
Q.1 (2xy sin x)dx + (x cos y)dy= 0. q.2 (1+ 2x/ y2) dx 2y x2 y2dy = 0. q.3
Join Teachoo Black. Ex 5.3, 7 Find 𝑑𝑦/𝑑𝑥 in, sin2 𝑦 +cos 𝑥𝑦 =𝜋 sin2 𝑦 +cos 𝑥𝑦 =𝜋 Differentiating both sides 𝑤.𝑟.𝑡.𝑥 . (𝑑 (sin2 𝑦 + cos 𝑥𝑦))/𝑑𝑥 = (𝑑 (𝜋))/𝑑𝑥 (𝑑 (sin2 𝑦))/𝑑𝑥 + (𝑑 (cos〖 𝑥〗 𝑦))/𝑑𝑥= 0 Calculating Derivative of.

cos(x+y).cos(xy)=cos^2ysin^2x Brainly.in
sin^2y+cos xy=k, find dy/dx.|CLASS 12|CBSE|MATHS|BOARDS|IMP TOPIC
How to solve zxp + yzq = xy Quora
In this video we will discuss some question from chapter - 5 of ncert exemplar problems with more than one methods and also some short or useful methods for.

[最新] y'=sin(x y) cos(x y) 508659(xdyydx)y sin(y/x)=(ydx+xdy)x cos(y/x)
Solve Solve for k k = cos(xy) + (sin(y))2 Quiz Trigonometry sin2y +cosxy = k Videos 03:27 Evaluar expresiones con dos variables: fracciones y decimales Khan Academy 06:27 Solving Quadratic Equations by Factoring 1 Khan Academy Evaluar expresiones con variables: problemas verbales (artículo) | Khan Academy khanacademy.org 05:38

Solved Consider the vector field F(x, y, z) = y cos (xy) i +
Solve your math problems using our free math solver with step-by-step solutions. Our math solver supports basic math, pre-algebra, algebra, trigonometry, calculus and more.

If sin(xy) + cos(xy) = 0 then dy/dx equals Q 39 JEE MAINS YouTube
Trigonometry Examples Popular Problems Trigonometry Expand the Trigonometric Expression sin (2y) sin(2y) sin ( 2 y) Apply the sine double - angle identity. 2sin(y)cos(y) 2 sin ( y) cos ( y)
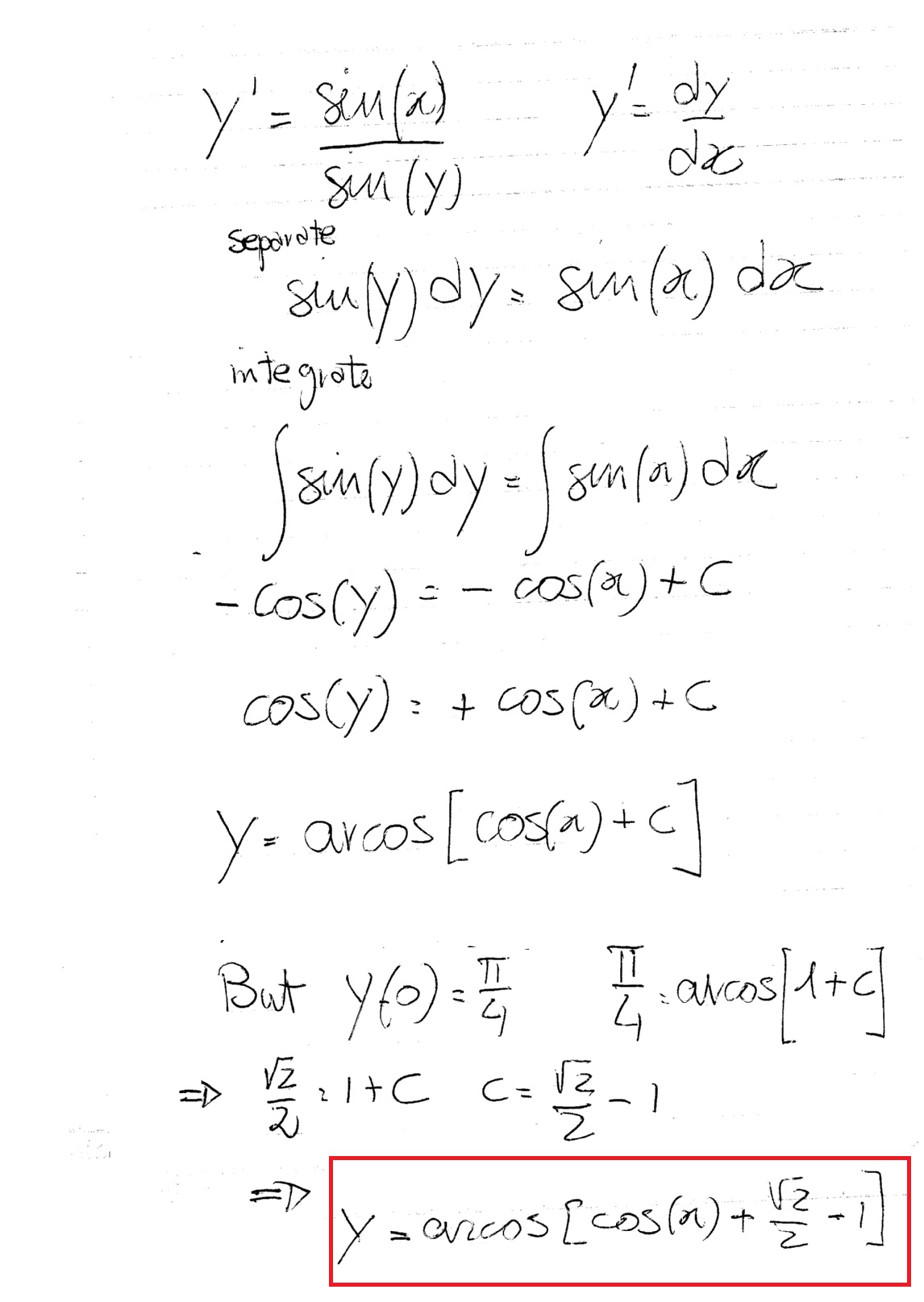
π/2sin^1x 278834π/2sin^1x Saesipjos5r8y
Best answer We are given with an equation sin2y + cos (xy) = k, we have to find [Math Processing Error] d y d x at x = 1, y = [Math Processing Error] π 4 by using the given equation, so by differentiating the equation on both sides with respect to x, we get,

Sin X Cos Y Identity patofia
`sin^(2)y + cos xy = k` Differentiate both sides w.r.t. x ` 2sin y cos y (dy)/(dx) + (-sin xy) (d)/(dx)(xy) =0` `rArr sin 2y (dy)/(dx)-sin xy(x(dy)/(dx)+ y .1)=0`

Find `(dy)/(dx)` in the following `sin^2x+cos^2y=1`... YouTube
Mathematics Integration by Parts Differentiate. Question Differentiate sin 2 y + cos x y = k.? Solution Differentiating sin 2 y + cos x y = k. Given sin 2 y + cos x y = k. Differentiate with respect to x, ⇒ 2 sin y cos y ( d y d x) - sin x y ( y + x d y d x) = 0 ∵ d d x f u = d d u f u × d u d x
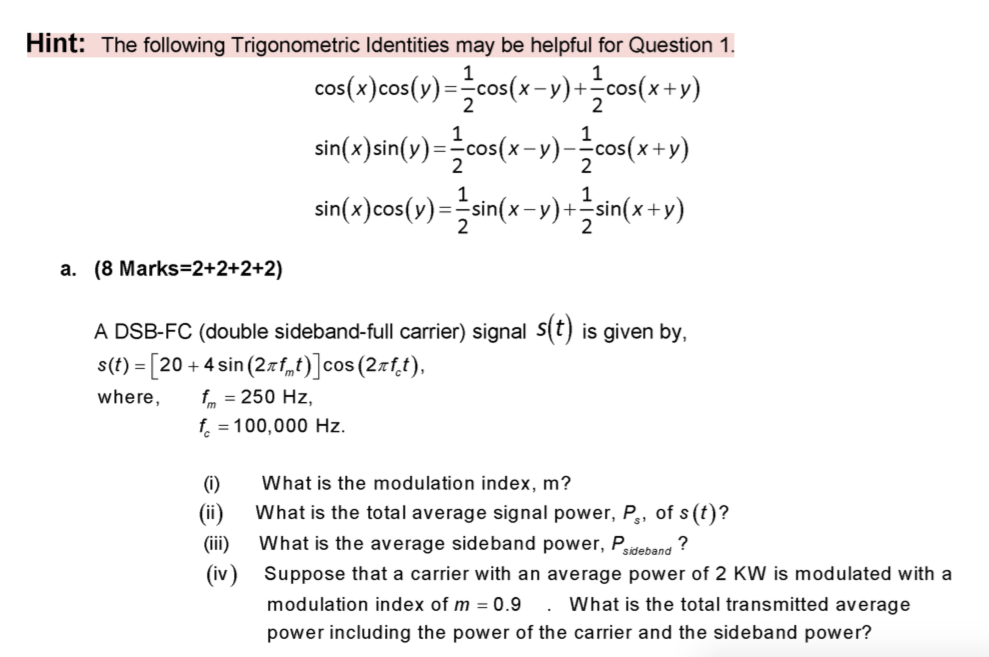
[最新] y'=sin(x y) cos(x y) 508659(xdyydx)y sin(y/x)=(ydx+xdy)x cos(y/x)
Solution Verified by Toppr We have, sin2y+cosxy = k Differentiating both sides with respect to x, we obtain ⇒ d dx(sin2y)+ d dx(cosxy) = d(π) dx = 0. (1) Using chain rule, we obtain d dx(sin2y)= 2siny d dx(siny) = 2sinycosydy dx.. (2) and d dx(cosxy) =−sinxy d dx(xy) = −sinxy[y d dx(x)+xdy dx]

Q25 If cos(xy)=k, where is a constant & xy≠nπ, n∈z, then dy/dx is YouTube
cos(x+y) = cos\\ x* cos\\ y - sin\\ x* sin\\ y cos(x-y) = cos\\ x*cos\\ y + sin \\ x*sin\\ y sin^2 x +cos^2\\ x= 1 cos(x+y) = cos\\ x* cos\\ y - sin\\ x* sin\\ y cos.

`sin^(2)y + cos xy = k` YouTube
Exercise : Find the gradient of. Answer. The directional derivative can also be generalized to functions of three variables. To determine a direction in three dimensions, a vector with three components is needed. This vector is a unit vector, and the components of the unit vector are called directional cosines.
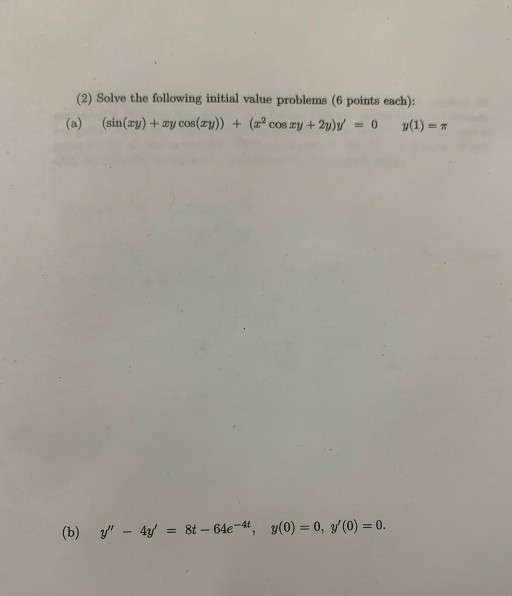
Solved (2) Solve the following initial value problems (6
Solution Verified by Toppr sin2y+cosxy =k 2sinycosydy dx+(−sinxy)(y+xdy dx)= 0 Put y = π 4,x = 1 2× 1 √2× 1 √2dy dx− 1 √2(π 4+ dy dx) = 0 dy dx− 1 √2 dy dx = π 4√2 dy dx = π 4(√2−1) Was this answer helpful? 0 Similar Questions Q 1 If y =(2−3cosx sinx), find dy dx at x = π 4 View Solution Q 2 Find dy dx in the following questions: sin2y+cos xy = k

Calculus Archive April 23, 2017
Solution Given, sin2y+cos xy =k Differentiating both sides w.r.t. x, we get d dx(sin2y+cos xy =k) = d dx(k) ⇒ d dx(sin2y)+ d dx(cos xy)= 0 2sin y cos ydy dx+(−sin xy) d dx(xy) =0 (U sing product rule d dx(f(g(x))) =f (x) d dxg(x)) ⇒ sin 2ydy dx−sin xy(xdy dx+y.1) =0 (∵ sin 2x= 2sin x.cos x)

(1) Given f(x,y,z) = y^2 z^2 sin(xy) Find fx, fy,
Learn Find Dy Dx Sin2y Cos X Y from a handpicked tutor in LIVE 1-to-1 classes Get Started Find dy/dx: sin 2 y + cos xy = κ Solution: A derivative helps us to know the changing relationship between two variables. Consider the independent variable 'x' and the dependent variable 'y'.
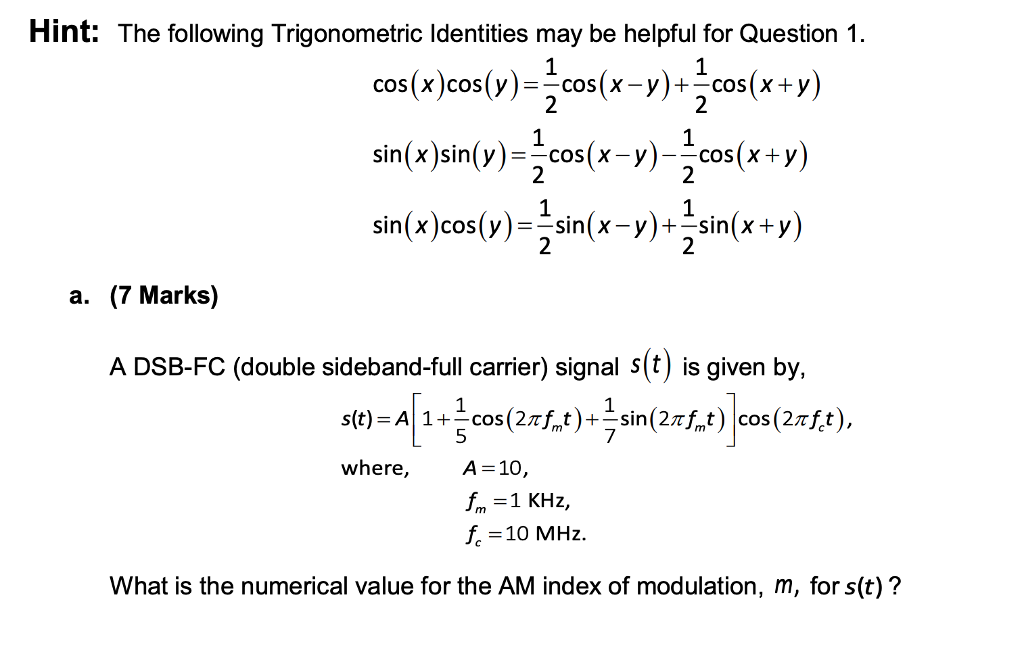
Solved Hint The following Trigonometric Identities may be
The following (particularly the first of the three below) are called "Pythagorean" identities. sin 2 ( t) + cos 2 ( t) = 1. tan 2 ( t) + 1 = sec 2 ( t) 1 + cot 2 ( t) = csc 2 ( t) Advertisement. Note that the three identities above all involve squaring and the number 1. You can see the Pythagorean-Thereom relationship clearly if you consider.