
coxal bone labeled Diagram Quizlet
Last Updated On June 29, 2021 by Dr. Andrew Chung The hip joint is a ball-and-socket type joint and is formed where the thigh bone (femur) meets the pelvis. The femur has a ball-shaped head on its end that fits into a socket formed in the pelvis, called the acetabulum.

Hip Bones and socket ("Gluteal Region"). Download Scientific Diagram
pelvis, in human anatomy, basin-shaped complex of bones that connects the trunk and the legs, supports and balances the trunk, and contains and supports the intestines, the urinary bladder, and the internal sex organs.The pelvis consists of paired hipbones, connected in front at the pubic symphysis and behind by the sacrum; each is made up of three bones—the blade-shaped ilium, above and to.
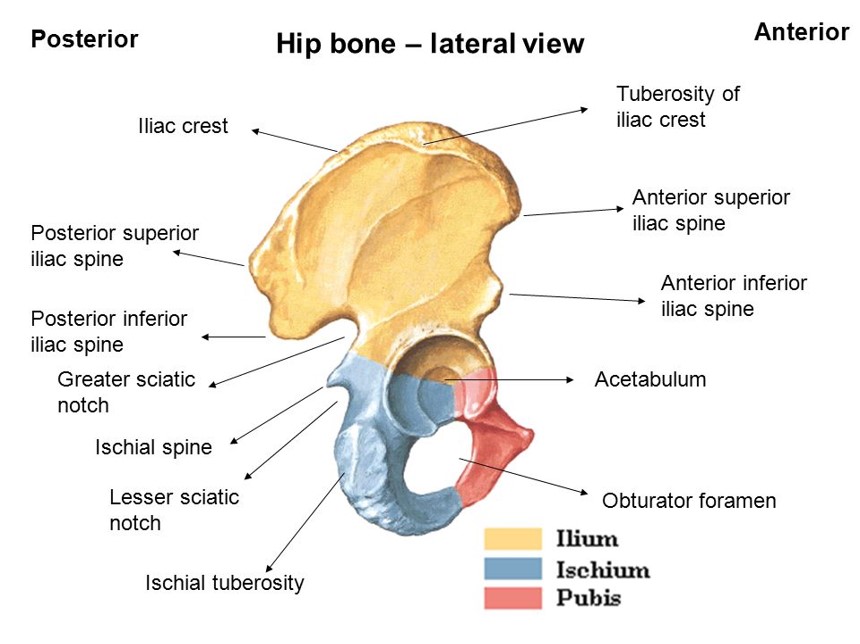
HIP BONE Coxal Bone / Innominate Bone
The hip bones are referred to by different names, such as os coxae or coxal bones, innominate bones, or the pelvic bones. The pelvic girdle is part of the appendicular skeleton, and it not only protects the organs in your pelvic region, but it also attaches the lower limbs of the appendicular skeleton to the sacrum of the axial skeleton.

HIP BONE Coxal Bone / Innominate Bone
Hip bone, also known as the coxal bone, innominate bone, or pelvic bone, is an irregular bone found on both sides of the body. These left and right hip bones join to form the pelvic girdle, where the delicate organs of the lower abdomen are found. Though it looks like a single bone, it comprises three fused bones: ilium, ischium, and pubis.

Human anatomy chart, Human skeleton anatomy, Human anatomy and physiology
The hip bones (a.k.a. the pelvic bones or the coxal bones) are large irregular bones that make up part of the pelvic girdle. They interconnect anteriorly through the pubic symphysis, a secondary cartilaginous joint, and posteriorly communicate with the sacrum at the sacroiliac joints, which are synovial joints. As components of the pelvic girdle, they assist in transferring the weight of the.

Hip Bone or Os Coxae Antomy Medial or Internal View Anatomy and
The pelvic girdle (hip girdle) is formed by a single bone, the hip bone or coxal bone (coxal = "hip"), which serves as the attachment point for each lower limb. Each hip bone, in turn, is firmly joined to the axial skeleton via its attachment to the sacrum of the vertebral column. The right and left hip bones also converge anteriorly to attach to each other.

The ischium of the right coxal bone. Anatomy bones, Human skeleton
The hip bone ( os coxae, innominate bone, pelvic bone [1] or coxal bone) is a large flat bone, constricted in the center and expanded above and below. In some vertebrates (including humans before puberty) it is composed of three parts: the ilium, ischium, and the pubis .

Coxal bone lateral view Diagram Quizlet
Bony pelvis (Pelvis ossea) The bony pelvis is a complex basin-shaped structure that comprises the skeletal framework of the pelvic region and houses the pelvic organs.. It is usually divided into two separate anatomic regions: the pelvic girdle and pelvic spine. The pelvic girdle, also known as the hip bone, is composed of three fused bones: the ilium, ischium and the pubic bone.

😀 A coxal bone includes the. Hip bone. 20190224
Hip bone anatomy lesson of pelvic girdle: The hip bones (also called innominate bones, os coxae, coxal bones, or pelvic bones) form part of the appendicular skeleton..more.
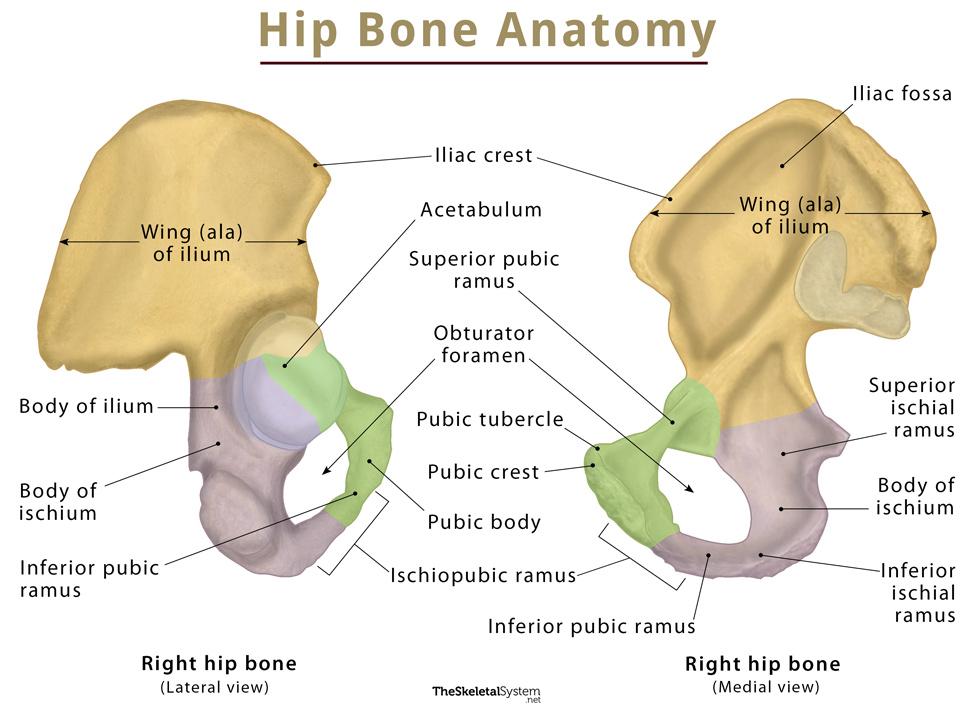
Hip Bone (Coxal Bone) Anatomy, Location, Functions, & Diagram
The hip bone (os coxae) is an irregularly shaped, bilateral bone of the bony pelvis which is also known as the innominate bone, pelvic bone or coxal bone. In reality, it is a compound structure which consists of three smaller bones: the ilium, ischium and pubis.

Coxal (Pelvic) bone, posterior view with labels Appendicular Skeleton
The hip bone (Latin: os coxae ), also known as the pelvic or coxal bone, is a paired anatomical structure formed by the fusion of three bones - the ilium, ischium, and pubis. The left and right hip bones join together at the pubic symphysis. Unlock interactive 3D models with Premium Check it out
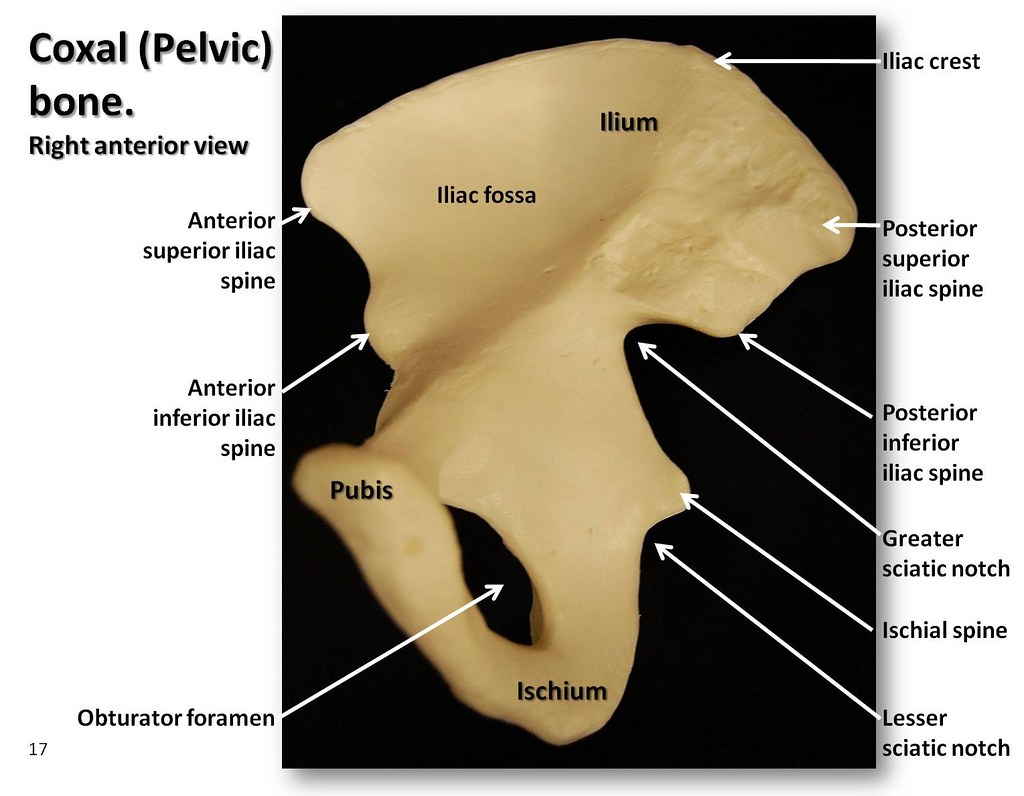
Coxal (Pelvic) bone, anterior view with labels Appendicular Skeleton
The hip bone, or coxal bone, forms the pelvic girdle portion of the pelvis. The paired hip bones are the large, curved bones that form the lateral and anterior aspects of the pelvis. Each adult hip bone is formed by three separate bones that fuse together during the late teenage years.
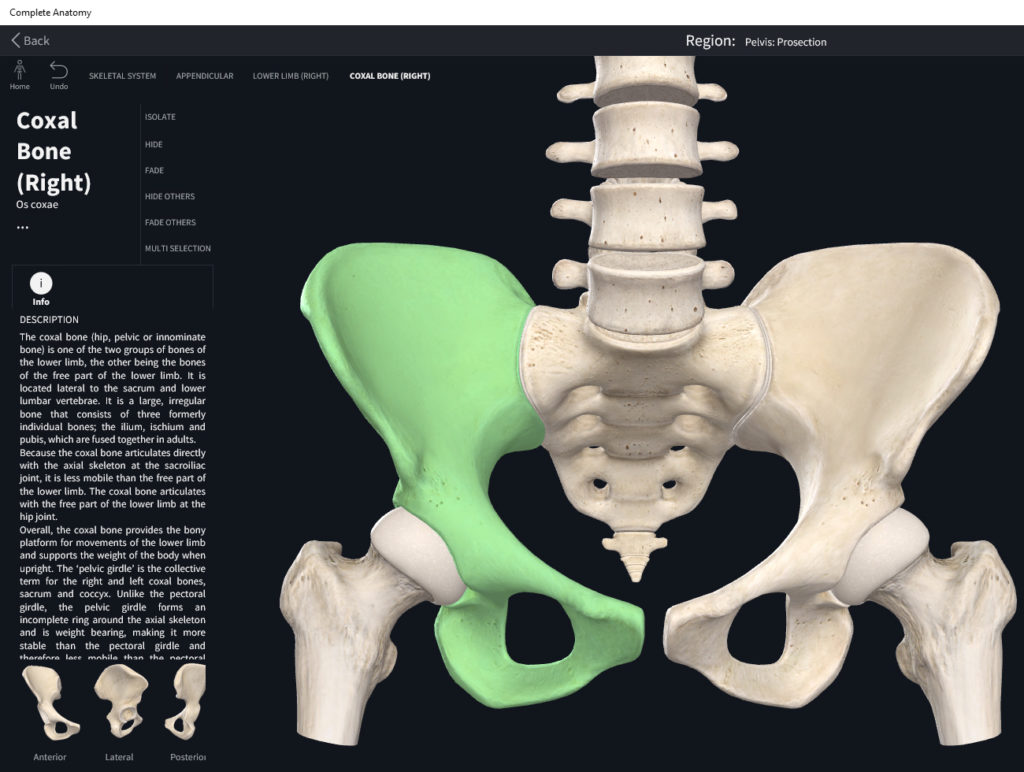
Slides Coxal Bone Basic Sciences
The pelvic girdle (hip girdle) is formed by a single bone, the hip bone or coxal bone (coxal = "hip"), which serves as the attachment point for each lower limb. Each hip bone, in turn, is firmly joined to the axial skeleton via its attachment to the sacrum of the vertebral column.

Image result for coxal bone Coxal, Hueso coxal
Your hip joint connects your torso (axial skeleton) to your lower legs. The function of your hip joint is to: Provide balance and support for your upper body. Move your upper leg. Hold your body weight. The ball-and-socket joint lets your upper leg move at 3 degrees so you can do the following movements: Flex. Extend.

17 Best images about Anatomy & Physiology on Pinterest Flashcard
⚡ Welcome to Catalyst University! I am Kevin Tokoph, PT, DPT. I hope you enjoy the video! Please leave a like and subscribe! 🙏INSTAGRAM | @thecatalystuniver.

Hip coxal Bone Medial View Anatomy Flash Card by Frank H. Etsy
The left and right hip bones (innominate bones, pelvic bones) are two irregularly shaped bones that form part of the pelvic girdle - the bony structure that attaches the axial skeleton to the lower limbs. The hip bones have three main articulations: Sacroiliac joint - articulation with the sacrum.