
Chromosome Structure
June 3, 2019 in Cell Biology, Genetics, Worksheets by Shannan Muskopf centromere, chromatid, chromosome, DNA, label, nucleus, practice, structure A diagram of a chromosomein the nucleus of the cell. Students label the chromatid, centromere, chromosomes, cell membrane, DNA, and nucleus.
For Keeping X Chromosomes Active, Chromosome 19 Marks The Spot 04/17/2017
However, the labeling achieved by this method is usually restricted to the genomic loci that consist of repetitive sequences, and has not been attempted to track an entire chromosome in a live.
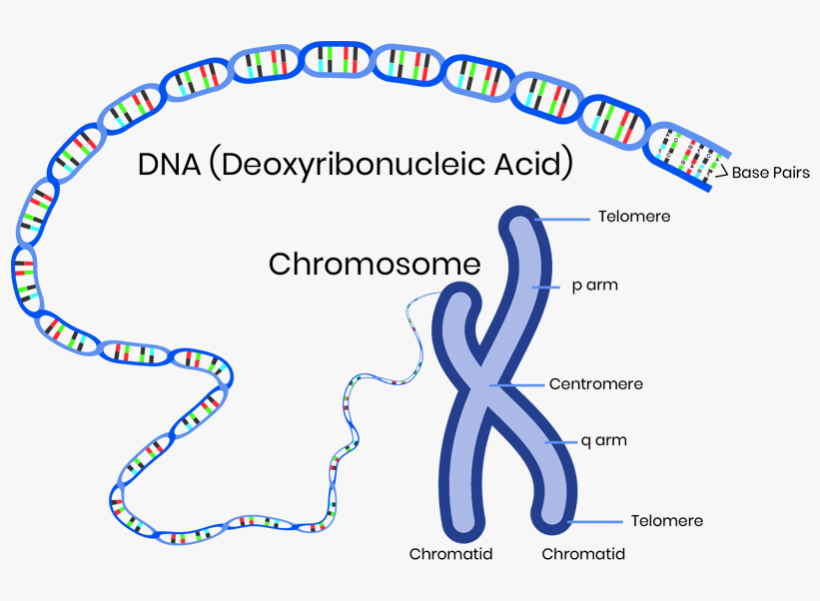
Download The Chromosomes, And Therefore Genes, Are Made Up Of Parts
< Prev Next > Chromosome Map Our genetic information is stored in 23 pairs of chromosomes that vary widely in size and shape. Chromosome 1 is the largest and is over three times bigger than chromosome 22. The 23rd pair of chromosomes are two special chromosomes, X and Y, that determine our sex.

Parts of Chromosome Diagram Quizlet
Chromosome number. Different species have different numbers of chromosomes. For example, humans are diploid (2n) and have 46 chromosomes in their normal body cells. These 46 chromosomes are organized into 23 pairs: 22 pairs of autosomes and 1 pair of sex chromosomes. The sex cells of a human are haploid (n), containing only one homologous.

Chromosome structure Chromosome, Chromosome structure, Structural biology
A karyotype is the number and appearance of chromosomes. To obtain a view of an individual's karyotype, cytologists photograph the chromosomes and then cut and paste each chromosome into a chart, or karyogram, also known as an ideogram. In a given species, chromosomes can be identified by their number, size, centromere position, and banding.
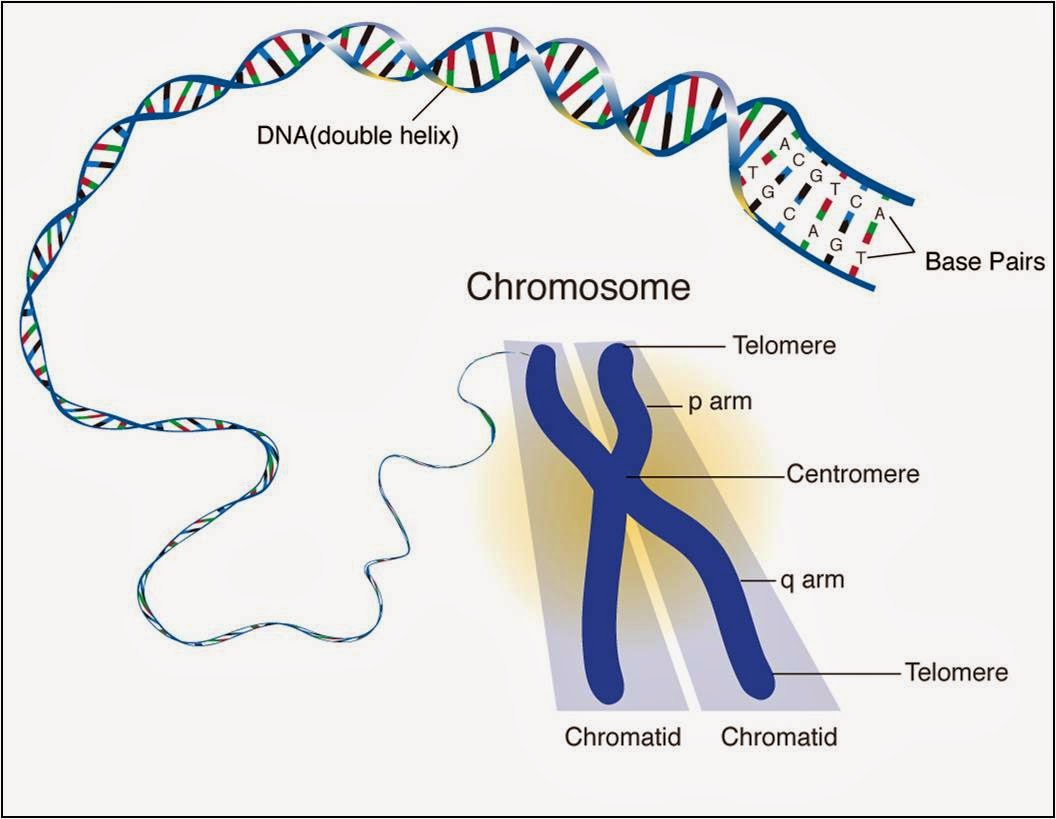
127 Chromosomes, DNA, genes and alleles Biology Notes for IGCSE 2014
Mitosis consists of four basic phases: prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. Some textbooks list five, breaking prophase into an early phase (called prophase) and a late phase (called prometaphase). These phases occur in strict sequential order, and cytokinesis - the process of dividing the cell contents to make two new cells - starts.
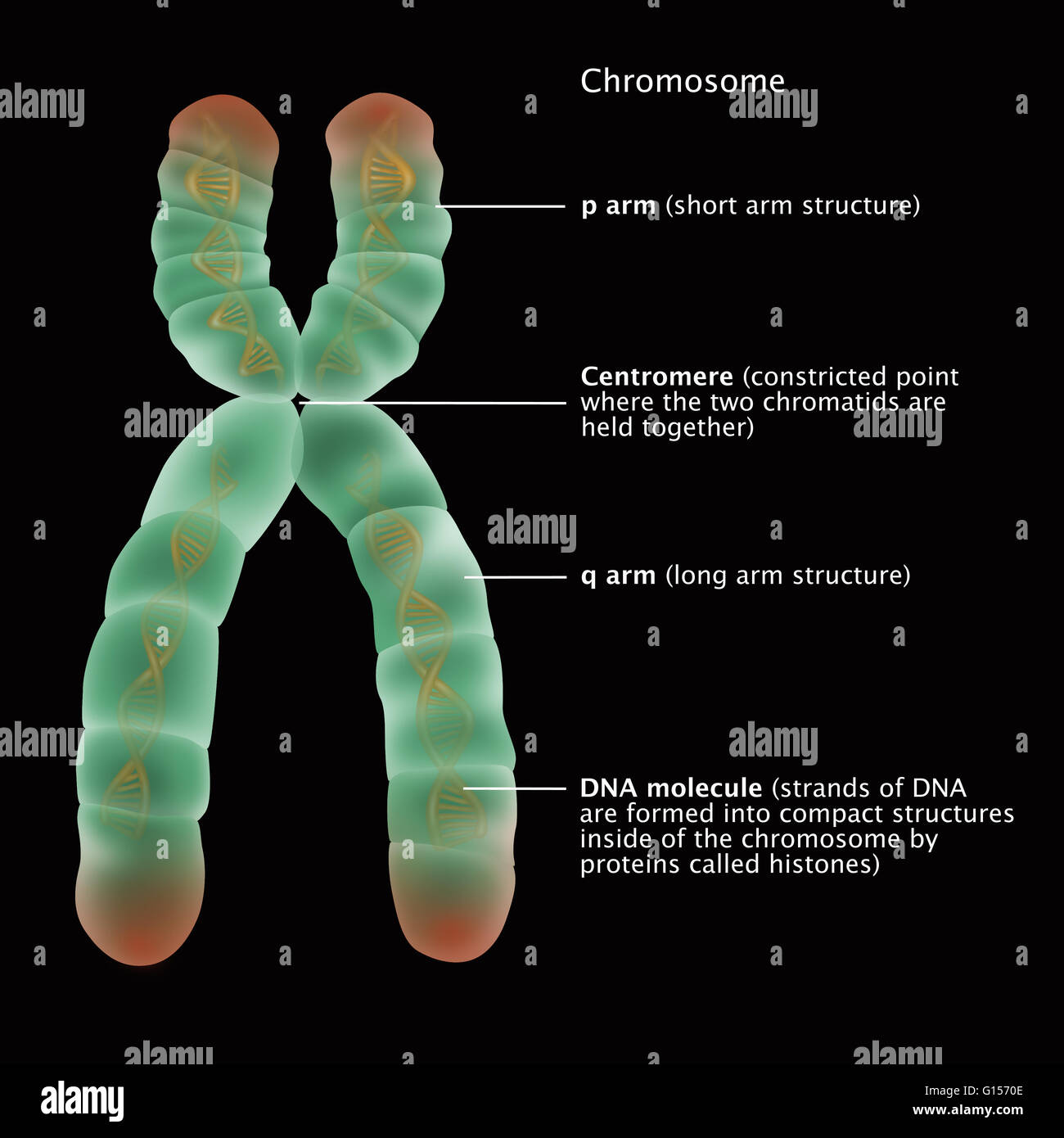
Illustration of the detailed structure of a chromosome. The p arm
The short arm of the chromosome is labeled the "p arm." The long arm of the chromosome is labeled the "q arm." The location of the centromere on each chromosome gives the chromosome its characteristic shape, and can be used to help describe the location of specific genes. DNA and histone proteins are packaged into structures called chromosomes.

Basic components of chromosome Telomeres, Cell Division, Chromosome
ADVERTISEMENTS: The following points highlight the six main parts of a chromosome. The parts are: 1. Pellicle and Matrix 2. Chromatids, Chromonema and Chromomeres 3. Centromeres 4. Secondary Constriction 5. Satellite 6. Telomere. Part # 1. Pellicle and Matrix: A membrane which surrounds each chromosome is said as pellicle. A jelly substance present inside the […]

Labeled Chromosome Structure Diagram imgprobe
The process of differentiating between cells is expressed by labeling the developmental tree. Tracing a path from the root to a specific cell in the tree reveals the history of its divisions. Normal human fetal cells will divide approximately 40 to 60 times before cell division halts as demonstrated by Hayflick [ 1 ].

Chromosome Structure (labeling) Free Worksheets Samples
Students label a simple diagram of a chromosome showing the centromere, chromatid, DNA, and the location of the chromosome within the nucleus of a cell.

Provide me a diagram of chromosomes and genes. Brainly.in
What is a chromosome? Chromosomes are thread-like structures located inside the nucleus of animal and plant cells. Each chromosome is made of protein and a single molecule of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA). Passed from parents to offspring, DNA contains the specific instructions that make each type of living creature unique.

Chromosomes Definition, Structure, Functions & Example
The first number or letter used to describe a gene's location represents the chromosome. Chromosomes 1 through 22 (the autosomes) are designated by their chromosome number. The sex chromosomes are designated by X or Y. The arm of the chromosome.

Chromosome labeling with EdU. a Labeled region localization and
Although currently CRISPR technology is mostly applied to gene editing and regulation 1, we and others have used it to label defined chromosomal loci to image the three-dimensional structure of.

Chromosomes, Genes, and DNA Worksheet Distance Learning Teaching
Below the image is the label gametes made and there are 4 different gametes shown. One gamete is labeled uppercase a uppercase B, 25 percent and has one blue line with an uppercase A at the top and a uppercase B at the bottom of the line.. Homologous chromosomes are paired chromosomes that carry the same genes, but may have different alleles.
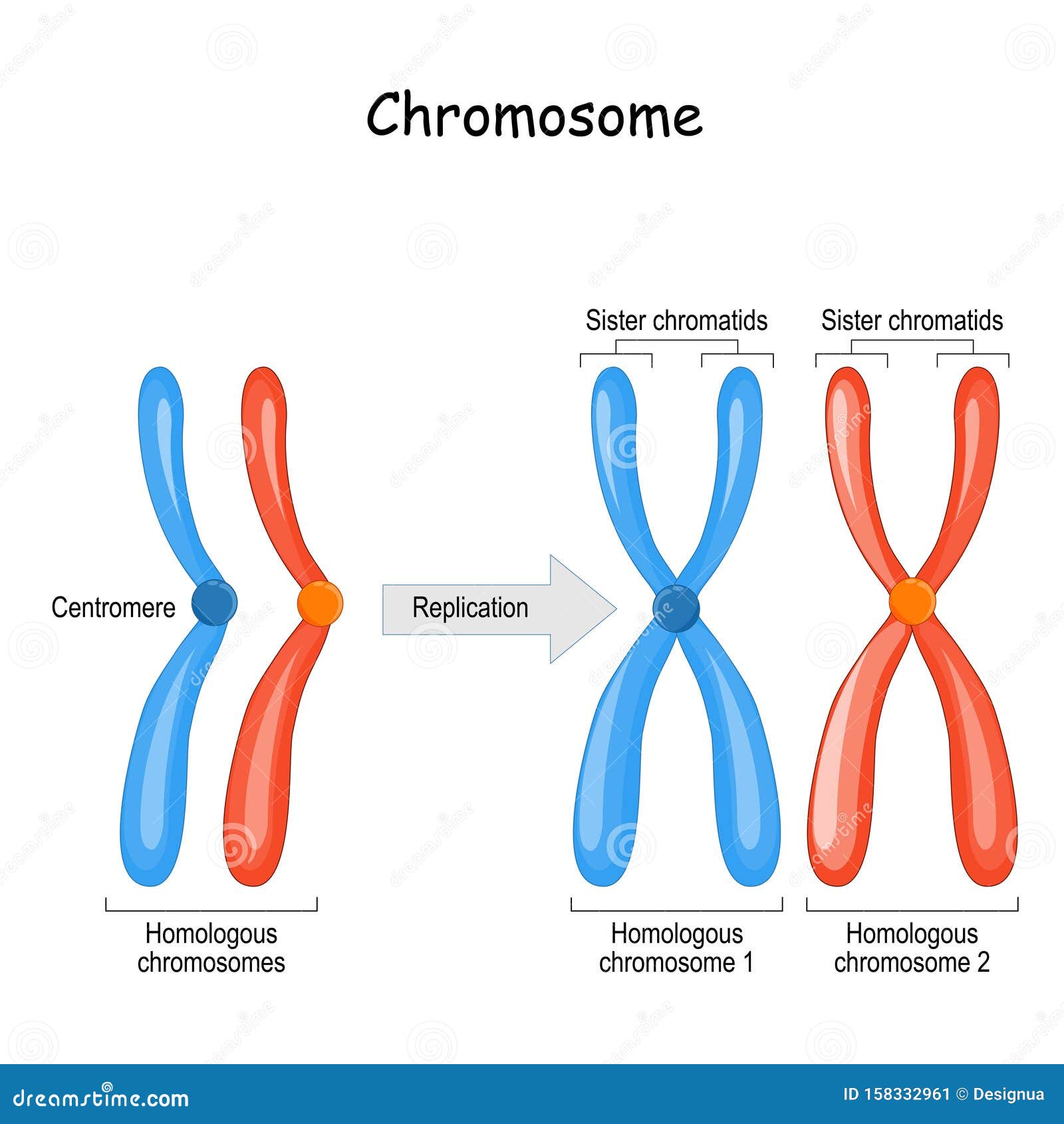
Homologous Chromosomes Stock Illustrations 33 Homologous Chromosomes
The process of differentiating between cells is expressed by labeling the developmental tree. Tracing a path from the root to a specific cell in the tree reveals the history of its divisions. Normal human fetal cells will divide approximately 40 to 60 times before cell division halts as demonstrated by Hayflick [ 1 ].
Mitosis Worksheet And Diagram Identification Answers
A chromosome is a thick ribbon-like structure containing the genetic material i.e., DNA made up of genes. This information is necessary for maintaining and making more copies of a cell.