
Parallel Axis Theorem for Area Moment of Inertia EngineerExcel
Moment of Inertia (Iz, Iy) - also known as second moment of area, is a calculation used to determine the strength of a member and it's resistance against deflection. The higher this number, the stronger the section. There are two axis here:
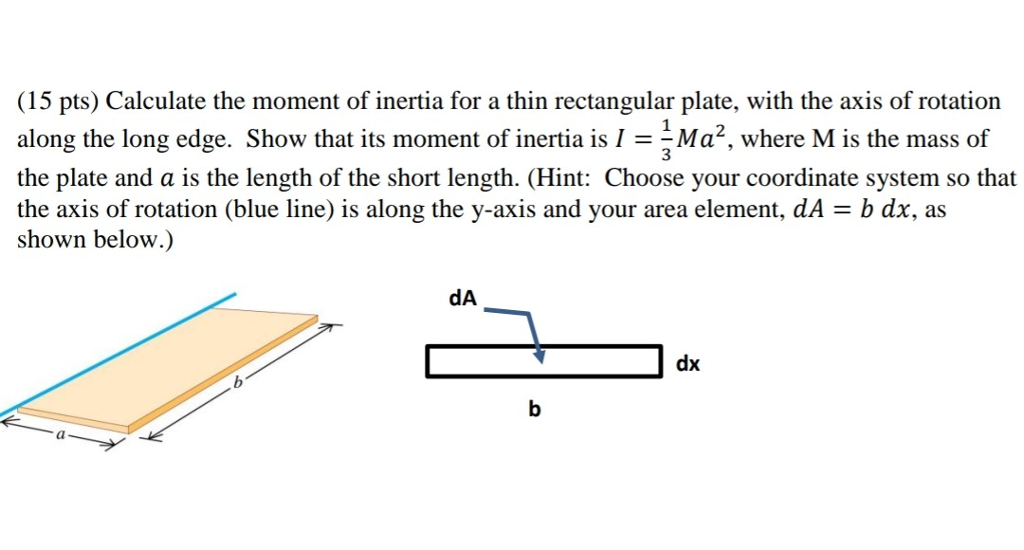
Solved (15 pts) Calculate the moment of inertia for a thin
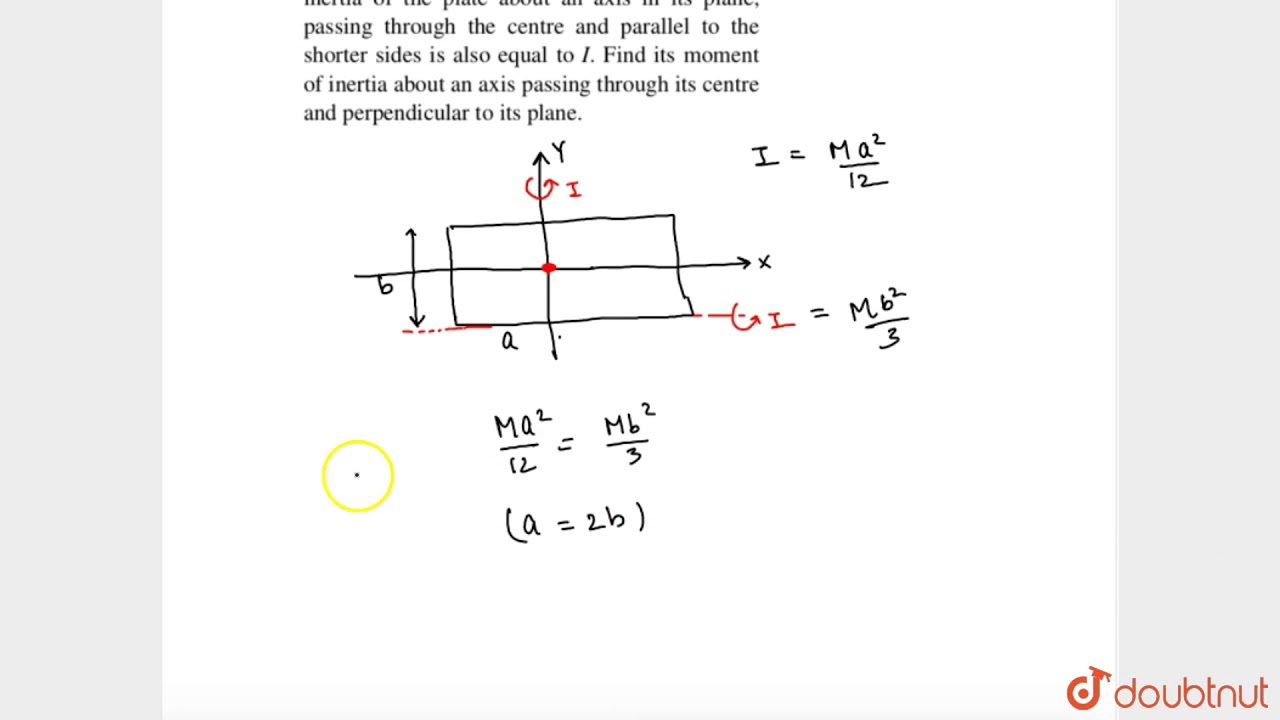
When we take a situation when the axis passes through the centroid, the moment of inertia of a rectangle is given as: I = bh 3 / 12 Here, b is used to denote the rectangle width (the dimension parallel to the axis) and h is said to be the height (dimension perpendicular to the axis). 2. An Axis Passing Through Its Base
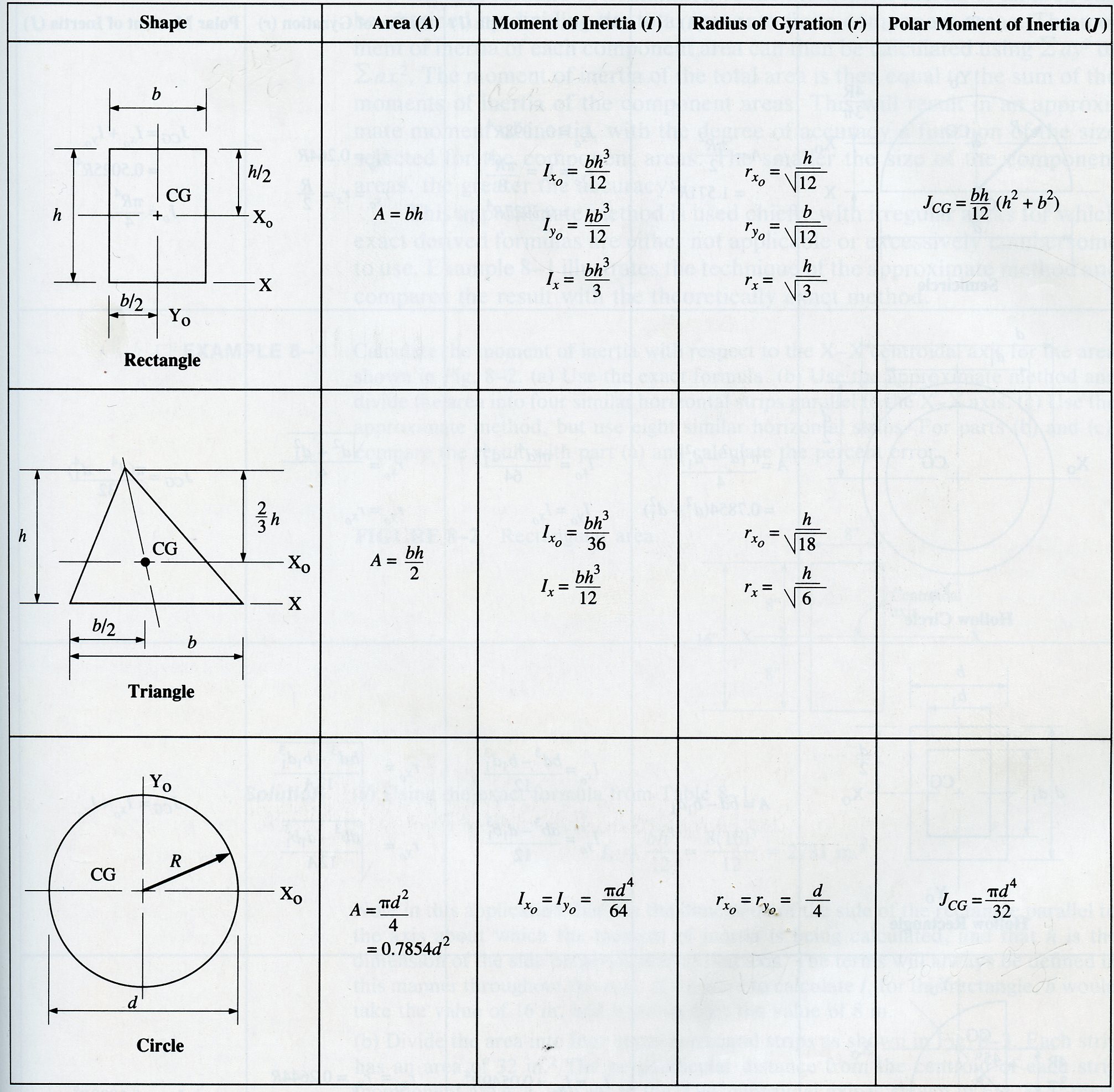
Polar Moment Of Inertia Rectangle slidesharedocs
The moment of inertia of the area A with respect to the y-axis is given by Polar moment of inertia Moment of inertia is the property of a deformable body that determines the moment needed to obtain a desired curvature about an axis. Moment of inertia depends on the shape of the body and may be different around different axes of rotation. Moment.
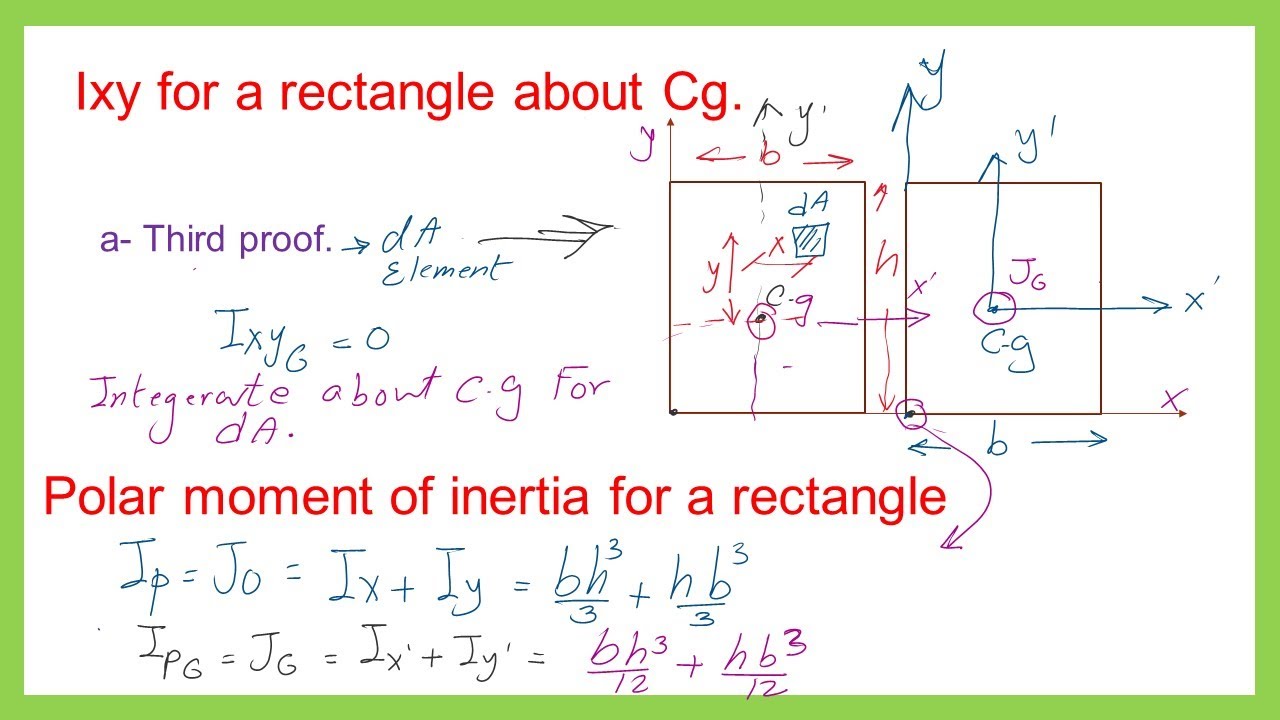
Moment of Inertia of Rectangle
Moment of Inertia of a Rectangle. Example 10.3.7. Interactive: Semi-Circle. Use this interactive to practice computing the area moments of inertia of the semi-circle about the centroidal \(x'\) axis, the bottom edge \(x''\text{,}\) and the system \(x\) axis. You can change the location and size of the semicircle by moving the red points..
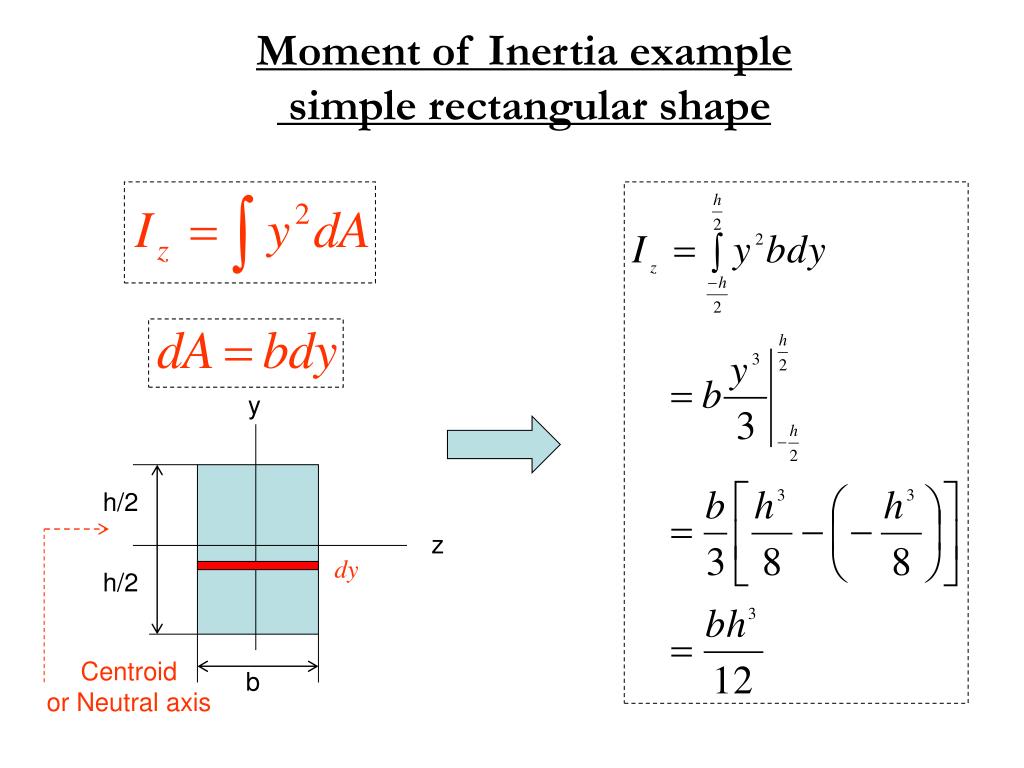
PPT Centroids & Moment of Inertia PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID6794315
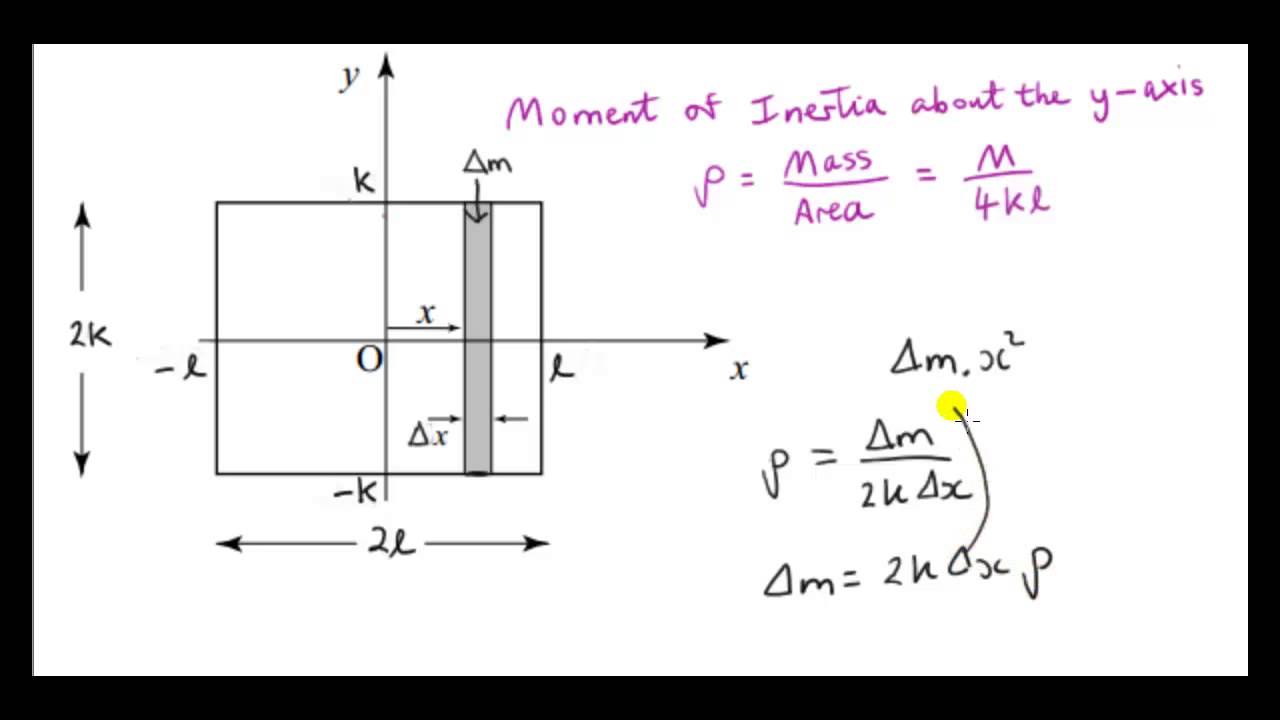
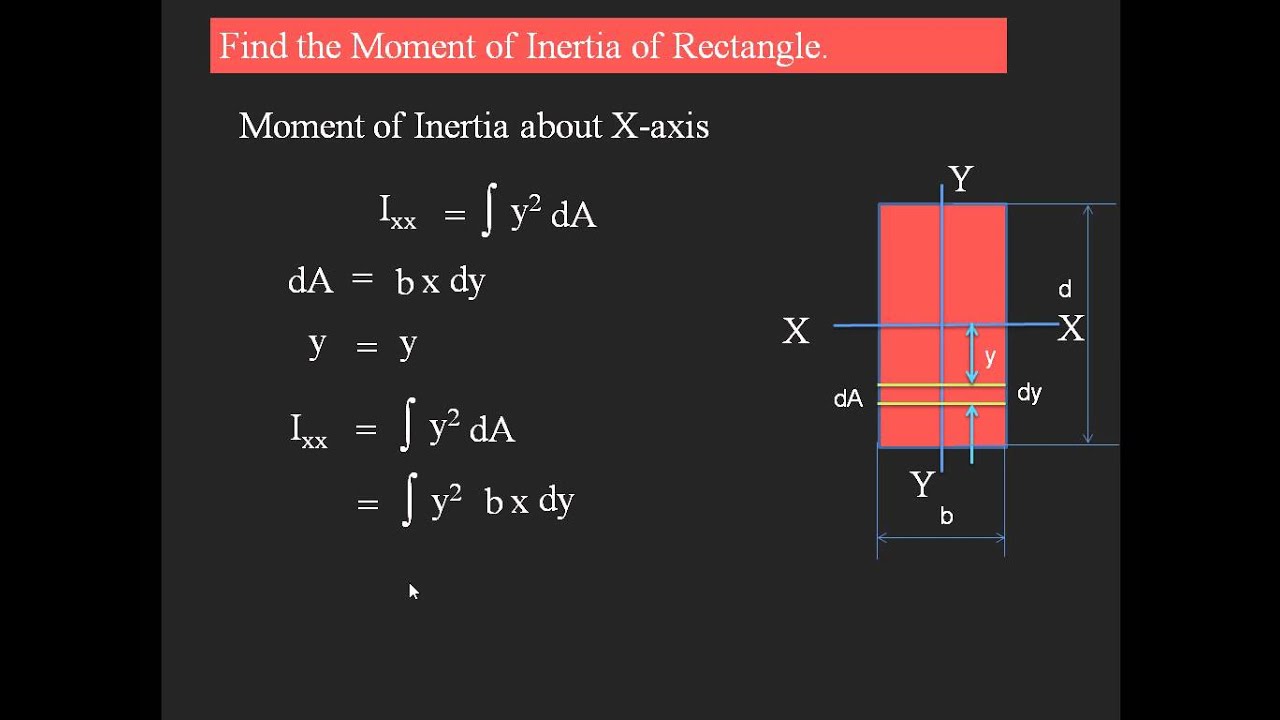
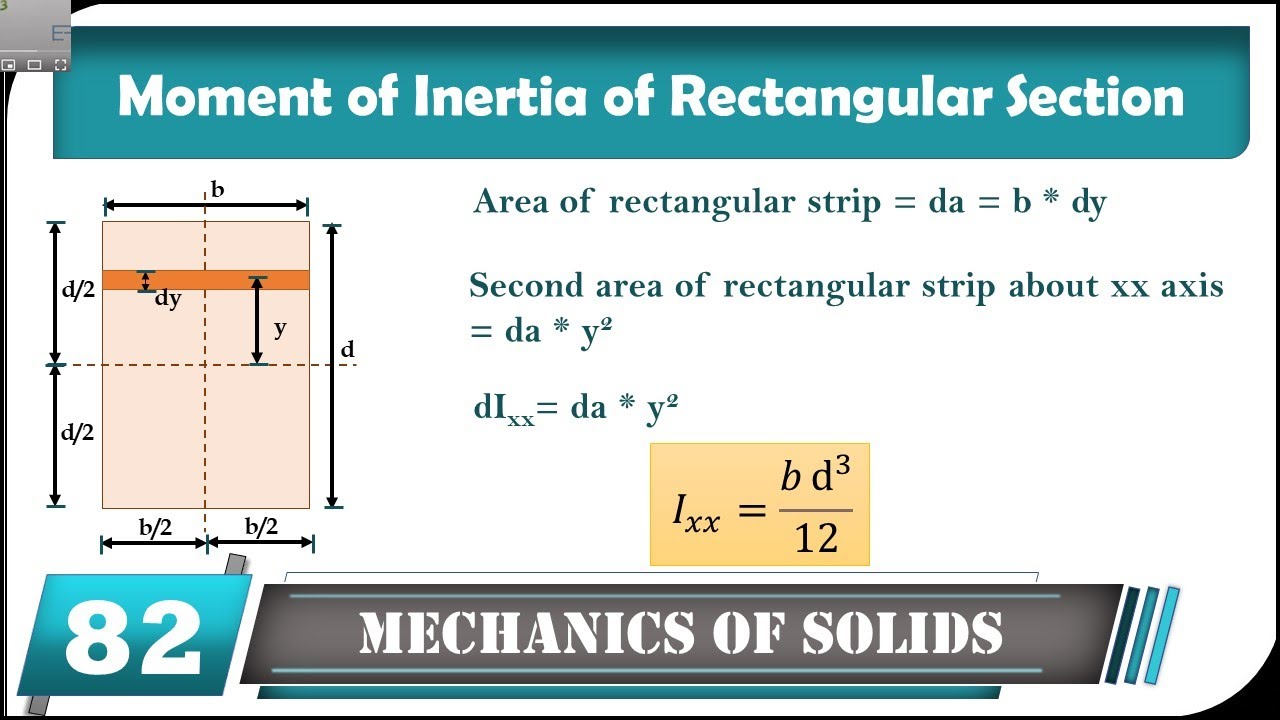
The moment of inertia of an object around an axis is equal to I = ∬ R ρ2dA where ρ is the distance from any given point to the axis. In the case of a rectangular section around its horizontal axis, this can be transformed into

Moment of Inertia Formula, Definition, Equations, Units, Examples
The moment of inertia is related to the rotation of the mass; specifically, it measures the tendency of the mass to resist a change in rotational motion about an axis. The moment of inertia \(I_x\) about the \(x\)-axis for the region \(R\) is the limit of the sum of moments of inertia of the regions \(R_{ij}\) about the \(x\)-axis. Hence
The Moment of Inertia of a Uniform Rectangular Lamina YouTube
Fundamentally, the moment of inertia is the second moment of area, which can be expressed as the following: Ix = ∫ ∫y2dA I x = ∫ ∫ y 2 d A Iy = ∫ ∫x2dA I y = ∫ ∫ x 2 d A To observe the derivation of the formulas below, we try to find the moment of inertia of an object such as a rectangle about its major axis using just the formula above.
Moment Of Inertia Rectangle
The moment of inertia, or more accurately, the second moment of area, is defined as the integral over the area of a 2D shape, of the squared distance from an axis: where A is the area of the shape and y the distance of any point inside area A from a given axis of rotation.
How To Calculate Mass Moment Of Inertia Of A Rectangle STOWOH
The moment of inertia of an area about an axis is a concept appearing in the formulations of several physical phenomena. The moment of inertia of an area is a geometric property of the area. Its value reflects how strong an object (i.e. stiffness) is against bending or twisting about some axis.
How to find Moment of Inertia of rectangular section YouTube
Now using the moment of inertia of rectangle on the side ( y y) coordinate (see example 3.3) ∫h 0 a(1 − y h)3dy 3 = a3h 4 (3.4.3.12) (3.4.3.12) ∫ 0 h a ( 1 − y h) 3 d y 3 = a 3 h 4. For two triangles attached to each other the moment of inertia will be sum. as a3h 2 a 3 h 2 The rest is under construction.

How To Calculate Mass Moment Of Inertia Of A Rectangle STOWOH
I parallel-axis = 1 2 m d R 2 + m d ( L + R) 2. Adding the moment of inertia of the rod plus the moment of inertia of the disk with a shifted axis of rotation, we find the moment of inertia for the compound object to be. Itotal = 1 3mrL2 + 1 2mdR2 + md(L + R)2. I total = 1 3 m r L 2 + 1 2 m d R 2 + m d ( L + R) 2.

Moment of Inertia Definition, Formula, Examples, Unit, Equations
The moment of inertia of a rectangle has been expressed as follows when an axis passes through the base: I = bh3 / 3. It is seamlessly determined by applying the Parallel Axis Theorem because the rectangle centroid is located at a distance equal to h/2 from the base.
Moment of Inertia of Rectangular Section YouTube
The rectangle's moment of inertia is defined as: The summation of products is obtained from the entire mass of every attached element of the rectangle and then multiplied the value by the square of the particles with respect to its distance from the central point.
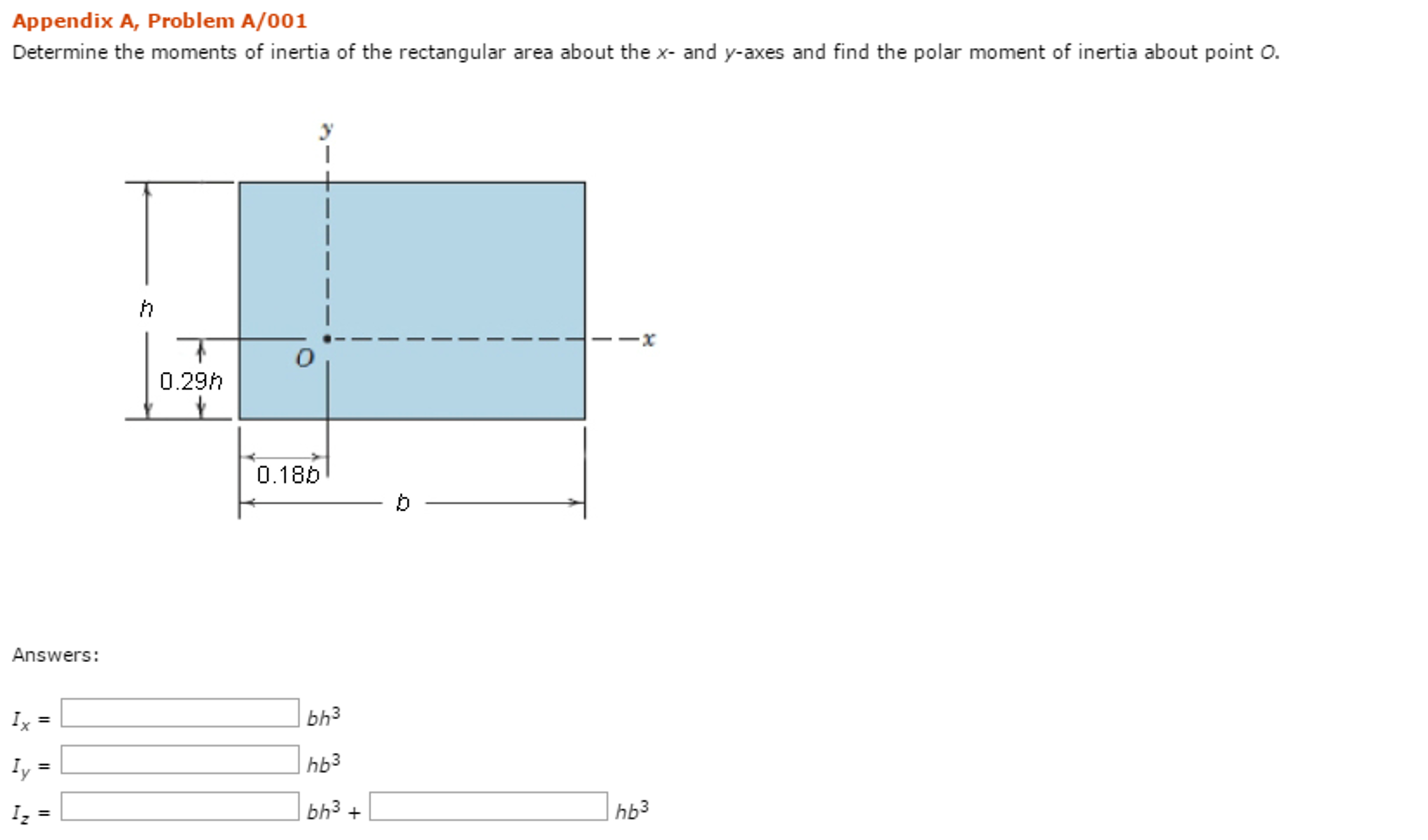
Solved Determine the moments of inertia of the rectangular
The parallel axis theorem can be used to determine the second moment of area of a rigid body about any axis, given the body's second moment of area about a parallel axis through the body's centroid, the area of the cross section, and the perpendicular distance ( d) between the axes. See also List of moments of inertia List of centroids
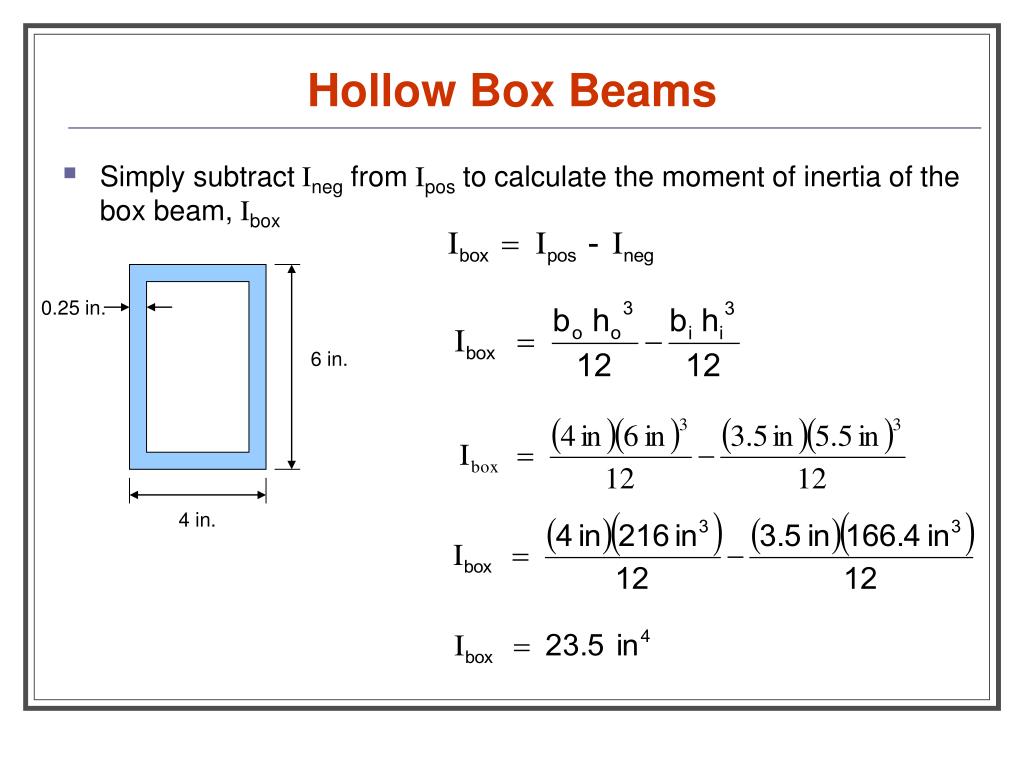
Moment Of Inertia Beam Torsional Moment Of Inertia Rectangular Beam New Images Beam
Its simplest definition is the second moment of mass with respect to distance from an axis . For bodies constrained to rotate in a plane, only their moment of inertia about an axis perpendicular to the plane, a scalar value, matters.

Moment of Inertia for circle and rectangle YouTube
1. Moment of inertia - Rectangular shape/section (formula) Strong Axis I y = 1 12 ⋅ h 3 ⋅ w Weak Axis I z = 1 12 ⋅ h ⋅ w 3 Dimensions of rectangular Cross-section. Example calculation h = 240 mm, w = 120 mm Strong axis: I y = 1 12 ⋅ h 3 ⋅ w = 1 12 ⋅ ( 240 m m) 3 ⋅ 120 m m = 1.3824 ⋅ 10 8 m m 4 Weak axis: