
Crystal structure of monoclinic Bi2O3; view towards (002) plane. The... Download Scientific
How are Crystal Systems Defined? There are six crystal systems, and all minerals form crystals in one of these six systems. Although you may have seen more than six shapes of crystals, they're all variations of one of these six habits. Each system is defined by a combination of three factors: How many axes it has The lengths of the axes
Crystal of the monoclinic system ClipArt ETC
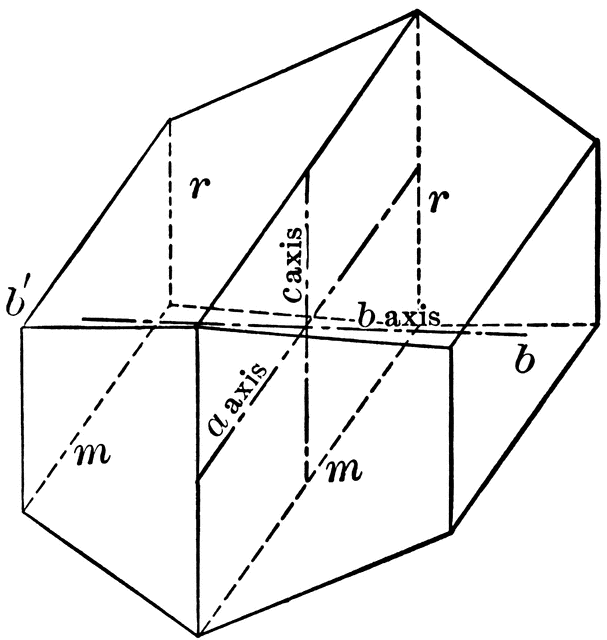
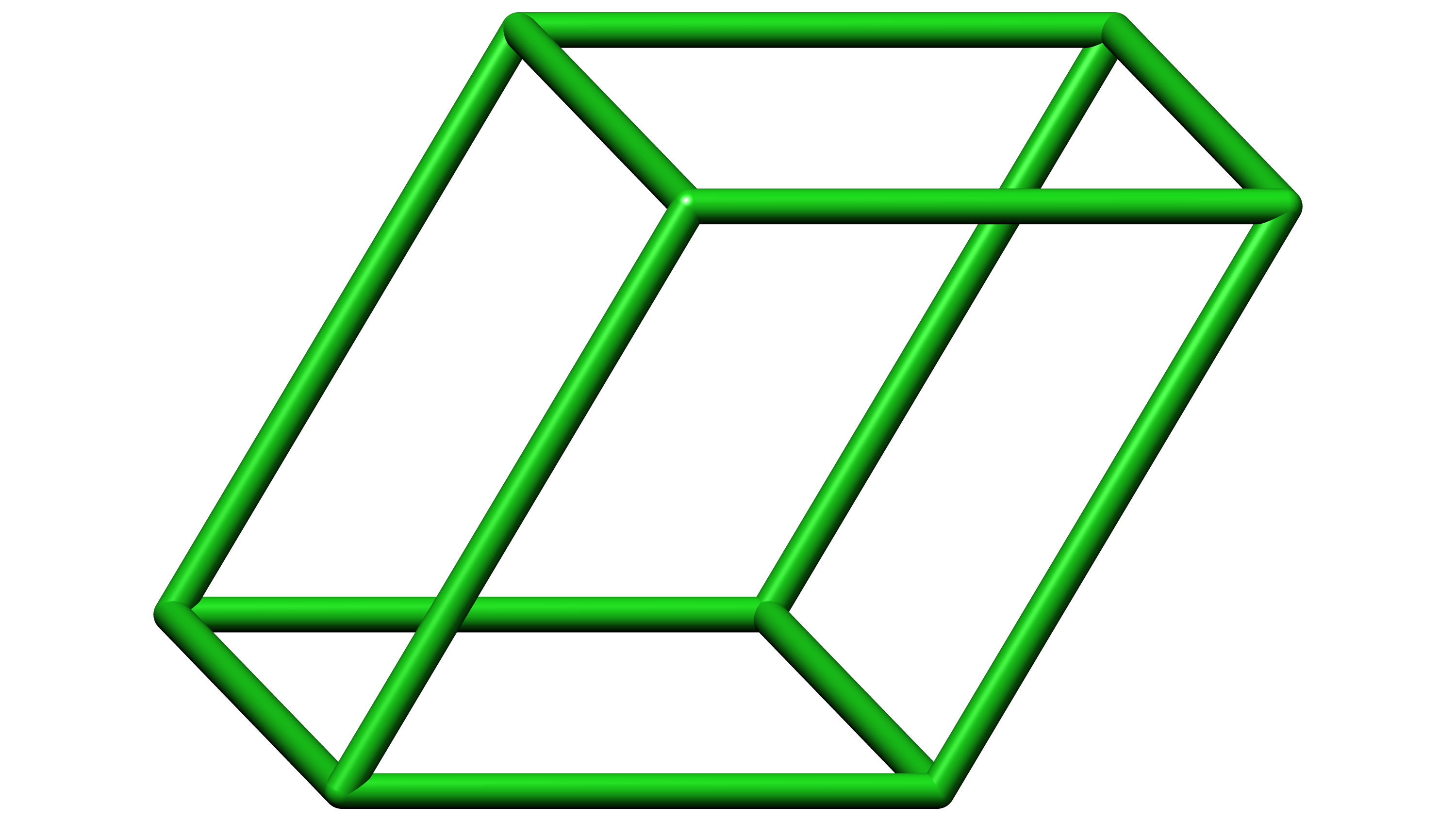
A crystal system is described by three vectors. In the monoclinic system, the crystal is described by vectors of unequal lengths, as in the orthorhombic system. They form a rectangular prism with a parallelogram as its base. Hence two vectors are perpendicular (meet at right angles), while the third vector meets the other two at an angle other.
Monoclinic Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary
In crystallography, the monoclinic crystal system is one of the seven crystal systems. A crystal system is described by three vectors. In the monoclinic system, the is described by vectors of unequal lengths, as in the orthorhombic system. They form a parallelogram prism.

Monoclinic crystal system Stock Vector Images Alamy
The two crystal classes of lowest symmetry are monoclinic and triclinic. In the first, one angle of the unit cell is non-orthogonal, for the latter all angles. Accordingly, the stress-strain.

Monoclinic system Definition & Facts Britannica
Note that the 32 crystal classes are divided into 6 crystal systems. The Triclinic System has only 1-fold or 1-fold rotoinversion axes. The Monoclinic System has only mirror plane(s) or a single 2-fold axis. The Orthorhombic System has only two fold axes or a 2-fold axis and 2 mirror planes.
Сингонии (Crystal systems) СТУДЕНТОРИЙ
Monoclinic system, a group of crystalline solids whose crystals have three axes of unequal length, with two being perpendicular to one another.

Azurite Malachite Mineral Chemical structure, Monoclinic Crystal System, blue, structure
In crystallography, the monoclinic crystal system is one of the seven crystal systems. A crystal system is described by three vectors. In the monoclinic system, the crystal is described by vectors of unequal lengths, as in the orthorhombic system. They form a parallelogram prism. Hence two pairs of vectors are perpendicular , while the third pair makes an angle other than 90°.

monoclinic system Definition & Facts Britannica
Cubic Systems In Bravais lattices with cubic systems, the following relationships can be observed. a = b = c 𝛂 = 𝞫 = 𝝲 = 90o The 3 possible types of cubic cells have been illustrated below. These three possible cubic Bravais lattices are - Primitive (or Simple) Cubic Cell (P) Body-Centered Cubic Cell (I) Face-Centered Cubic Cell (F)

monoclinic minerals Google Search Crystal system, Crystals, Symmetry
The 7 crystal systems are: Cubic, Hexagonal, Tetragonal, Trigonal, Orthorhombic, Monoclinic, Triclinic. The crystal systems are listed in order of decreasing symmetry. Note that "rhombohedral" is NOT a crystal system (but it is a crystal lattice).

Crystal structure ( 2 ) of monoclinic ( P 2/ ) NiWO 4 [15, 18]. The... Download Scientific Diagram
The MONOCLINIC system 6. The TRICLINIC system Every Crystal System involves a number of Crystal Classes. y. CRYSTALLOGRAPHIC AXES Refer to the axes in the order - a, b, c The point of intersection of the three axes is called the AXIAL CROSS. By using these crystallographic axes we can

monoclinic minerals Google Search Crystal system, Crystals, Minerals
The seven crystal systems are triclinic, monoclinic, orthorhombic, tetragonal, trigonal, hexagonal, and cubic. Informally, two crystals are in the same crystal system if they have similar symmetries (albeit there are many exceptions). Classifications Crystals can be classified in three ways: lattice systems, crystal systems and crystal families.

Monoclinic crystal system Crystal structure Crystallography Primitive cell, jadeit, angle
Representation of the crystal structure of compound ganciclovir A3. (A) Portion of the hydrogen bonding network ( yellow dashed lines) viewed along the (100) direction. (B) Crystal packing viewed in perspective along the (001) direction. Symmetry code: (xxvi) x, 1.5 − y, 1/2 + z.

monoclinic crystal Google Search Crystal system, Crystals, Rock minerals
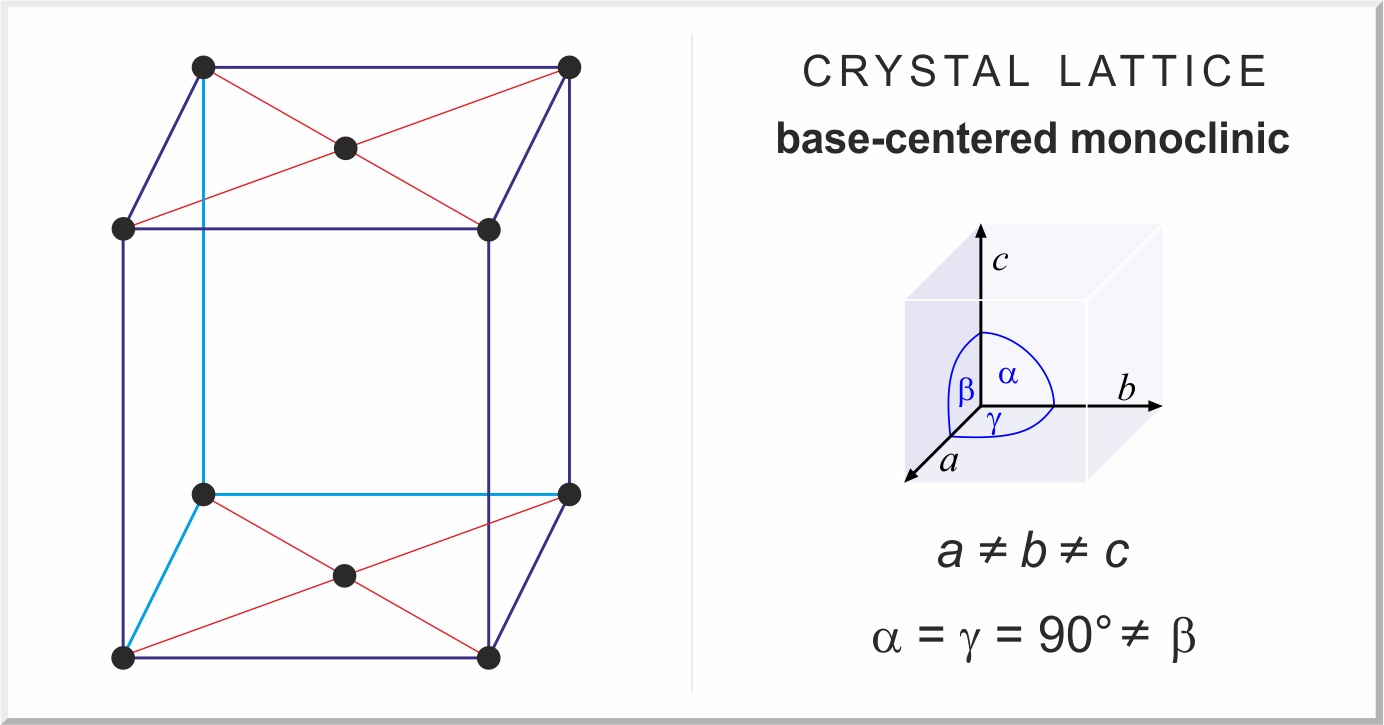
The monoclinic structure has two unit cells. The primative cell (P) has fractional lattice points at the corners of the cell, and the base-centered cell (C) has additional fractional lattice points at the center of the basal planes of the unit cell.. The constraints on the primative vectors and angles for this system are: a < b < c;.

Q 3 The type of crystal system shown is (1) Cubic (2) Orthorhombic (3) Monoclinic (4) Tetragonal
Characteristics of Monoclinic Crystals: Three crystallographic axes of unequal lengths; A single 2-fold symmetry axis; Common Minerals of the Monoclinic System
Monoclinic crystal system Crystal structure Semiconductor, cubic transparent background PNG
The monoclinic lattice has no sides of equal length, but two of the angles are equal to 90°, with the other angle (usually defined as β) being something other than 90°.. This crystal system has the lowest symmetry and must be described by 3 lattice parameters (a, b, and c) and the 3 angles (α, β, and γ). Atom Positions, Crystal.

(a) The crystal structure of monoclinic clinobisvanite BiVO 4. The... Download Scientific Diagram
In crystallography, the monoclinic crystal system is one of the practical crystal systems. Three vectors describe a crystal system. In the monoclinic system, the quartz is described by vectors of inequitable lengths, as in the orthorhombic system forming a rectangular type prism with a parallelogram base.