
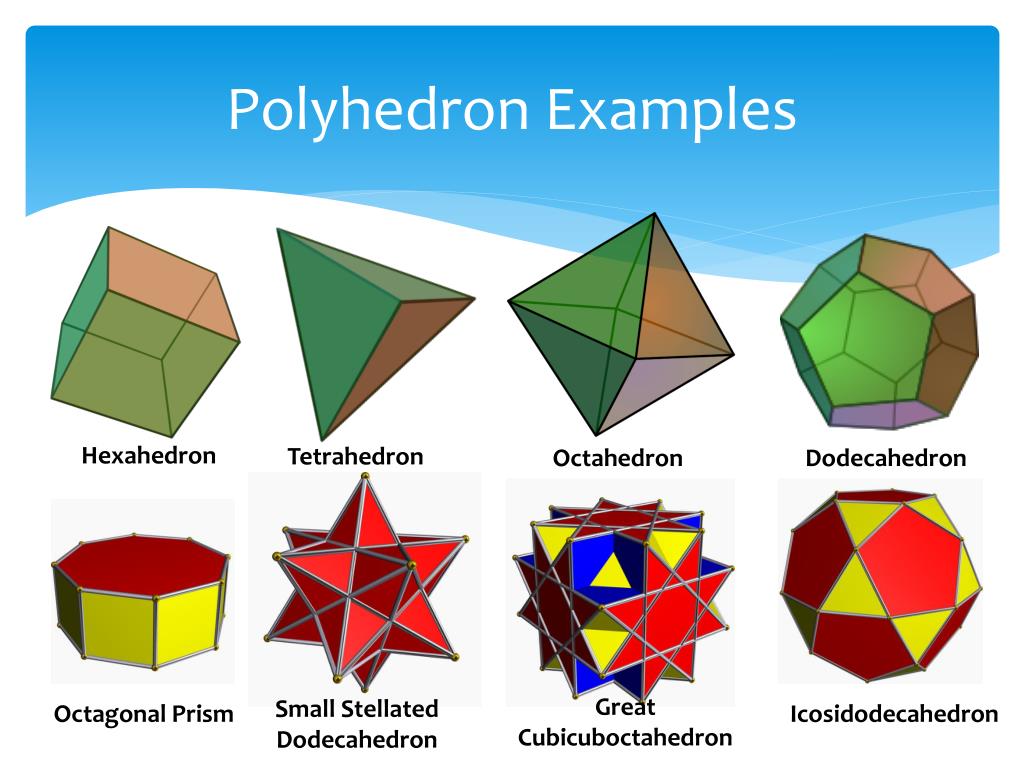
Polyhedron Poster from Acme Klein Bottle Topology, Platonic solid, Polyhedron
We can also check if a polyhedron with the given number of parts exists or not. For example, a cube has 8 vertices, 6 faces, and 12 edges. F = 6, V = 8, E = 12. Applying Euler's formula, we get F + V - E = 2. Substituting the values in the formula: 6 + 8 - 12 = 2 ⇒ 2 = 2 . Hence, the cube is a polyhedron.
polyhedra definition What is
Definition of polyhedral adjective in Oxford Advanced Learner's Dictionary. Meaning, pronunciation, picture, example sentences, grammar, usage notes, synonyms and more.

Convex Polyhedrons Definition, Properties, Types, FAQs
Polyhedral functions include in particular, functions that can be expressed as a maximum of a finite number of affine functions: where , , . Indeed, the epigraph of : can be expressed as the polyhedron. Example: The -norm function, with values , is polyhedral, as it can be written as the maximum of affine functions:
PPT Polyhedron Inspired Art! PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID2568293
Look up polyhedral in Wiktionary, the free dictionary. Polyhedral may refer to: Dihedral (disambiguation), various meanings. Polyhedral compound. Polyhedral combinatorics. Polyhedral cone. Polyhedral cylinder. Polyhedral convex function. Polyhedral dice.
Polyhedral Paper Printable Graph Paper Printable Graph Paper
The meaning of POLYHEDRON is a solid formed by plane faces. Recent Examples on the Web Euler implicitly assumed his polyhedra were convex, meaning a line segment joining any two points stayed completely within the polyhedron. — quantamagazine.org, 26 Jan. 2021 Mold that box into a pyramid or tetrahedron or any other everyday polyhedron. — Devin Powell, Discover Magazine, 20 Mar. 2019 Euler.

Polyhedral models of a) 230 and b) 220 space groups in type... Download Scientific
Regular polyhedron. A regular polyhedron is a polyhedron whose symmetry group acts transitively on its flags. A regular polyhedron is highly symmetrical, being all of edge-transitive, vertex-transitive and face-transitive. In classical contexts, many different equivalent definitions are used; a common one is that the faces are congruent regular.
Obsession? The evolution of making Polyhedrals. Alien Design
Polyhedra cannot contain curved surfaces - spheres and cylinders, for example, are not polyhedra. The polygons that make up a polyhedron are called its faces. The lines where two faces are connected are called edges, and the corners where the edges meet are called vertices.. Polyhedra come in many different shapes and sizes - from simple cubes or pyramids with just a few faces, to complex.
12 Sided Polyhedron
A polyhedron is a solid with flat faces, such as a cube or a dodecahedron. Learn how to count the number of faces, vertices and edges of a polyhedron using Euler's formula and explore some common polyhedra and their properties.
Polyhedral Structures — English
Polyhedral definition: . See examples of POLYHEDRAL used in a sentence.

What is a Polyhedron Definition, Types, Formula, Examples
Regular polyhedra generalize the notion of regular polygons to three dimensions. They are three-dimensional geometric solids which are defined and classified by their faces, vertices, and edges. A regular polyhedron has the following properties: faces are made up of congruent regular polygons; the same number of faces meet at each vertex. There are nine regular polyhedra all together: five.
Polyhedral Model Kit
Polyhedron. In geometry, a polyhedron ( pl.: polyhedra or polyhedrons; from Greek πολύ (poly-) 'many', and ἕδρον (-hedron) 'base, seat') is a three-dimensional shape with flat polygonal faces, straight edges and sharp corners or vertices . A convex polyhedron is a polyhedron that bounds a convex set.

Regular Polyhedra Brilliant Math & Science Wiki
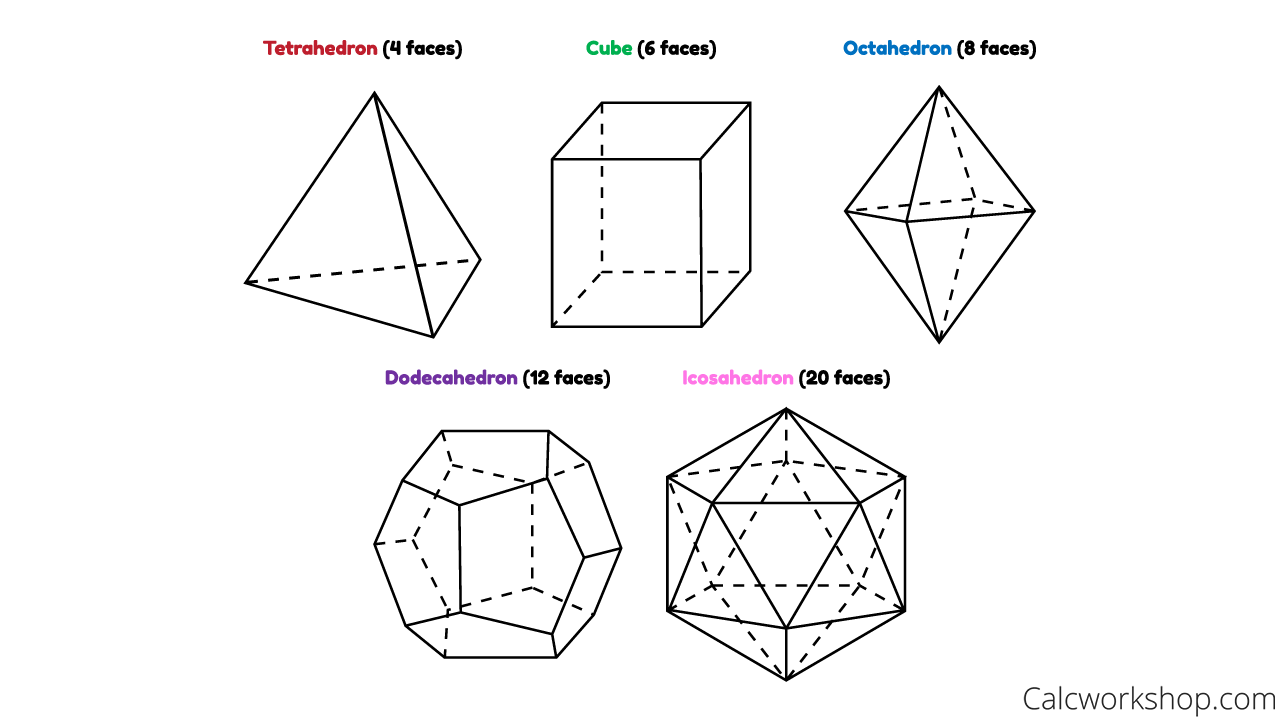
A Platonic solid, also referred to as a regular polyhedron, is a polyhedron whose faces are all congruent regular polygons. In a Platonic solid, the same number of faces meet at each vertex. There are only 5 Platonic solids, and their names indicate the number of faces they have. The 5 Platonic solids are the tetrahedron, cube, octahedron.

Polyhedral representations showing (a) the edgesharing octamer and the... Download Scientific
4.1. POLYHEDRA, H-POLYTOPES AND V-POLYTOPES 51 For example, we may have C i =(H i)+ and C j =(H i)−, for the two closed half-spaces determined by H i.)As A ⊆ E,wehave A = A∩E = p i=1 (Ci ∩E), where C i ∩ E is one of the closed half-spaces determined by the hyperplane, H i = H i ∩ E, in E.Thus,A is also an H-polyhedron in E. Conversely, assume that A is an H-polyhedron in E and that.
Polyhedra
A simple polyhedron, also called a simplicial polyhedron, is a polyhedron that is topologically equivalent to a sphere (i.e., if it were inflated, it would produce a sphere) and whose faces are simple polygons. The number of simple polyhedra on n=1, 2,. nodes are 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 2, 5, 14, 50, 233, 1249,. (OEIS A000109). The skeletons of the simple polyhedra correspond to the triangulated.
Obsession? The evolution of making Polyhedrals. Alien Design
The word polyhedron has slightly different meanings in geometry and algebraic geometry. In geometry, a polyhedron is simply a three-dimensional solid which consists of a collection of polygons, usually joined at their edges. The word derives from the Greek poly (many) plus the Indo-European hedron (seat). A polyhedron is the three-dimensional version of the more general polytope (in the.
Combined ballandstick and polyhedral representation of a molecular... Download Scientific
The volume of a polyhedron composed of N triangular faces with vertices (a_i,b_i,c_i) can be computed using the curl theorem as V=1/6sum_(i=1)^Na_i·n_i, where the normal n_i is given by the cross product n_i=(b_i-a_i)x(c_i-a_i). This formula can be applied to polyhedra with arbitrary faces since faces having more than three vertices can be triangulated. Furthermore, the formula applies to.