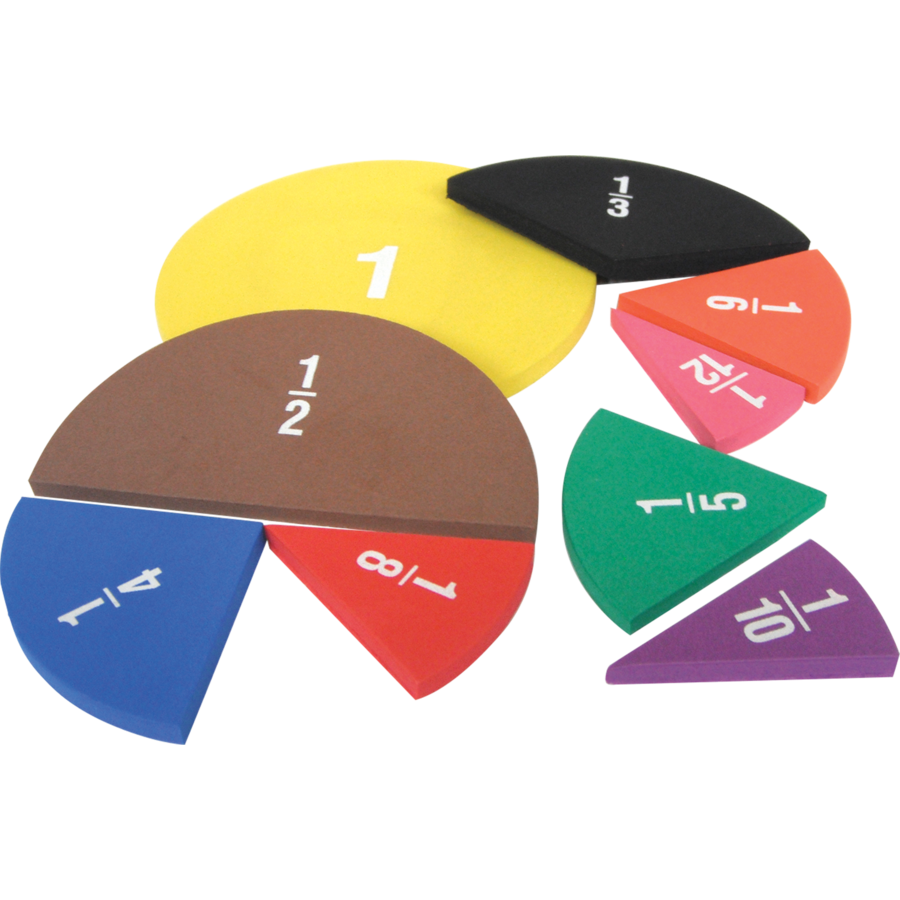
Foam Fraction Circles TCR20611 Teacher Created Resources
A unit circle is just a circle that has a radius with a length of 1. But often, it comes with some other bells and whistles. Contents Why Is the Unit Circle Important? Step 1: 4 Pizza Slices Step 2: 3 Pies for $6 Step 3: 2 Square Tables Step 4: 1, 2, 3 Angles in Degrees Using the Unit Circle in Practice Why Is the Unit Circle Important? Fig. 1.

Fractions Chart Fraction chart, Fractions, Fraction circles
Diablo Valley College. The core concepts of trigonometry are developed from a circle with radius equal to 1 unit, drawn in the xy -coordinate plane, centered at the origin. This circle is given a name: the unit circle (Figure 7.1.1 below). Just like a 12 -hour clock with values of time from 1 to 12, trigonometric functions are periodic, meaning.
Fraction Clipart
1 Learn that ASAP means "All, Subtract, Add, Prime." You can remember it using the acronym "A Student Always Practices." This handy acronym can help you remember how to find the radians for each angle. Unfortunately, the radians aren't the same across the different quadrants, though they do share common denominators.

Circle Correct Fraction Representing Shaded Part Worksheet Turtle Diary
In Figure 2.2.3 2.2. 3 there are 24 equally spaced points on the unit circle. Since the circumference of the unit circle is 2π, 2 π, each of the points is 124 ⋅ 2π = π 12 1 24 ⋅ 2 π = π 12 units apart (traveled along the circle). Thus, the first point counterclockwise from (1, 0) ( 1, 0) corresponds to the distance t = π 12 t = π 12.
Openclipart Clipping Culture
The unit circle is a circle of radius 1, centered at the origin of the \((x,y)\) plane. When measuring an angle around the unit circle, we travel in the counterclockwise direction, starting from the positive \(x\)-axis.. A radian is a measurement of an angle that arises from looking at angles as a fraction of the circumference of the unit.

1 3 fraction clipart 10 free Cliparts Download images on Clipground 2023
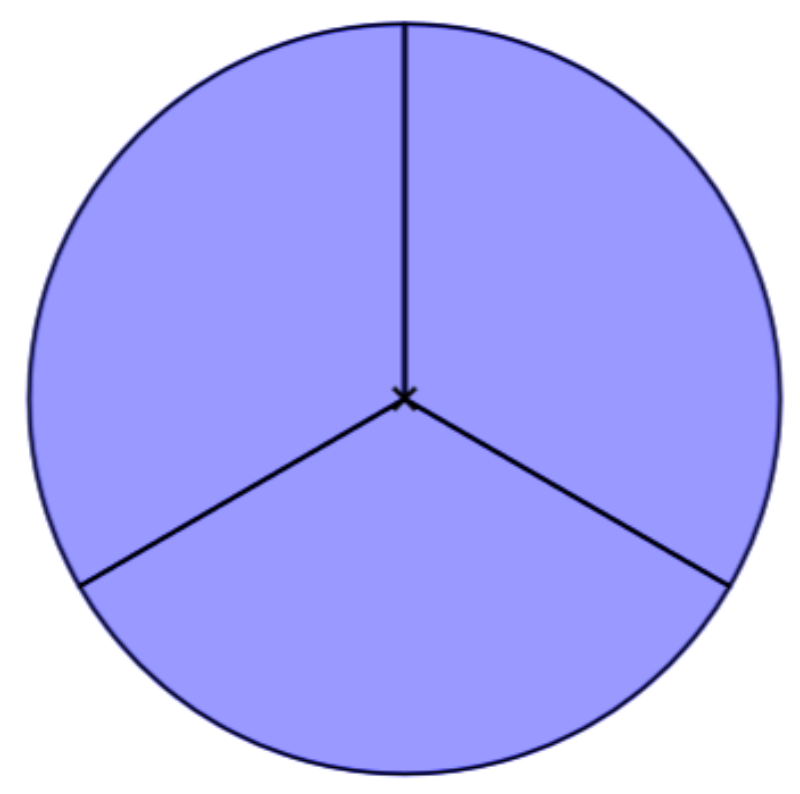
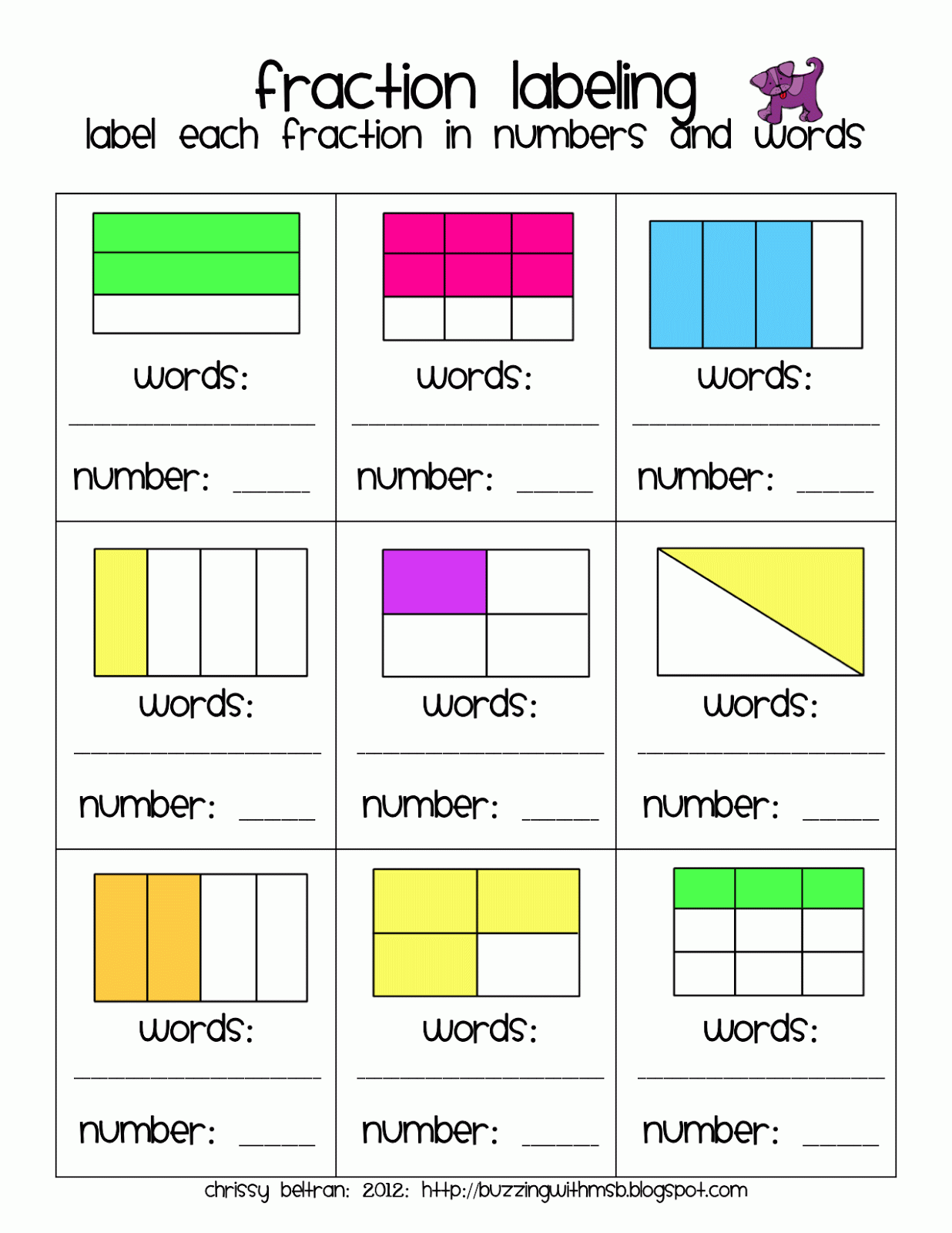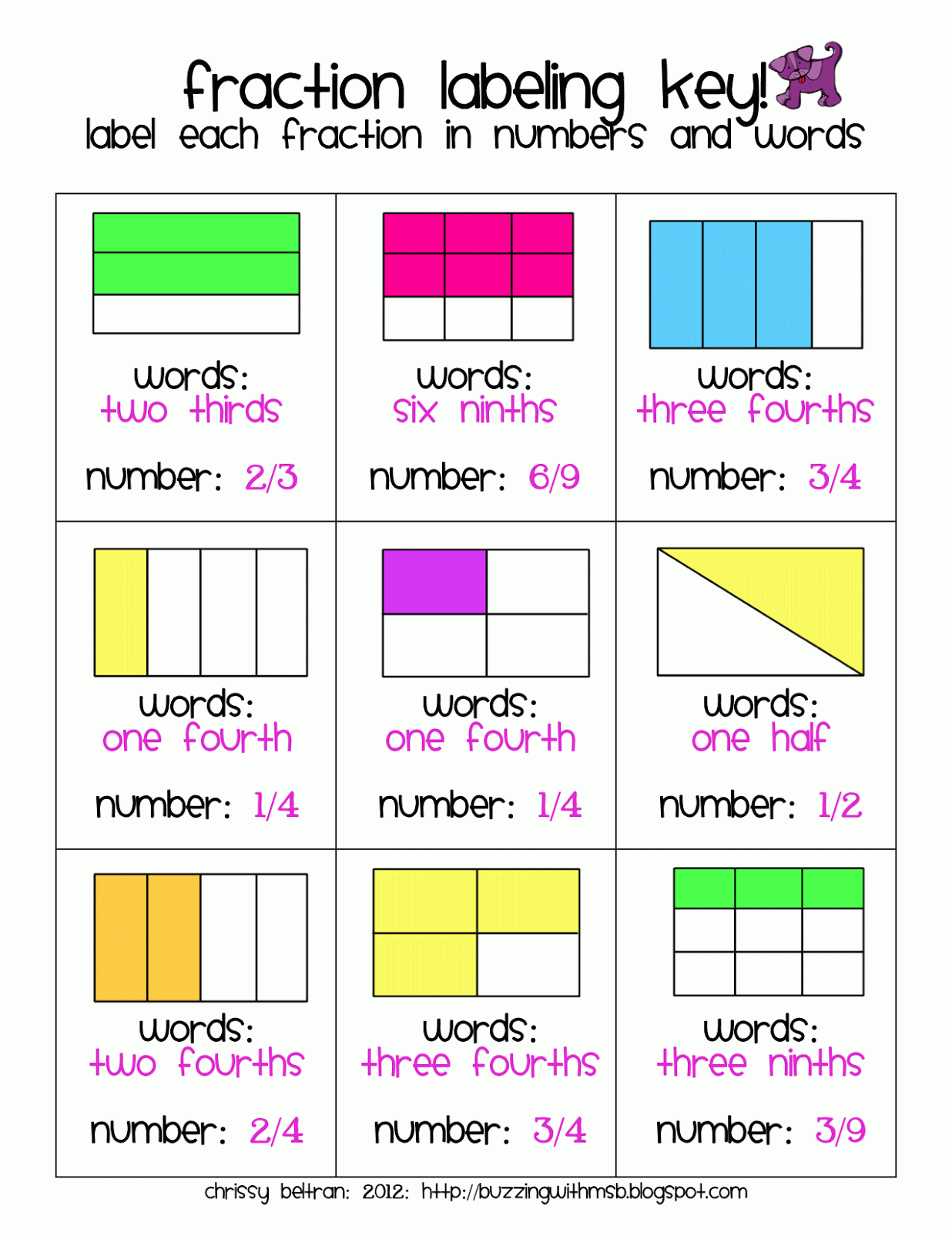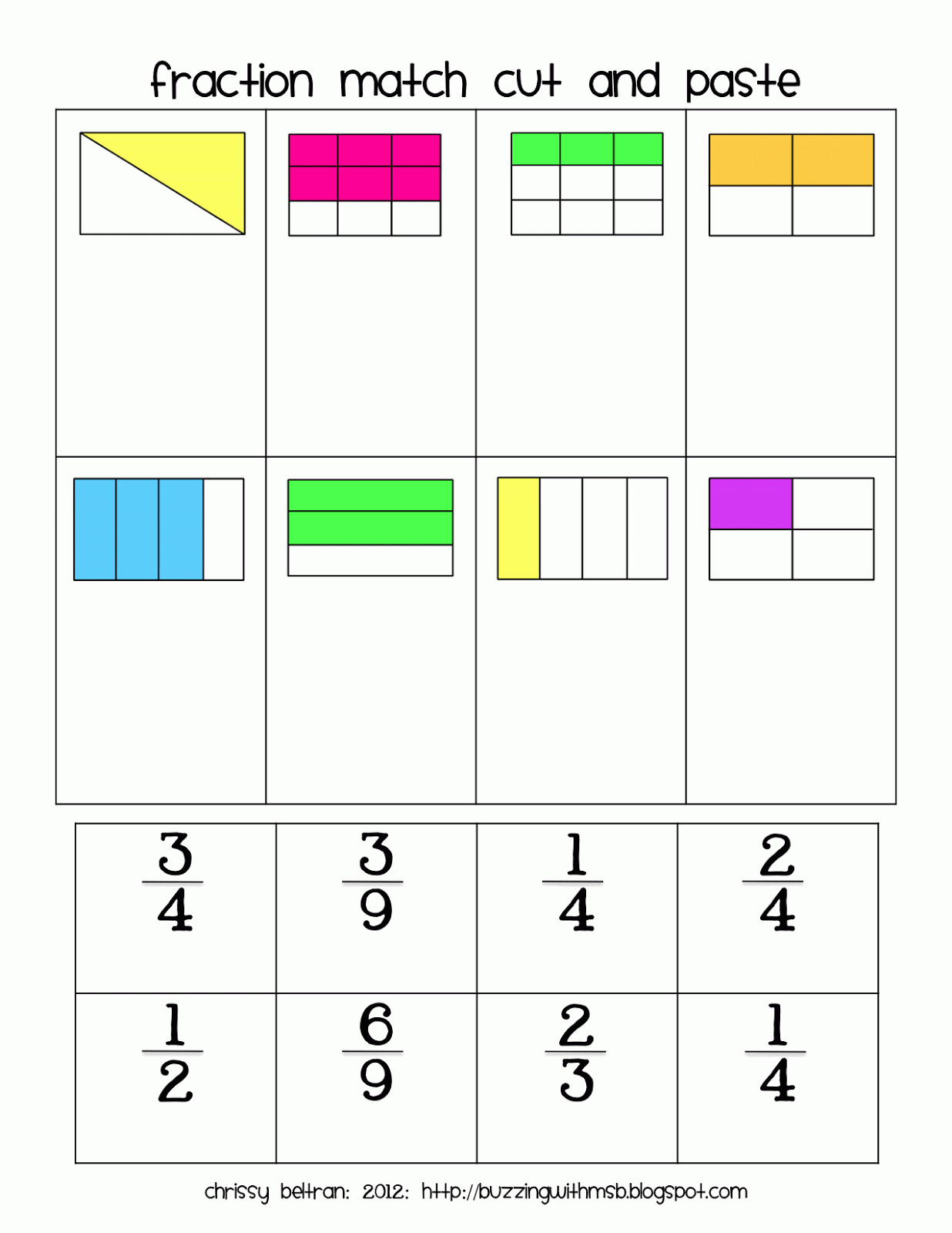
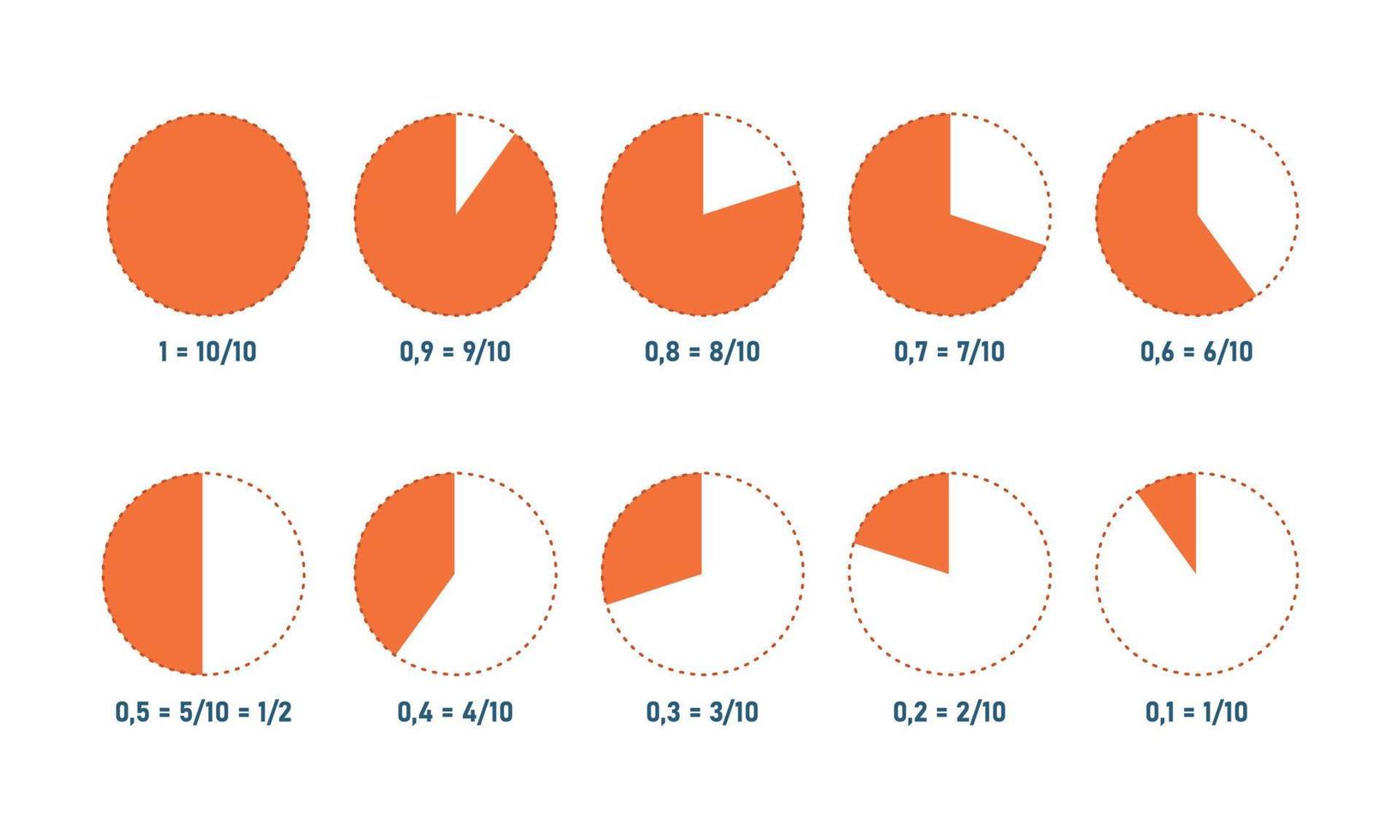
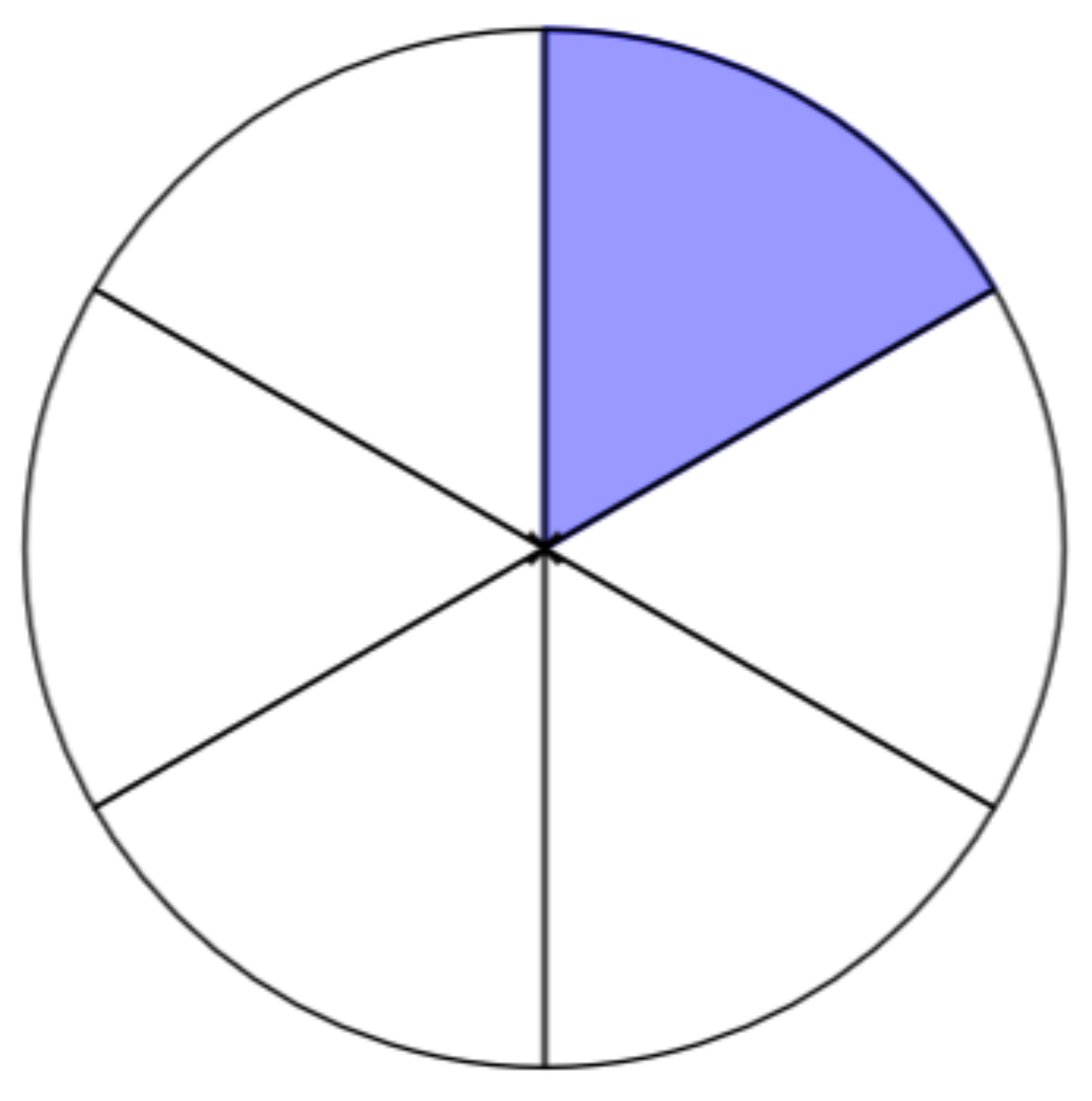
A fraction is a way to represent parts of a whole. The denominator represents the number of equal parts the whole has been divided into, and the numerator represents how many parts are included. The denominator, , cannot equal zero because division by zero is undefined. In Figure , the circle has been divided into three parts of equal size.
Free Rectangle Fraction Cliparts, Download Free Rectangle Fraction Cliparts png images, Free
1 Know what the unit circle is. The unit circle is a circle, centered at the origin, with a radius of 1. Recall from conics that the equation is x 2 +y 2 =1. This circle can be used to find certain "special" trigonometric ratios as well as aid in graphing.
Fraction Circles
View Difference Between Unit and Non-unit Fraction While a unit means one, a non-unit represents any number other than one. Hence, a non-unit fraction is a fraction with a numerator other than one. The denominator can be any whole number except 0. Examples: 2/3, 3/5, 4/7, etc. How to Multiply Unit Fractions
Trig Addendum Modified Radian Fraction Cutouts Insert Clever Math Pun Here
TL;DR Unit circle relations for sine and cosine: Sine is the y-coordinate; and Cosine is the x-coordinate 🙋 Do you need an introduction to sine and cosine? Visit our sine calculator and cosine calculator! Standard explanation: Let's take any point A on the unit circle's circumference. The coordinates of this point are
Definition of unit fraction circle. School education. Vector illustration 6683549 Vector Art at
About Transcript Learn how to use the unit circle to define sine, cosine, and tangent for all real numbers. Created by Sal Khan. Questions Tips & Thanks Sort by: Top Voted Vamsavardan Vemuru 11 years ago Do these ratios hold good only for unit circle? What if we were to take a circles of different radii? • 2 comments ( 186 votes) Upvote Downvote

fraction manipulatives circles pie
unit circle problems called the triangle method. What is the unit circle? The unit circle has a radius of one. The intersection of the x and y-axes (0,0) is known as the origin. The angles on the unit circle can be in degrees or radians. The circle is divided into 360 degrees starting on the right side of the x-axis and moving

hand2mind Plastic Connecting Fraction Circles, Fraction Manipulatives, Unit Fraction, Rainbow
By understanding and memorizing "the unit circle" we are able to breeze through otherwise calculation-heavy problems, and make our lives a whole lot easier. The unit circle, in it's simplest form, is actually exactly what it sounds like: A circle on the Cartesian Plane with a radius of exactly 1 u n i t 1 unit 1 u ni t. Like this blank unit.

hand2mind Plastic Connecting Fraction Circles, Fraction Manipulatives, Unit Fraction, Rainbow
The unit circle gives an easy method of defining the sine and cosine functions that you have probably met before, since for an arbitrary angle (see diagram below), the radius making an angle with the x-axis cuts the unit circle at the point whose x-coordinate is cos and whose y-coordinate is sin . This is really useful because using this method.

hand2mind Plastic Connecting Fraction Circles, Fraction Manipulatives, Unit Fraction, Rainbow
Welcome to Learning Easier !! Here will Learn about Circle Unit Fractions. Here will learn about Unit Fraction. Unit Fraction is a Fraction having One 1 as N.
6 In Fraction Boxfirepress
We know that cos t is the x -coordinate of the corresponding point on the unit circle and sin t is the y -coordinate of the corresponding point on the unit circle. So: x = cos t = 1 2 y = sin t = √3 2. Try It 2.2.1. A certain angle t corresponds to a point on the unit circle at ( − √2 2, √2 2) as shown in Figure 2.2.5.
Fractions clipart template, Fractions template Transparent FREE for download on WebStockReview 2023
recognise, find and name a quarter as one of four equal parts of an object, shape or quantity. In Year 2, pupils use fractions as 'fractions of' discrete (whole numbers) and continuous (any numerical value e.g. 3.6) quantities by solving problems using shapes, objects and quantities. They connect unit fractions to: equal sharing and grouping;