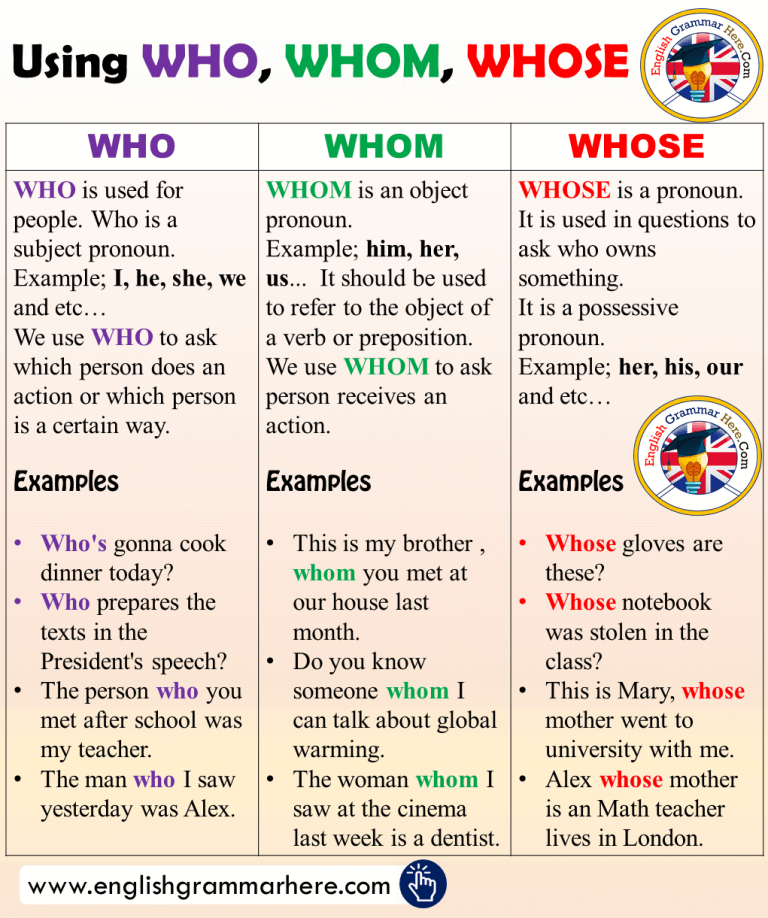
Using WHO, WHOM, WHOSE and Example Sentences in English English Grammar Here
Not all of these adjective clauses use whose. 1. My brother makes a lot of money. My brother's company has branches in 42 countries. 2. Titanic was a great movie. Titanic's budget was over $200 million. 3. I visited a country. The country's people love to go hiking..

Who? Whom? Which? That? Adjective Clauses/Relative Pronouns YouTube
An adjective clause is a multi-word adjective that includes a subject and a verb. For example: The painting we bought last week is a fake. When we think of an adjective, we usually think about a single word used before a noun to modify its meanings (e.g., tall building, smelly cat, argumentative assistant). However, an adjective can also come.

(PPT) Adjective Clauses who whom which that whose when where LAY SENGHOR1
Choose the correct answer: who, whom, which or whose. are required to fix his old car. helped Sara recover from her illness. didn't surprise people who knew her. parents were were arrested.. is on the table. did it. managed to escape, broke into a bank downtown. fingerprints were on the knife.

using Who/whom/which in Adjective clauses YouTube
Adjective clauses are used to describe a noun in the main sentence. In the example above, the adjective clause tells us about "the man." Just ignore the main sentence and look at the adjective clause when deciding whether to use "who," "whom" or "whose." Ask yourself if the adjective clause requires a subject, object, or possessive form.

Adjectival Clause part 1 (who, whom, whose & which) + KEY ESL worksheet by Ayrin
Who, whom - English Grammar Today - a reference to written and spoken English grammar and usage - Cambridge Dictionary

Grammar ( 2 ) CH12 L2 Using who/whom/which in Adjective clauses (1) YouTube
Whom is a relative pronoun used to introduce subordinate clauses that refer to people, not things, as in example sentences below. Because it is an object pronoun, whom cannot be the subject of a subordinate clause. The pattern is: whom + subject + verb. Main clause + subordinate (adjective) clause: Isn't he the man whom we saw earlier.
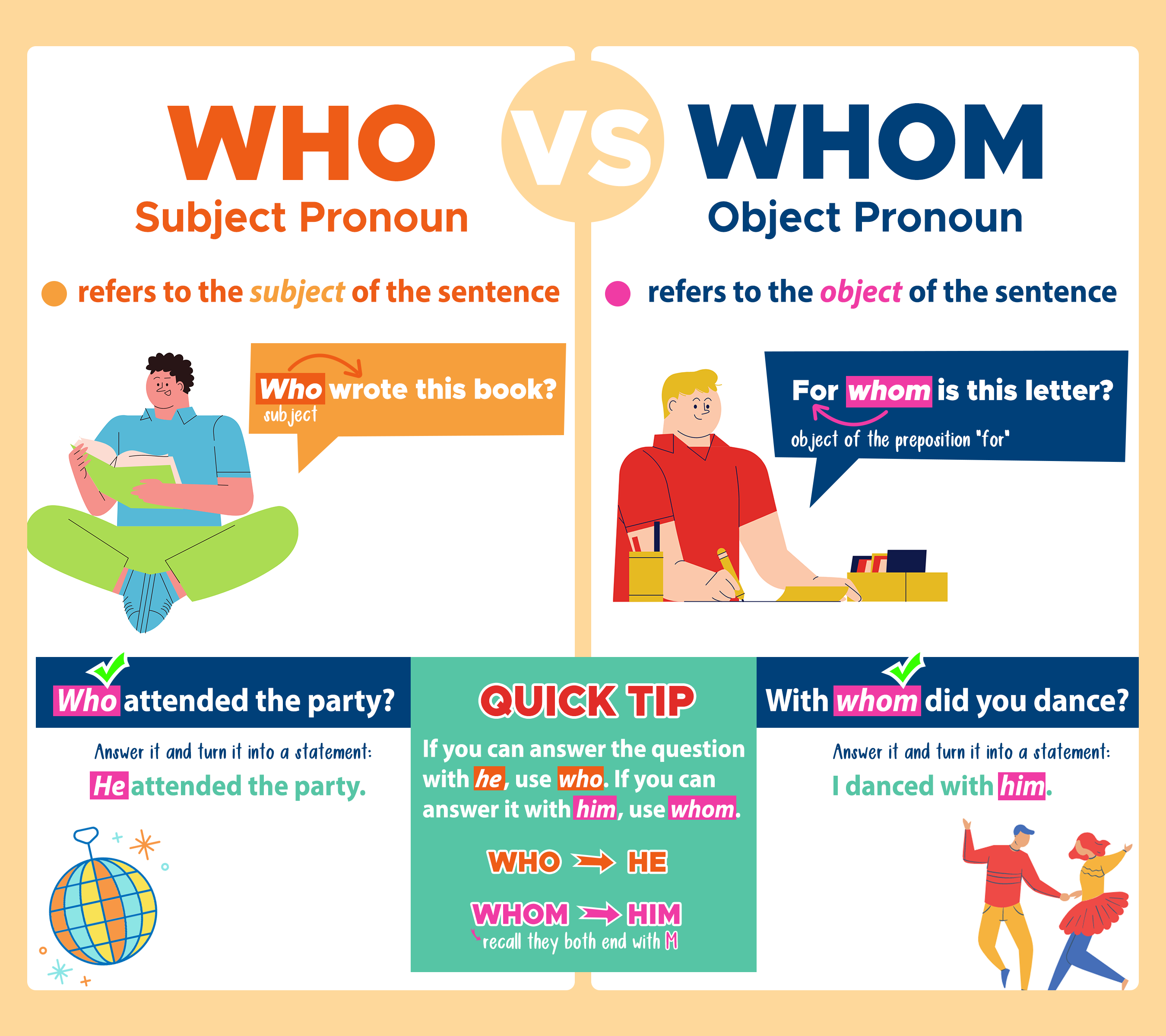
Who vs Whom What's the Difference? Curvebreakers
An adjective clause is a type of dependent clause that functions as an adjective in a sentence. It provides additional information about a noun or pronoun, such as describing its characteristics, qualities, or attributes. An adjective clause always contains a subject and a verb, but it cannot stand alone as a complete sentence.

Using WHOM and WHOSE, Example Sentences English Grammar Here English grammar, English
The teacher had called his WHOSE name. Step 3: Move the relative pronoun (whose) and the noun it modifies to the beginning of the clause. The boy stood up {WHOSE name the teacher had called}. Step 4: Move the {adjective clause} behind the noun it describes (the boy) The boy {whose name the teacher had called} stood up.

Using "Who" or "Whom" in Adjective Clauses YouTube
Relative pronouns and relative adverbs introduce relative clauses. 'Who' - 'whose' - 'whom' - 'that' and 'which' - are relative pronouns. 'Where' is a relative adverb. There is often confusion about the use of who, whose, whom, that, which or where. We use who when referring to people or when we want to know the person.

Using WHO, WHOM, WHOSE and Example Sentences in English English Grammar Here English grammar
relative pronouns - who, which, that, whose, whom | relative clauses | adjective clauses | defining, non-defining, restrictive, non-restrictive Hi Everyone,.

PPT Adjective Clauses who whom which that whose when where PowerPoint Presentation ID146865
Most of the time, relative clauses are introduced by certain words called relative pronouns.. who, whom, whose, that, which. The person who made the mess needs to clean it. (The clause is modifying person.); The girl whom you teach is my sister. (The clause is modifying girl.); People whose cats shed need to vacuum often. (The clause is modifying people.; This is the house that Jack built.

Relative Clauses with Whose, Whom Vocabulary Home
The man is doing yoga. The man at whom we are looking is doing yoga. The relative pronoun "who" replaces a human subject. People do yoga. People are flexible. People who do yoga are flexible. "Whose" replaces a possessive adjective. It is used along with a subject noun. It shows that the noun subject in the adjective clause belongs to.

Relative Pronouns Who, Whom, Which, Why, When, Where, Whose, That,… English language learning
Relative pronouns are words that introduce adjective clauses.. who, whom, whose, that, which. Relative adverbs can also introduce adjective clauses.. where, why, when. You're about to learn how to diagram adjective clauses, and you'll be able to see how relative pronouns and relative adverbs connect the dependent adjective clause to the independent clause.

11 Example Sentences Who, Whose,Whom and Definitions English Study Here
PDF Exercises: Worksheet 1 / 2. Multiple Choice Quizzes: Relative Clauses Quizzes 1. Combining Sentences with which, who, in which, of which, whose, whom. Try the given relative pronouns on the sentences below. 1) February, which is the second month of the year, is the month ---- many of my colleagues take vacation for skiing.

Adjective Clauses with who, whom, and whose 8 YouTube
Adjective clauses, also known as adjectival clauses or relative clauses, are a type of dependent clause that describes or modifies nouns, just like individual adjectives do. Like all clauses, adjective clauses contain a subject and a verb. You can identify adjective clauses because they usually begin with a relative pronoun like that, which, or.

WHO vs WHOM Useful Usage and Example Sentences ESL Forums
Relative pronouns 3. GapFillDragAndDrop_MTU4OTE= Relative pronouns 4. GapFillTyping_MTU4OTI= Level: intermediate. whose and whom. We use whose as the possessive form of who:. This is George, whose brother went to school with me. We sometimes use whom as the object of a verb or preposition:. This is George, whom you met at our house last year. (whom is the object of met).