaan radiologi khusus, serta selama operasi ginekologi dan perut. Subjek terlentang, berbaring sehingga kepala berada di bawah lutut dan panggul.
PPT HAEMOPTISIS PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID2122220
As a result, the Trendelenburg position may have detrimental effects in patients with coronary artery disease and ischemia of the lower limbs, decreased vital capacity such as in the obese, and increased intraocular and intracranial pressure and cerebral edema.18 Because many of the studies reviewed assessed the effects of 200 or less, the.

Berbagai Posisi Berbaring Pasien Kavacare
Reverse Trendelenburg position is commonly used in OR for the head, neck, and upper abdominal surgeries. But rarely used in day-to-day inpatient care. The nurse sometimes uses reverse Trendelenburg position during nasogastric (NG) tube insertion and feeding, if the patient must remain in the supine position.
PPT POSITIONING IN OPERATING THEATRE PowerPoint Presentation ID225230
Posisi Trendelenburg adalah posisi pembedahan di mana pasien berbaring telentang dengan kaki yang terangkat lebih tinggi dari kepala. Posisi ini merupakan variasi dari supine atau posisi telentang. Nama posisi ini diambil dari nama ahli bedah Jerman, Friedrich Trendelenburg (1844-1924), yang awalnya menggunakan posisi ini untuk meningkatkan.

Reverse Trendelenburg Postioning
1. Tujuan video ini adalah unk mendeskripsikan prosedur pelaksanaan tiap pengaturan posisi pasien. 2. Posisi trendelenburg adalah posisi berbaring di tempat.

Pengaturan Posisi Pasien Panduan Lengkap untuk Perawat Nerslicious
Bagaimana dan kapan posisi Trendelenburg terbalik dipraktikkan. Ini dipraktekkan di tempat tidur rumah sakit yang diartikulasikan dan melibatkan memiringkan tempat tidur pada 25-30 ° sehingga kepala dan dada berada di bidang yang lebih tinggi daripada kaki (pasien terlentang). Ini memiliki manfaat pada tengkorak untuk perpanjangan kontra.
The Ultimate Guide to the Trendelenburg Position
The Trendelenburg position is a form of postural treatment that involves placing a patient in a supine position on a bed, but it is inclined (10-35 degrees) such that the head is lower than the feet. It is regularly used during lower abdominal surgery to direct other organs towards the head, facilitating access to the site of interest.

Storm Anesthesia Trendelenburg
Trendelenburg sign is a physical examination finding seen when assessing for any dysfunction of the hip. A positive Trendelenburg sign usually indicates weakness in the hip abductor muscles consisting of the gluteus medius and gluteus minimus. A positive sign is defined by a contralateral pelvic drop during a single leg stance. Named after a German surgeon, Friedrich Trendelenburg, the.
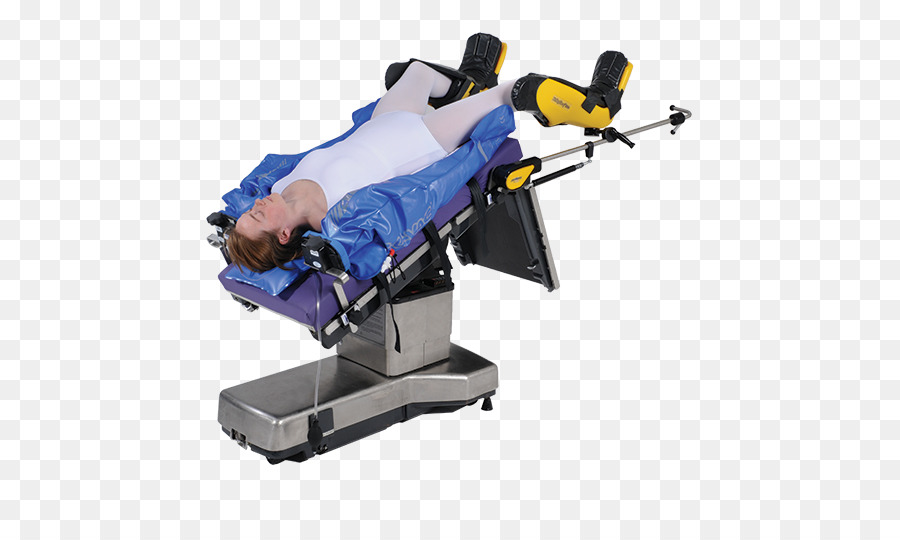
Posisi Trendelenburg, Bedah Posisi, Ginekologi gambar png
The Trendelenburg Position is a position in which the patient is laid supine, with the head declined to an angle between 30-45 degrees. The Trendelenburg position is most often used in surgical procedures of the lower abdomen, pelvis and genitourinary system as it allows gravity to pull the abdominal contents away from the pelvis. The.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/fowlers_trendelenburg-5bb0f23d4cedfd0026f89796.jpg)
Anatomical Position Definitions and Illustrations
Sejarah dan penggunaan awal. Penciptaan posisi Trendelenburg dikaitkan dengan Friedrich Trendelenburg, seorang ahli bedah Jerman abad ke-19. Awalnya, ahli bedah menggunakan teknik ini untuk meningkatkan paparan dan visibilitas organ panggul (3). Selama Perang Dunia Pertama, Walter Cannon, seorang ahli fisiologi Amerika, menganjurkan PT sebagai.

Posición de Trendelenburg Wikia Radiologia Fandom
Posisi Trendelenburg: ketika manajemen pasien ini relevan. By Cristiano Antonino On 25 Mei 2023. Kesehatan slider. Posisi Trendelenburg sangat penting dalam berbagai prosedur pasien. Disebut "anti-shock" karena memfasilitasi perfusi organ vital, tetapi pada kenyataannya juga digunakan dalam seluruh rangkaian prosedur pembedahan.
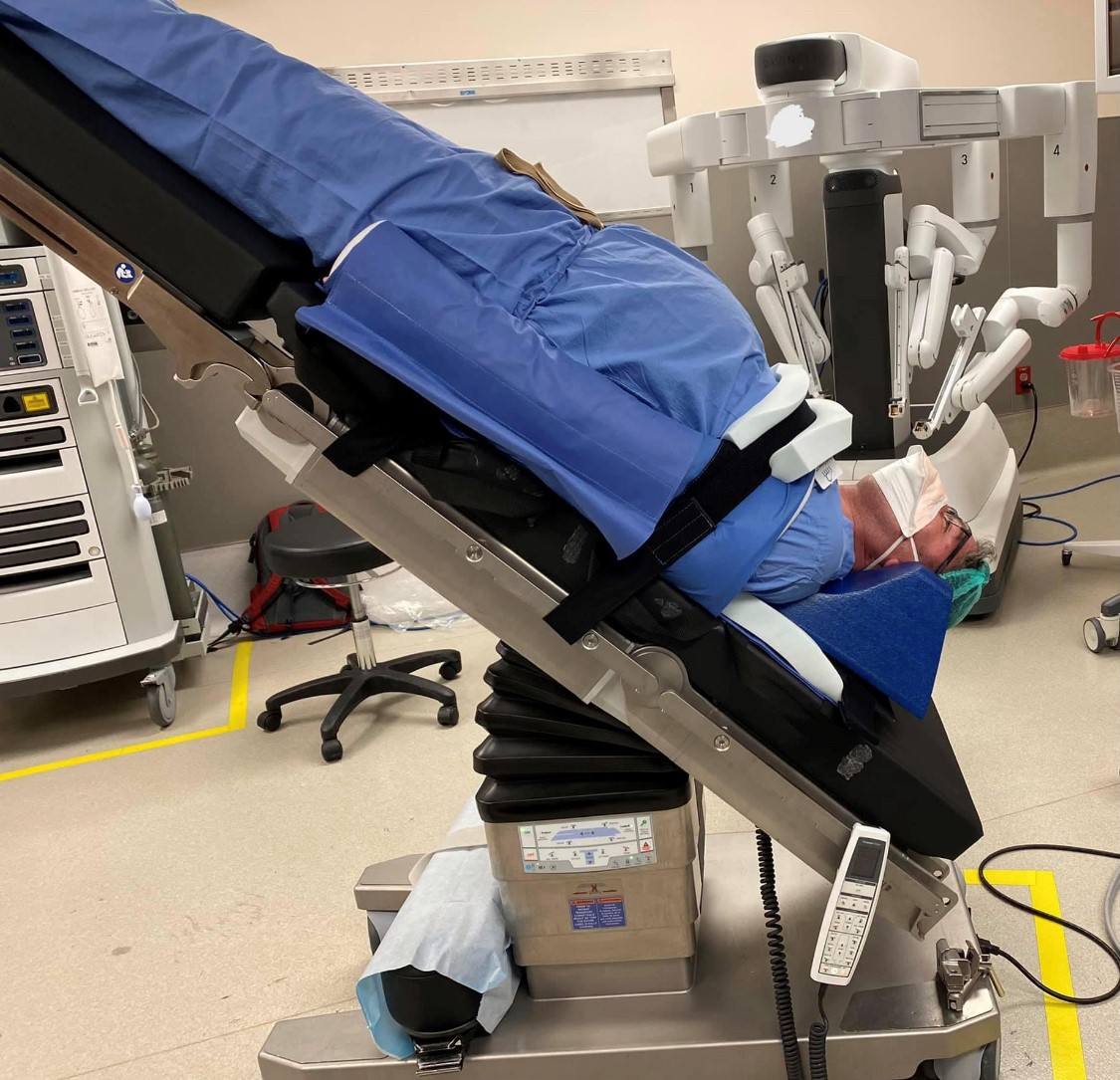
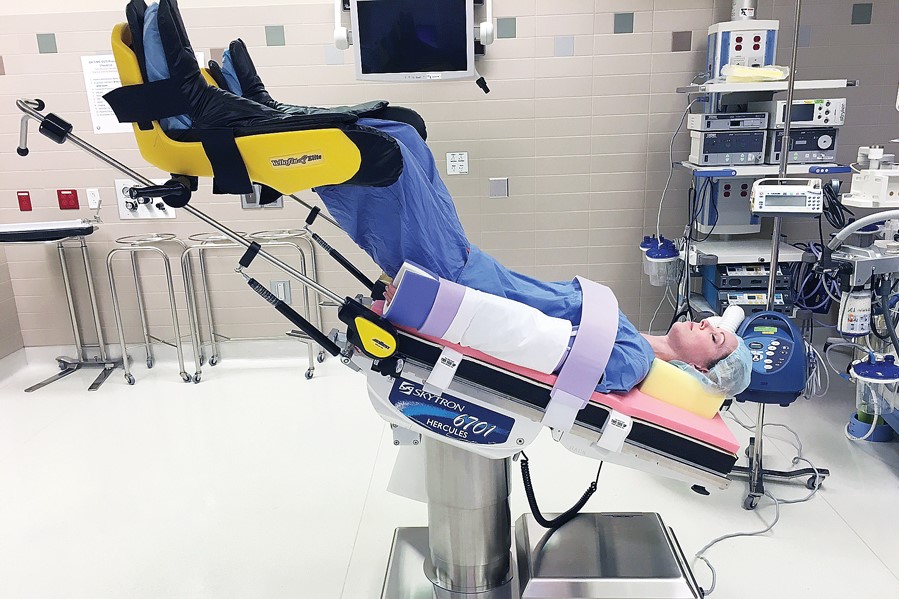
Trendelenburg Positioning System and Robotic Surgery Face Protection
In steep Trendelenburg position, the patient is angled at 30 - 40 degrees in the head-down position. This version of Trendelenburg is most often used for robotic pelvic procedures. Risks associated with steep Trendelenburg position include altered pulmonary function, airway edema, increased intracranial and intraocular pressure, and nerve.