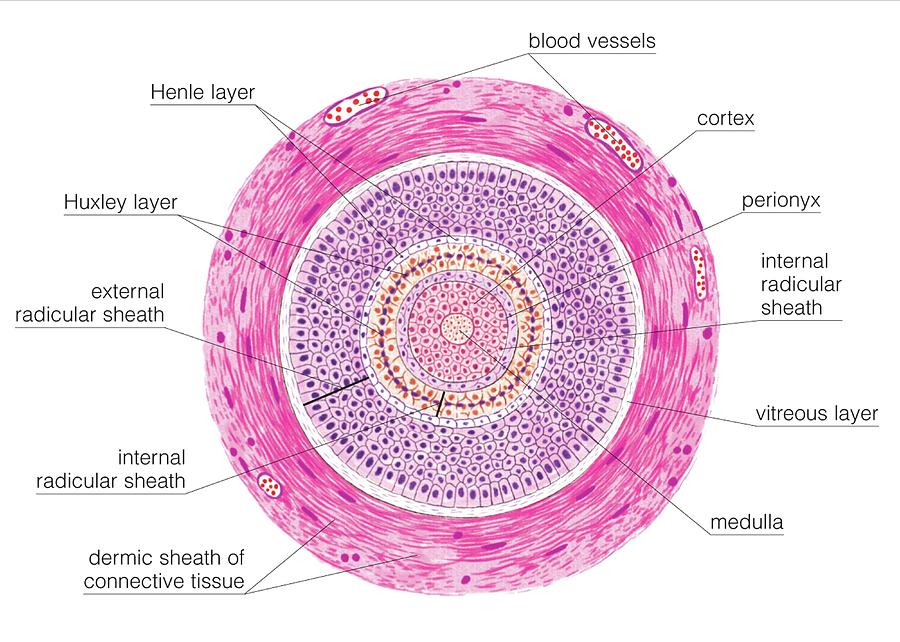
Anatomy Of A Hair Follicle
The hair follicle regulates via a complex interaction between neuropeptides immune cells [1] This complex interaction induces the hair follicle to produce different types of as seen on different parts of the body.
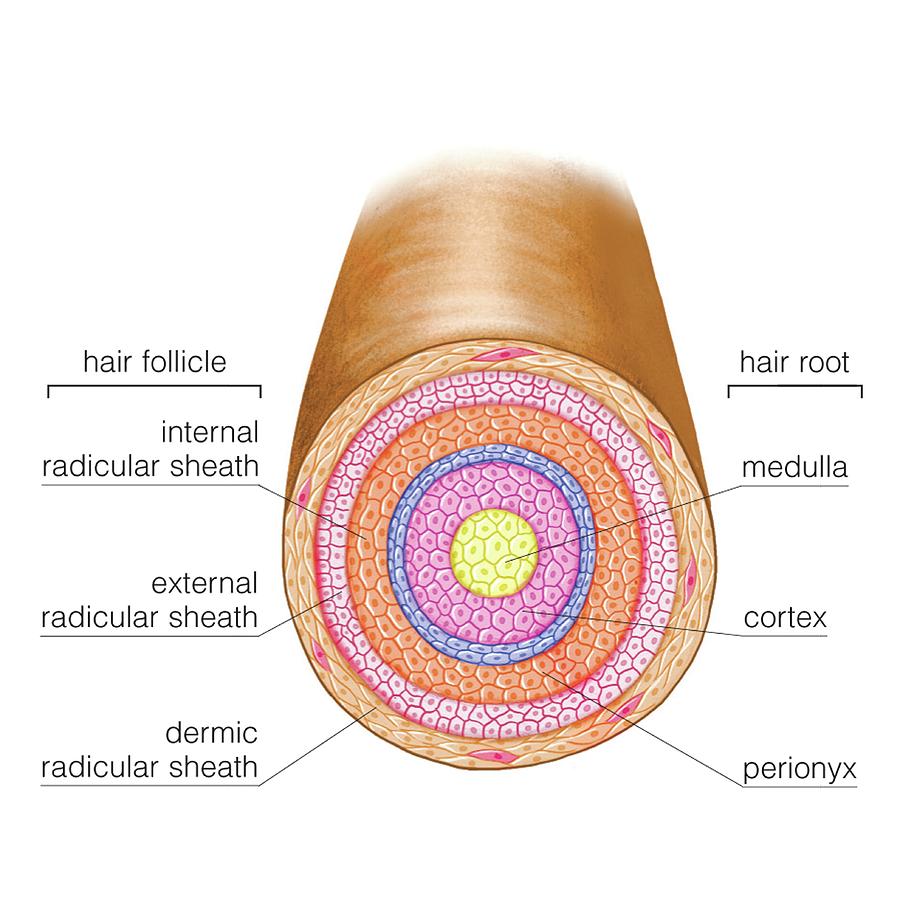
Hair Anatomy
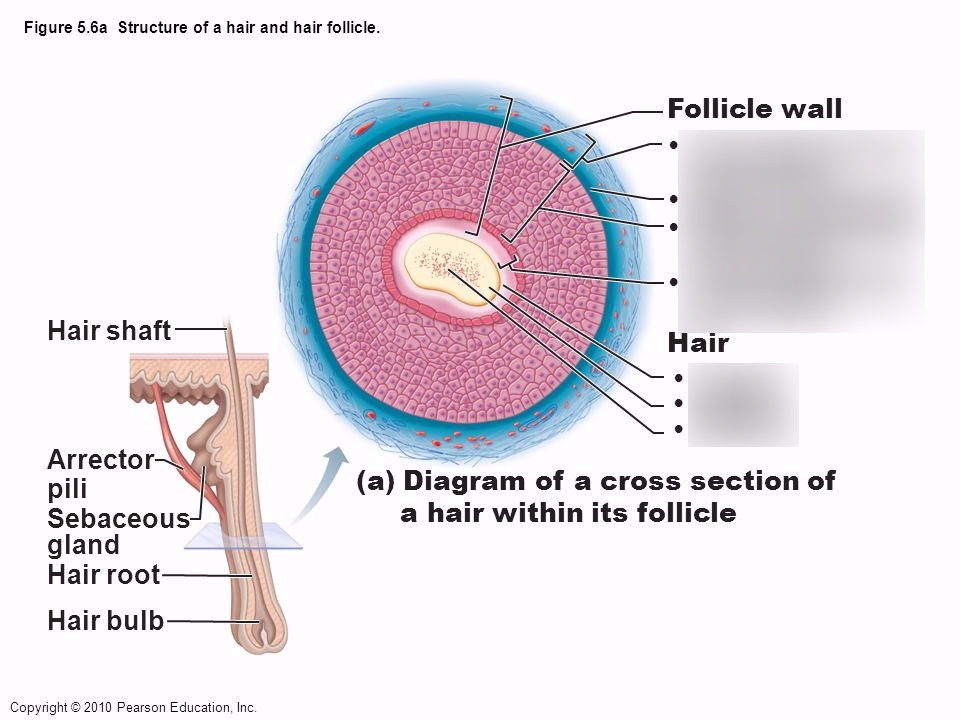
Hair primarily serves for protection, warmth, and sensation. Human hair is made of keratin. The structure of the hair follicle includes the papilla, matrix, root, and bulb. The different types of hair on the human body include lanugo, vellus hair, and terminal hair. Attached to the follicle is a tiny bundle of muscle fiber called the arrector pili.
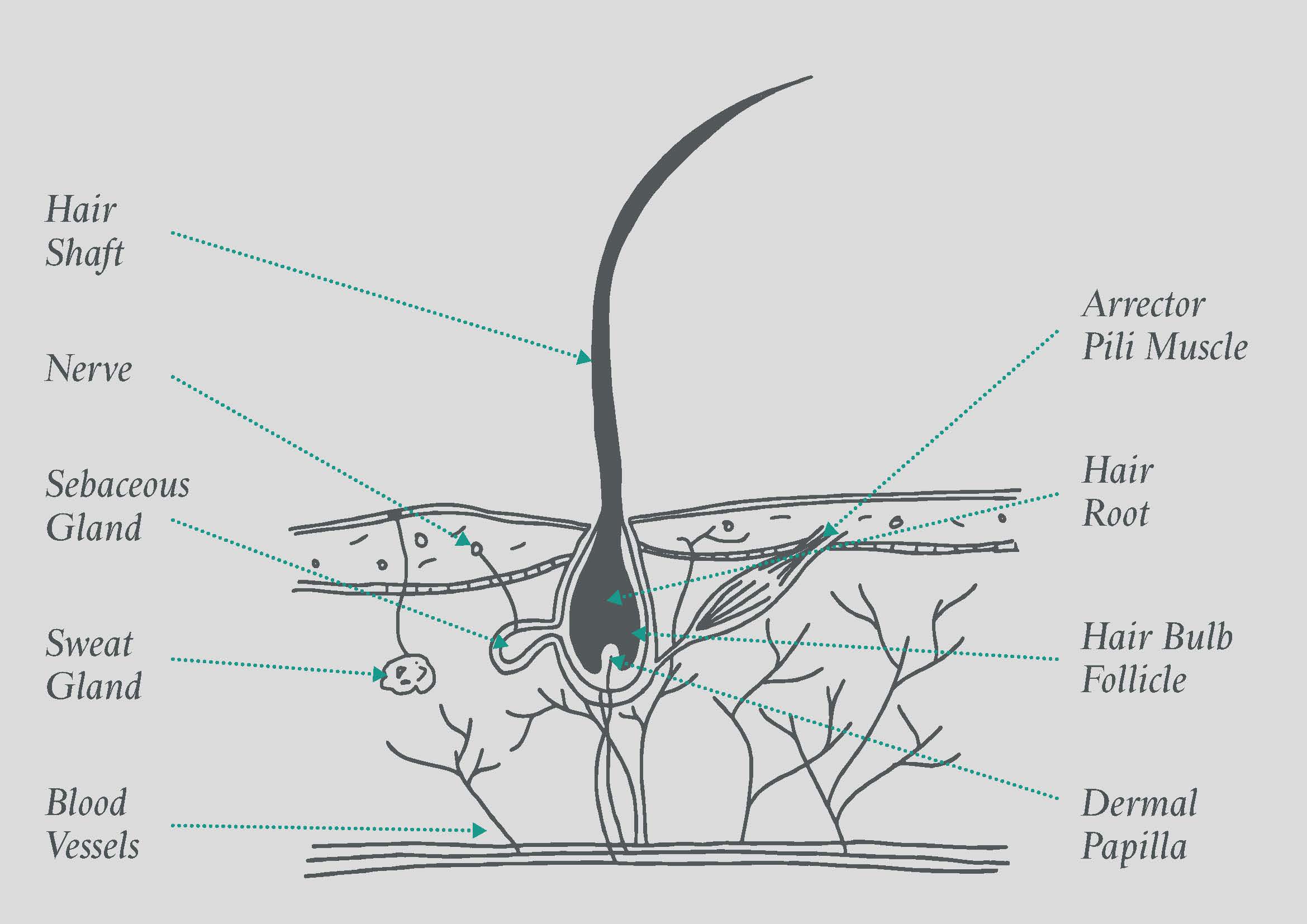
The Hair Structure
It is divided into upper and lower segments: the upper comprises the follicular infundibulum (extending from the free surface to the sebaceous gland) and the isthmus (extending from the sebaceous gland to the arrector pili muscle); the lower comprises the hair bulb and the part sometimes referred to as the stem.

What is a hair follicle? myhair
Learning Outcomes. Describe the structure and function of hair. Figure 1. Hair follicles originate in the epidermis and have many different parts. Hair is a keratinous filament growing out of the epidermis. It is primarily made of dead, keratinized cells. Strands of hair originate in an epidermal penetration of the dermis called the hair.
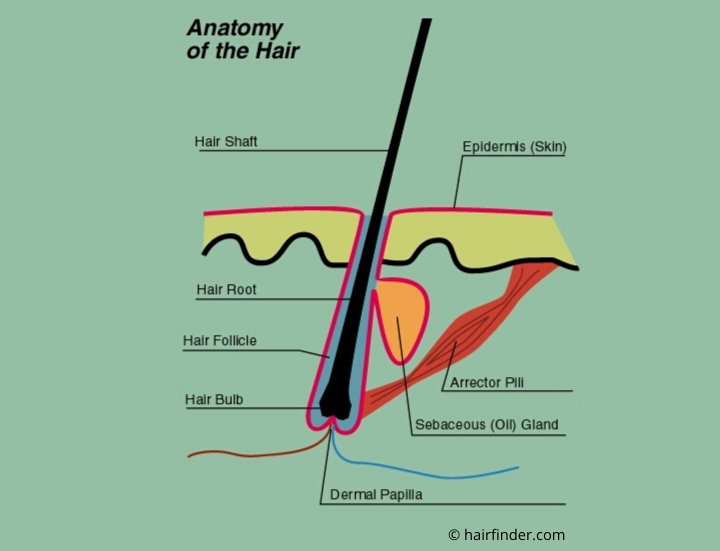
Anatomy of the Hair graphic
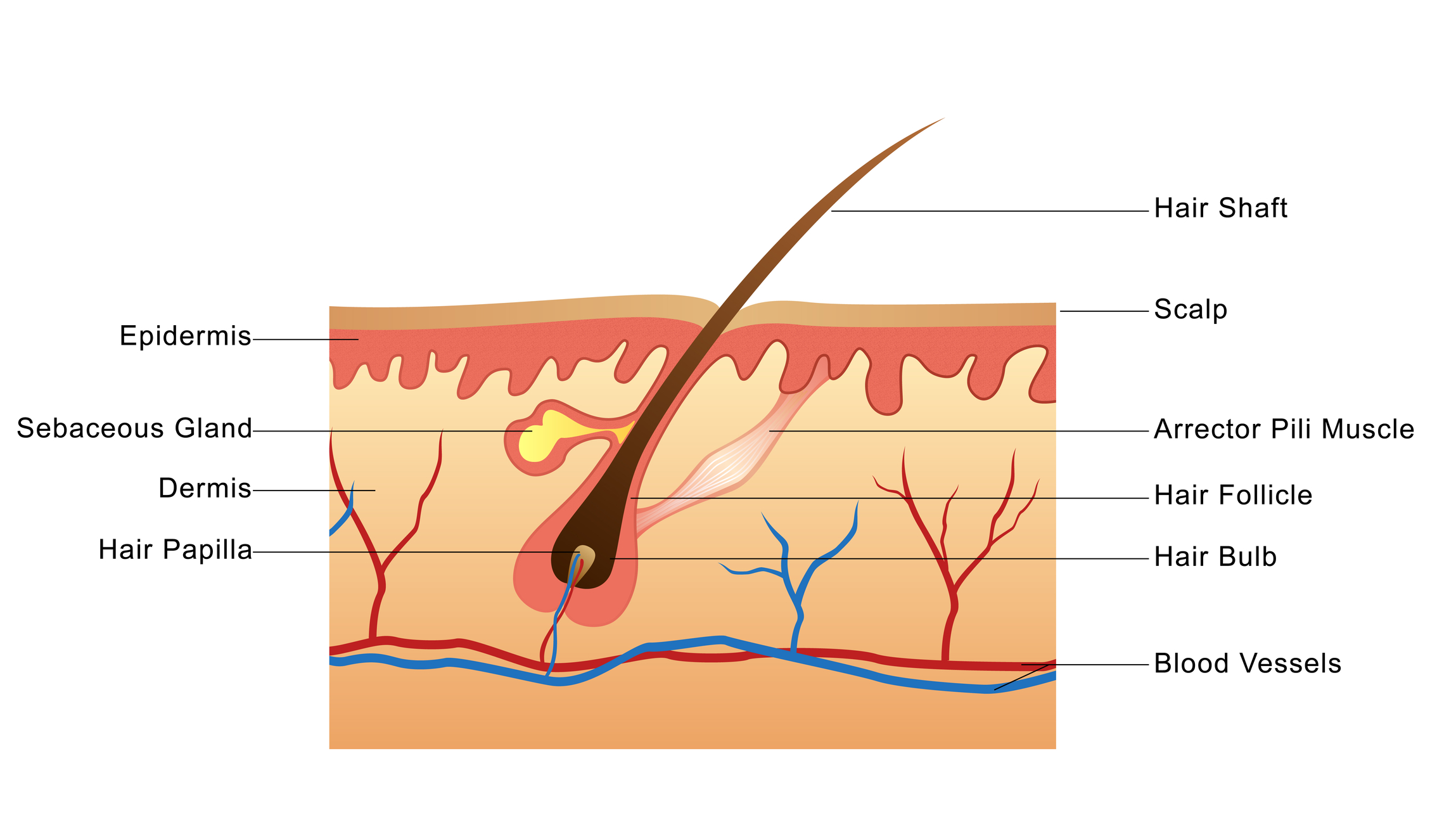
A hair follicle is a tunnel-shaped structure in the epidermis (outer layer) of the skin. Hair starts growing at the bottom of a hair follicle. The root of the hair is made up of.
Cross Section of a Hair Follicle Diagram Diagram Quizlet
A hair follicle is a tube-like structure (pore) that surrounds the root and strand of a hair. Hair follicles exist in the top two layers of your skin. You're born with over 5 million hair follicles in your body and over one million hair follicles on your head. As you age, hair grows out of your hair follicles.
Understanding Hair Growth Basics NJoy Essentials
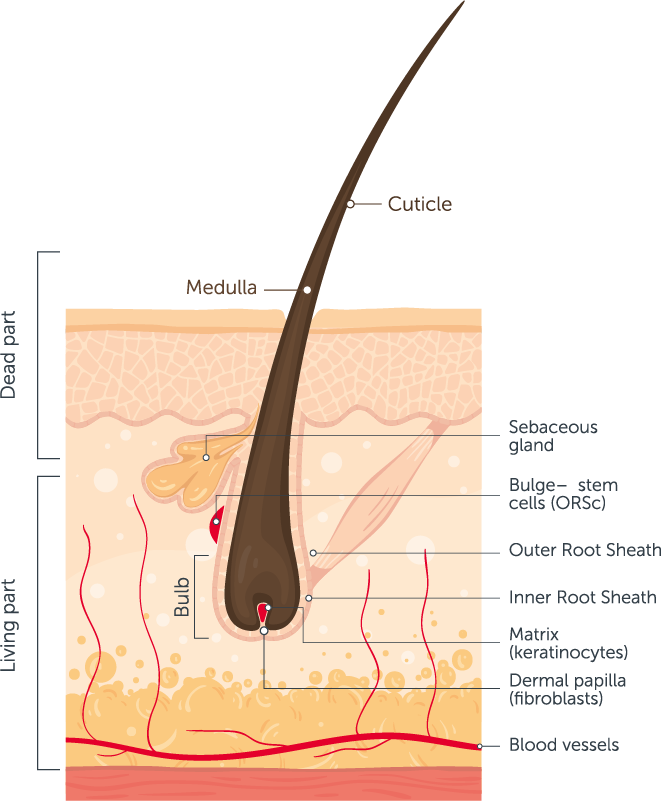
Diagram of proximal hair follicle. Outer root sheath (ORS) extends from the epidermis at the infundibulum and continues to the hair bulb and its cells change considerably throughout the follicle. In the infundibulum, it resembles epidermis, whereas in the isthmus level, ORS cells begin to keratinize in a trichilemmal mode..
Hair Follicle Biology Stemson Therapeutics
The structural, or pilosebaceous, unit of a hair follicle consists of the hair follicle itself with an attached sebaceous gland and arrector pili muscle.

Hair science
The two main types of hair are the shorter and thinner "vellus" hairs (peach fuzz) found on the body and the longer and thicker "terminal" hairs. Examples of terminal hairs include the hair on your head, facial hair, eyelashes, eyebrows, pubic hair, chest hair and belly hair.
Hair care Basics around hair structure & growth cycle Revalid®
The follicle is lined by an inner and outer sheath that protects and molds the growing hair. The inner sheath follows the hair and ends just before the opening of the oil gland, or sebaceous gland. The outer sheath continues all the way up to the gland. The sebaceous gland produces sebum, or oil, which is the body's natural conditioner.

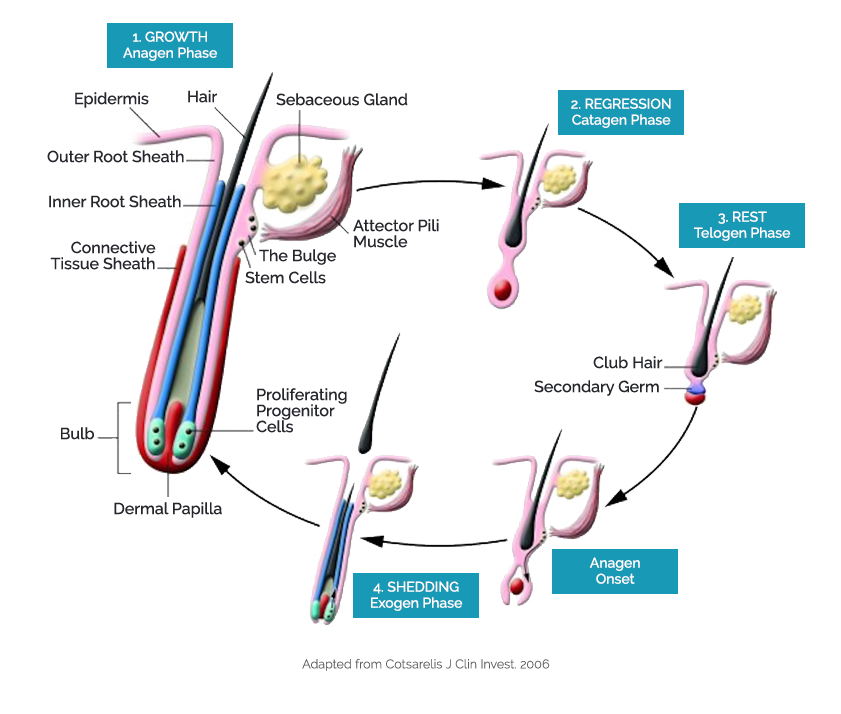
Diagram of a hair follicle niche showing the main cell types that make
HHS USA.gov Hair is a component of the integumentary system and extends downward into the dermal layer, where it sits in the hair follicle. Humans have approximately five million hair follicles, which offer protection from cold and UV radiation, produce sebum, and can have a significant psychological impact when growth or structure is unbalanced.

The long and short of hair growth Right Ringlets
Diseases affecting the hair follicle are common in domestic animals, but despite the importance of an intact skin barrier and a fully functional hair coat, knowledge about the detailed morphological features and the diversity of these complex mini-organs are often limited, although mandatory to evaluate skin biopsies with a history of alopecia.

Hair Shaft, Follicle, Structure, Hair Bulb Root & Function
There are three segments of hair follicles: Infundibulum Isthmus Inferior segment The infundibulum is the portion from the invagination of the epidermis to the level of opening of the sebaceous gland. The infundibulum is part of the pilosebaceous unit where sebum is expressed.

Schematic of the human hair follicle. The hair follicle contains both
What Is Hair Follicle? Hair follicles [ 1] are tiny holes or pores in your skin. Their main function is to grow hair. The scalp of your head too has hair follicles. In biological terms, hair follicle looks like a tunnel-shaped structure situated in the epidermis (outer layer of the skin) [ 2 ]. Hair growth starts at the bottom of the hair follicle.
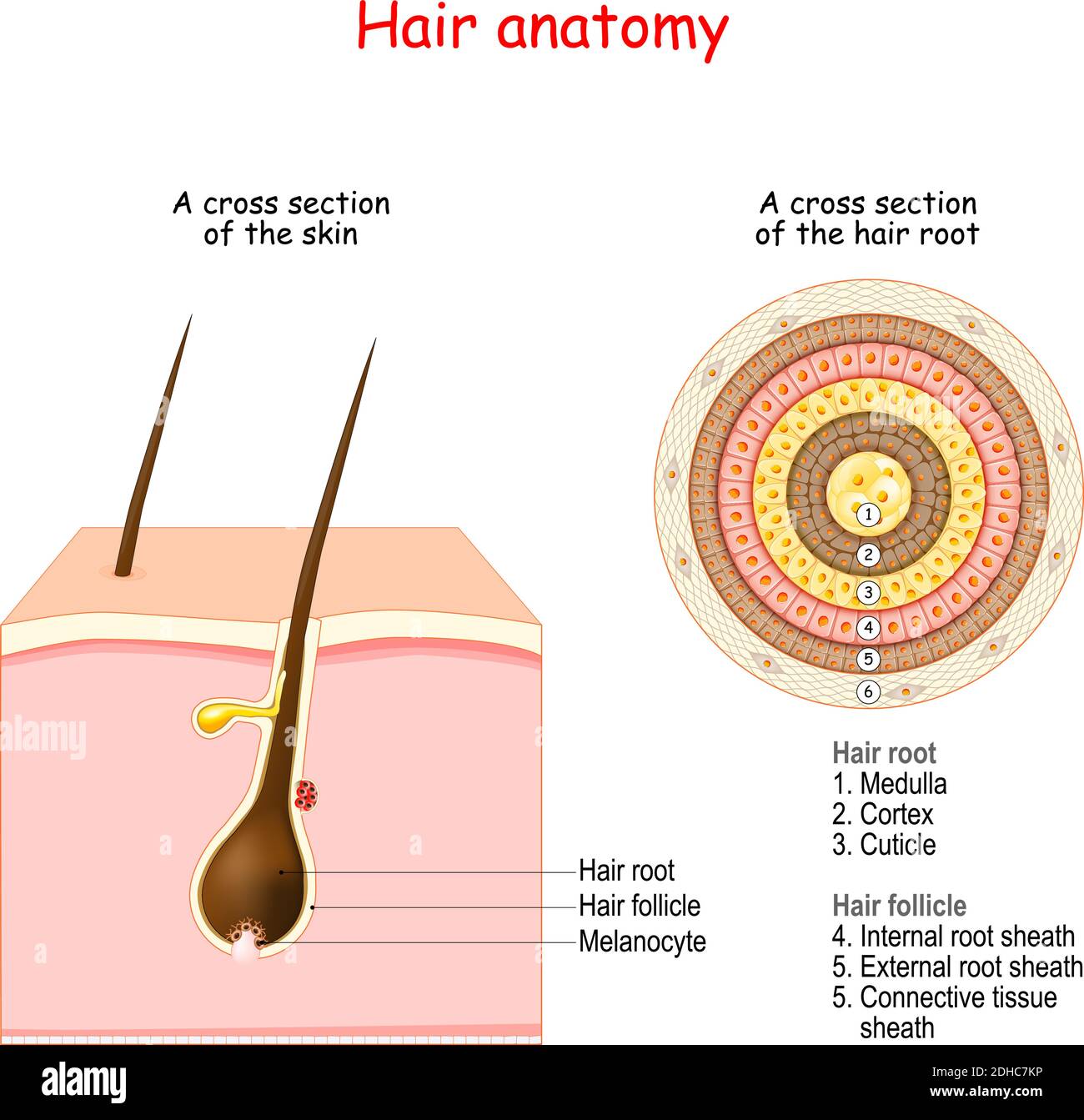
Hair follicle structure and anatomy. Cross section of the human skin
A hair follicle consists of two main layers, an inner (epithelial) root sheath and an outer (fibrous) root sheath. At the base of the hair follicle is the hair bulb, which houses the dermal papillae and hair matrix cells. The hair bulb and inner epithelial layer generates hair.

Hair Follicle Photograph By Asklepios Medical Atlas Pixels, 48 OFF
A hair follicle is a stocking-like structure that contains cells and connective tissue and surrounds the root of a hair. It exists within the dermis and the epidermis, the two top layers of the skin. For a helpful visual, think of the hair follicle as a vase and the hair as the stem of a flower. Hero Images / Getty Images